* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Date Of Origin
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Epinephrine autoinjector wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
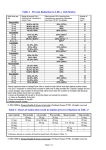
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru336 Topic: High-Cost Lipid-Modifying Medications: - atorvastatin (Lipitor®) - fluvastatin (generic, Lescol®) - fluvastatin ER (Lescol XL®); - lovastatin ER (Altoprev®); - omega-3 acids (Epanova®, Lovaza®, Omtryg®, Vascepa®, generics) - pitavastatin (Livalo®); - simvastatin/ezetimibe (Vytorin®) - simvastatin/niacin (Simcor®) Date of Origin: March 14, 2014 Committee Approval Date: September 9, 2016 Next Review Date: July 2017 Effective Date: October 1, 2016 IMPORTANT REMINDER This Medication Policy has been developed through consideration of medical necessity, generally accepted standards of medical practice, and review of medical literature and government approval status. Benefit determinations should be based in all cases on the applicable contract language. To the extent there are any conflicts between these guidelines and the contract language, the contract language will control. The purpose of medication policy is to provide a guide to coverage. Medical Policy is not intended to dictate to providers how to practice medicine. Providers are expected to exercise their medical judgment in providing the most appropriate care. Description Fluvastatin ER (Lescol XL), fluvastatin (Lescol), lovastatin ER (Altoprev), pitavastatin (Livalo), and simvastatin/ezetimibe (Vytorin) are oral medications used to treat high LDL cholesterol. This policy does not apply to rosuvastatin (Crestor®), or ezetimibe (Zetia®). This policy also addresses certain high cost lipid modifying agents in which comparable, yet lower cost, generic and/or over-the-counter (OTC) products are available. © 2016 OmedaRx. All rights reserved. dru336.5 Page 1 of 6 Policy/Criteria I. Most contracts require prior authorization approval certain high cost lipid modifying agents prior to coverage. High cost lipid modifying agents may be considered medically necessary when criterion A or B below is met. A. Fluvastatin (Lescol, Fluvastatin ER (Lescol XL), lovastatin ER (Altoprev), pitavastatin (Livalo), and simvastatin/ezetimibe (Vytorin) may be considered medically necessary when at least two generic statin products have been ineffective after at least two months of treatment, have been not tolerated, or are not indicated. OR B. Lipid modifying agents included in Table 1 may be considered medically necessary when there is an intolerance or contraindication to an inactive ingredient in all specified alternative(s) listed in Table 1. Table 1. High cost lipid modifying agents with alternatives II. High Cost Drug Alternative(s) Epanova omega-3 acids (OTC) Lipitor atorvastatin Lovaza omega-3 acids (OTC) Omtryg omega-3 acids (OTC) omega-3 acids (generic) omega-3 acids (OTC) Simcor niacin (OTC or Rx) + simvastatin Vascepa omega-3 acids (OTC) Administration, Quantity Limitations, and Authorization Period A. OmedaRx considers the medications in this policy to be self-administered. B. Authorization may be reviewed at least annually to confirm that current medical necessity criteria are met and that the medication is effective. Position Statement - Statins have been proven to reduce cardiovascular events and mortality. - Other medication classes, including omega-3 acids, may improve cholesterol levels, but there is insufficient evidence that they improve clinically meaningful outcomes. - There is no evidence that branded medications, statin or non-statin, are safer or more effective than generic treatment options at optimized doses. Generics are available for statins, fibrates, and omega-3-acids. © 2016 OmedaRx. All rights reserved. dru336.5 Page 2 of 6 - There are many generic statin options available, including those with high-intensity LDL-lowering ability (see Appendix 1) and provide the best value. Fluvastatin ER (Lescol XL), lovastatin ER (Altoprev), pitavastatin (Livalo), and simvastatin/ezetimibe (Vytorin) have not been proven to be safer or more effective than other equipotent-dosed statins, but are more costly. AB-rated generic products are lower cost and considered to be pharmaceutical equivalents of the branded products, with the same clinical effect and safety profile when administered to patients under the conditions specified in the package labelling. Patients who are adherent, yet do not respond to equivalent doses of the generic/OTC product(s) are not likely to respond to the branded product. Clinical Efficacy - Several outcomes trials have demonstrated that statins reduce the risks of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. [1-4] - Reduction in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular risk is not unique to any specific statin and has been demonstrated with many of the available statins in a variety of patient populations, such as in patients with coronary heart disease, high cholesterol levels, normal cholesterol levels, hypertension, diabetes and previous stroke. [1-4] - Several primary or secondary prevention trials with simvastatin, pravastatin, lovastatin, and atorvastatin consistently demonstrate that reductions in cardiovascular events correlate with LDL-C reduction. [1-4] - When given at equipotent doses, statins