* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Información general del proyecto
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
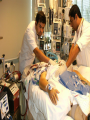
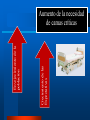
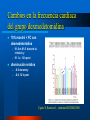
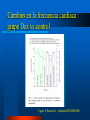
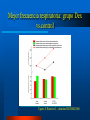
Integración del Farmacéutico en UCI Dr. Sebastián Ugarte ICU INDISA Clinic – Andrés Bello University President FPIMCTI Council WFSCCM Envejecimiento de la población Aumento de la necesidad de camas críticas Crecimiento de las Expectativas Aumento de la necesidad de camas críticas Crecimiento de las Expectativas Envejecimiento de la población Aumento de la necesidad de camas críticas Ecases de camas UCI Chile: ocupación es 92%. Australia: en algunos hospitales es 90%* Irlanda: no hay camas de UCI para el 30% que requiere.** *http://www.dhs.vic.gov.au/ahs/archive/icu/servlev.htm **http://www.icmed.com/archive/publications/Adult%20In tensive%20Care%20Capacity%20Planning%20and%20D evelopment%20in%20Ireland.doc Escasez de los Profesionales de UCI Crecimiento de las Expectativas Envejecimiento de la población Aumento de la necesidad de camas críticas Profesionales críticos ¿EL TEMA ES QUIENES ESTARÁN A CARGO DE LOS PACIENTES CRÍTICOS? UCI es un trabajo de equipo TENS Nutricionistas Enfermeras Psicólogos Kinesiólogos-Terapistas Médicos Farmacéuticos – Farmecéuticos clínicos 4 Requerimientos de FARMACIA en Chile 1. 2. 3. 4. QF 24/7 Farmacólogo clínico 11 horas UCI Política de calidad de medicamentos Dispensadores automáticos SOCHIMI –SOCHINF 2011 Pharmacy evolved Curricula has changed To prepare as clinicians: – – – – – – pharmacotherapeutics, pharmacokinetics, pathophysiology, human anatomy and physiology, physical assessment, and pharmacoeconomics Additional training for graduates (residencies, fellowships in critical care). Pharm.D Pharmacotherapy. 2002;22(11) Critical Care evolved ¿Qué tienen en común? Alto costo Full teconolgía Velocidad Riesgos ¿Qué más tienen en común? ¿Qué más tienen en común? Trabajo en equipo ¿Qué más tienen en común? Trabajo en equipo Wellcome to the ICU Drug-Drug Interaction Drug-Nutrient Interaction Altered pharmacokinetics ↑ ADE 2013: a global view Ph have been performing clinical services > 3 decades. Drug Intell Clin Pharm 1986;20:33-48. ↑ research articles and surveys have identified areas in which critical care Ph make significant contributions to patient care. Am J Hosp Pharm 1993;50:1371-404. Pharmacotherapy 1994;14:282-304. Am J Hosp Pharm 2000;57:2171-87. N Engl J Med 1972;287:151. Drug Intell Clin Pharm 1973;7:298-308. Am J Hosp Pharm 1995;52:980-4. 5 areas of contribution: or more? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Assisting physicians in pharmacotherapy decision making, Pharmacokinetic consultations Monitoring drug efficacy and safety, Drug information, and Medical education to physicians, nurses, and patients CPR team Pharm.D Pharmacotherapy. 2002;22(11) 3 Specific to the CPR team Provide artificial respiration Administer chest compressions Relative to drugs: – – – – – – prepare drugs, administer drugs, record drug administration, provide drug information, calculate dosages and infusion rates, set up or operate intravenous pump devices. Pharm.D Pharmacotherapy. 2002;22(11) Science of Safety and Patient Health In the U.S. health care system – 7 % of patients suffer a medication error – On average, every patient admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU) suffers an adverse event – 78% of serious medical errors in the ICU Crit Care Med 2005, 33:1694-1700. 