* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Trigonometry - TangHua2012-2013
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
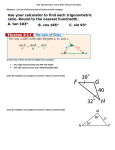
TRIGONOMETRY Lesson 4: Solving Problems Involving 2 Right Triangles and Direct or Indirect Measure Todays Objectives • Students will be able to develop and apply the primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) to solve problems that involve right triangles, including: • Solve a problem that involves one or more right triangles by applying the primary trigonometric ratios or the Pythagorean theorem • Solve a problem that involves indirect and direct measurement, using the trigonometric ratios, the Pythagorean theorem and measurement instruments such as a clinometer or meter stick Solving Problems Involving 2 Right Triangles • Many problems involving right triangles require more than a single calculation in order to find the desired information. In some questions the order of these calculations is unimportant, while in others, the order is crucial to determine the unknown values. Example • Determine the length of side x to the nearest tenth of a centimeter. y x 15 cm 30° 20° z • Solution: x=y+z For this question, it does not matter which length is calculated first • Since the value of x is the sum of the lengths of two legs of two right triangles, assign variables to those two legs and find their values separately. Example • Apply the tangent ratio. • tan30º = • tan20º = 𝑦 ,𝑦 15 𝑧 ,𝑧 15 = 15tan30º = 15tan20º • 𝑥 = 𝑦 + 𝑧, 15tan30º + 15tan20º = 𝑥 • 𝑥 = 14.1 𝑐𝑚 • The length of side x is approximately 14.1 cm. • *Do not calculate the values of 15tan30º and 15tan20º until the final step to avoid error that may affect your final answer! Solving Problems Involving 2 Right Triangles • In some problems, the required unknown value cannot be calculated directly because it is part of a triangle with insufficient information (side lengths and angle measures). • These problems require determining a side length or angle measure of a triangle that shares a common side with the one containing the required unknown. Example • Determine the length of side x to the nearest tenth of a meter. y 43° 47° x z 47° 43° 22 m • Solution: • Begin by filling in any of the measures that you can determine easily. In this case, we can determine the measures of the acute angles in the diagram because we know the sum of angles in a triangle = 180º. Example • Since the lengths of all the sides for the right triangle that x is part of are unknown, the first step is to determine the length of one other side of the triangle containing side x. The sides labeled y and z in the previous diagram are possibilities. y x z • Knowing the value of either y or z allow you to calculate side length x. However, the value of x is probably more easily obtained by first determining the value of z, as follows: Example • Apply the tangent ratio. • tan47º = 𝑧 , 22tan47º 22 = 𝑧 (expression for z) • 𝑧 = 23.59 (approximate value for z) • Now x can be determined using the approximate value of z, or the expression for z. • *Use 22tan47º instead of 23.59 to reduce error! • Apply the sine ratio. 𝑧 , 𝑥𝑠𝑖𝑛43º = 𝑧 𝑥 𝑧 22tan47 ,𝑥 = ,𝑥 sin43° sin43 • sin43º = • 𝑥 = = 34.6 • The length of side x is approximately 34.6 meters. Example (You do) • Determine the length of side x to the nearest tenth of a centimeter. 6 cm 4 cm y 50° • Solution: • Apply the sine ratio. • sin50º = 6 ,𝑦 𝑦 = x 6 ,= sin50 7.8 • Apply the Pythagorean theorem to find x. 6 )2, = sin50 • 𝑥2 = 42 + ( 16 + 61.3, = 77.3 • Take the square root of both sides. • 𝑥 = 8.8 • The length of side x is approximately 8.8 centimeters. Example • From a position in a tower 120 meters above the ground, a forest ranger named Laughing observes a fire that is directly west at an angle of depression of 18º. The ranger also observes a herd of deer directly east of the tower at an angle of depression of 35º. How far is the fire from the herd of deer, to the nearest meter? • Solution: First, sketch and label a diagram Tower 18° 35° 120 m 35° 18° x y Example • Notice that the angles of depression from the tower to the fires and to the deer are equal to the angles of elevation from the fire and from the deer. The distance between the deer and the fire is x + y. • Apply the tangent ratio to solve for x. • tan18º = • 𝑥 = 120 , 𝑥𝑡𝑎𝑛18º 𝑥 = 120 120 tan18 • Apply the tangent ratio to solve for y. • tan35º = • 𝑦 = 120 , 𝑦𝑡𝑎𝑛35º 𝑦 = 120 120 tan35 • Distance = x + y • 120 tan18 120 + tan18 = 541 𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑠. • The fire is approximately 541 meters from the herd of deer. Example (You do) • Jackie Chan is standing on the street 60 m from the base of a tall office building that has a flagpole on the top edge that he is facing. He uses a clinometer to measure the angles of elevation from his position on the street to the top of the building and to the top of the flagpole as 48º and 54º, respectively. How high is the flagpole, to the D nearest tenth of a meter? • Solution: Draw a diagram, then calculate C y A 48° 54° 60 m B x Example • Apply the tangent ratio in triangle ABC to solve for y. • tan48º = 𝑦 ,𝑦 60 = 60tan48º • Similarly, apply the tangent ratio in triangle ABD to solve for x. • tan54º = 𝑥 ,𝑥 60 = 60tan54º • The required length is the difference between x and y. • 𝑥 – 𝑦 = 60tan54º − 60tan48º = 60(tan54º − tan48º) • =15.9 • The flagpole is approximately 15.9 meters high.