provide similar reductions in LDL-C. [3] - The 2013 American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) treatment guidelines recommend choosing a specific statin based on the magnitude of LDL-lowering desired (e.g. low-, moderate-, or high-intensity). [5] Safety [7] - All marketed statin-containing medications have safety records that are consistent for the statin class. - Rhabdomyolysis is a rare side-effect of all statins (0.1%). - ∗ Myopathy (muscle weakness) and rhabdomyolysis are commonly linked to additional factors that may increase statin serum levels, such as impaired hepatic and renal function, hypothyroidism, or concomitant use of certain medications, such as fibrates or azole antifungals. ∗ Based on clinical trial safety data and world-wide post-marketing adverse reports, the incidence of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis among available statins is similar. Hepatotoxicity occurs rarely (less than 1%) with statins. ∗ Statins are contraindicated in patients with active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevations of serum transaminases. ∗ At equipotent doses, there are no differences in rates of clinically relevant elevations in LFTs among statins. © 2016 OmedaRx. All rights reserved. dru336.5 Page 3 of 6 ∗ Prescribing information indicates initial and routine liver function tests (LFTs) (as clinically indicated) are necessary with all statins. - Increases in HbA1c and fasting serum glucose levels have been reported with all statins. - The FDA issued a statement in June 2011 to recommend limiting the use of simvastatin 80 mg to those patients who have been taking this dose for 12 months without evidence of muscle injury. Labeling was also updated to reflect new contraindications and dose limitations for use with certain medications (see Appendix 3).[8] - Risks for certain drug-drug interactions are inherent with all statins (see Appendix 3). Half Tablet Program - Atorvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin are eligible medications under the OmedaRx Half-Tablet Program. ∗ As part of this program, when a higher strength tablet of these statins can be split and used for the prescribed dose, the member pays only one copayment for a two month supply of medication. ∗ More information about the OmedaRx Half-Tablet Program can be found at http://www.omedarx.com/node/43. © 2016 OmedaRx. All rights reserved. dru336.5 Page 4 of 6 Appendix 1: Statin Comparison Chart [5, 7] % LDL- C Lowering Preferred/ Formulary fluvastatin 20 mg, 40 mg √ lovastatin 10 mg, 20 mg lovastatin ER (Altoprev®) 20 mg pitavastatin (Livalo®) 1 mg √ pravastatin 10 mg, 20 mg √ simvastatin 5 mg, 10 mg √ atorvastatin 10 mg, 20 mg fluvastatin ER (Lescol XL®) 80 mg lovastatin 40 mg lovastatin ER (Altoprev®) 40 mg, 60 mg pitavastatin (Livalo®) 2 mg, 4 mg √ pravastatin 40 mg, 80 mg √ rosuvastatin 5 mg, 10 mg simvastatin 20 mg, 40 mg √ simvastatin/ ezetimibe (Vytorin®) 10 mg/ 10 mg √ atorvastatin 40 mg, 80 mg rosuvastatin 20 mg, 40 mg simvastatin/ ezetimibe (Vytorin®) 10 mg/20 mg, 10 mg/40 mg √ Highintensity: ≥ 50% Strength √ Lowintensity: < 30% Moderate -intensity: 31% - 49% Statin Name √ Cross References Juxtapid™, lomitapide, dru302 Kynamro™, mipomersen, dru301 © 2016 OmedaRx. All rights reserved. dru336.5 Page 5 of 6 Codes Number Description N/A References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Taylor, F, Huffman, MD, Macedo, AF, et al. Statins for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2013;1:CD004816. PMID: 23440795 Fodor, G. Primary prevention of CVD: treating dyslipidaemia. Clinical evidence. 2010;2010. PMID: 21418693. Smith MEB, Lee NJ, Haney E, Carson S. Drug Class Review: HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) and Fixed-dose Combination Products Containing a Statin: Final Report Update 5 [Internet]. Portland (OR): Oregon Health & Science University; 2009 Nov. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=statins09. Manktelow BN, Potter JF. Interventions in the management of serum lipids for preventing stroke recurrence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jul 8 ;(3):CD002091. Review. Stone, NJ, Robinson, J, Lichtenstein, AH, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013. PMID: 24222016 Sharma M, Ansari MT, Soares-Weiser K, Abou-setta AM, Ooi TC, Sears M, Yazdi F, Tsertsvadze A, Moher D. Comparative Effectiveness of Lipid-Modifying Agents [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2009 Sep. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=cer16. DRUGDEX® System. [Internet database]. Greenwood Village, Colo: Thomson Reuters (Healthcare) Inc. Updated periodically. FDA Drug Safety Communication: New restrictions, contraindications, and dose limitations for Zocor (simvastatin) to reduce the risk of muscle injury. [cited February 5, 2014]. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm256581.htm. Revision History Revision Date Revision Summary 09/09/2016 Added drugs that were previously included in dru420 [Epanova, Lipitor, Lovaza, Omtryg, omega-2 acids (generic), Simcor, Vascepa]. Added Crestor, effective January 2017 06/10/2016 12/11/2015 No criteria changes • Retitled policy “High-Cost Lipid-Modifying Medications” • Removed Omega-3 fatty acids from policy • Added fluvastatin (Lescol) and fluvastatin generics to policy © 2016 OmedaRx. All rights reserved. dru336.5 Page 6 of 6