6 On average, every patient admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU) suffers an adverse event 6 areas of contribution: or more? Assisting physicians in pharmacotherapy decision making, 2. Pharmacokinetic consultations 3. Monitoring drug efficacy and safety, 4. Drug information, and 5. Medical education to physicians, nurses, and patients 6. CPR team 7. Cost containment issues 8. Nutrition support, and 9. Clinical research Crit Care Med 1999;27:422-6 10. Academic 1. ¿Y esto cambió los resultados? Measurable clinical effects? ↓ Drug errors and adverse drug events ↓ morbidity and mortality rates ↓ $$ On average, every patient admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU) suffers an adverse event ↓ Drug errors and adverse drug events Altered organ function and polypharmacy contribute to ADEs in ICU patients. Clinical pharmacists can reduce drug errors and ADEs in a hospital setting JAMA 1999;282:267-70. Prospective Study 2 phases, baseline and intervention ICU with a pharmacist rounding vs. control coronary care unit. Within 9 months: – ↓ 66% in preventable ADEs (10.4 before to 3.5/1000 patientdays after) – 99% of recommendations were accepted by physicians. JAMA 1999;282:267-70. Can affect clinical end points ↓ Fluid intake in fluid-restricted patients in the ICU Optimal antimicrobial selection in streptococcal pneumonia ↓Nephrotoxicity associated with aminoglycosides – with a ↓ cost > $90,000/100 patients studied. Identifying appropriate indicators to ensure that drug therapy leads to a measurable outcome Drug Intell Clin Pharm 1991;25:208-10. Presence vs absence of a clinical pharmacist Shorter hospital stays Benefit:cost ratio of 6:1 Lower percentage of medical patients required transfer back into the ICU Am J Hosp Pharm 1993;50:1875-84. Reduction in hospital mortality rates number of pharmacists/average daily census and combined hospital wide clinical pharmacy services, were associated with a ↓in mortality – pharmacists in patient-care areas and participation on medical rounds, – availability of therapeutic drug and ADE monitoring – pharmacokinetic services – patient drug counseling – nutrition recommendations – admission histories – clinical research, and drug information services. Pharmacotherapy 1994;14:620-30. 1029 hospitals Patient mortality rates decrease as pharmacy staffing/occupied bed increases specific services having greatest impact: – participation on medical rounds – On CPR teams, – absolute reduction in mortality of 40,000 patients Pharmacotherapy 1999;19:130-8. Pharmacotherapy 1999;19:556-64. Positive economic impact 41% lower drug costs (mean $73.75 vs $43.40, p<0.001) $7900 approximate savings (95% CI $900-14,800) extrapolated to an annual savings of $113,000 (95% CI $13,000-212,000) based on 80,000 patientdays in those areas in 1997. Crit Care Med 1994;22:1044-8. Pharmacotherapy 1999;19:1354-62 Am J Hosp Pharm 1986;43:3008-13. Economic impact Pharmacotherapy 1999;19:1354-62 Economic impact in the ICU Am J Hosp Pharm 1986;43:3008-13. Protocolo de infusión Dex Ugarte S, Ramirez J, submitted RCHMI 2008 Cambios en la frecuencia cardíaca del grupo dexmedetomidina 70% mostró < FC con dexmedetomidina – 91.8 vs 81.6 durante la infusión y – 91.1 a 12 h post disminución relativa – - 8.6 durante y – - 0.8, 12 h post Ugarte S, Ramirez J, submitted RCHMI 2008 Cambios en la frecuencia cardíaca : grupo Dex vs.control Ugarte S, Ramirez J, submitted RCHMI 2008 Mejor frecuencia respiratoria: grupo Dex vs.control Ugarte S, Ramirez J, submitted RCHMI 2008 Conclusions Pharmacy has evolved into a profession that clearly complements the practice of medicine. Critical care pharmacists can have a positive impact in the ICU by decreasing ADEs, improving morbidity and mortality rates, and decreasing overall health care costs. The education and training that pharmacists receive prepare these clinicians to be valuable members of multidisciplinary health care teams. Thank you