* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EXPERIMENT NO.(5) RC OSCILLATORS
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stage monitor system wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
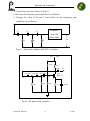
Electronics II Laboratory EXPERIMENT NO.(5) RC OSCILLATORS Object To study the characteristics of RC oscillators namely: 1) Phase shift oscillators. 2) Wein bridge oscillators. Equipments Components 1- Dual Power supply 2- Oscilloscope 3- Operational amplifier 4- Transistors 5- Components as shown in figures 6- Function generator Theory The oscillator is an amplifier with positive feedback that generates a number of waveforms usually used in instrumentation and test equipments. An oscillator that generates a sinusoidal output is called a harmonic oscillator; the transistor is usually acts in the active region. The output of the relaxation oscillator is not sinusoidal depending on the transient rise and decay of voltage in RC or RL circuits. There are two types of RC oscillators: 1. Phase shift oscillators in which the output of an amplifier must be 180o out of phase with input. A general circuit diagram of a phase shift oscillator is shown in Fig.(l), where the amplifier is an ideal one. A phase shift network (usually a resistor-capacitor network) is used to Jassim K. Hmood 1 3-2011 Electronics II Laboratory produce an additional phase shift of 180 at one particular frequency to develop the required positive feedback. From the mesh network equations of the feedback network, we find the feedback factor β as, Vf 1 2 Vo 1 5 j 6 3 Where= 1 / RC The phase shift of the feedback network must be 180 then: 6 3 0 6 so, f 1 2 6RC At this frequency = 1/29 and it is required that (A) must be at least 29 to satisfy oscillation condition as shown in Fig.(2). The phase shift oscillator is used to the range of frequencies for several hertz to several kilohertz and so includes the range of audio frequencies. The frequency depends on the impedance elements in the phase shift network. The phase shift oscillator circuit is not very suitable for generating variable frequency because the resistors and capacitors must be simultaneously changed to obtain the required frequency control over a wide range therefore it is used mostly in fixed frequency applications. 2. The Wien bridge oscillator is used to obtain variable frequency signal. The frequency of oscillation can be changed by using two gang variable capacitors or two gang variable resistors. The circuit diagram is shown in Fig.(3). In this circuit, there are two types of feedback:a. positive feedback through Z1 and Z2 whose components determine the frequency of oscillation. Jassim K. Hmood 2 3-2011 Electronics II Laboratory b. negative feedback through Rl and R2 whose elements affect the amplitude of oscillation. B V f Vo A1 Z2 Z1 Z2 R1 R2 Moreover, the loop gain BA is given by BA R1 . 1 R2 3 j( 1 2 ) ; Where RC Now to satisfy the oscillation condition with BA = 1 requires = 1 Then; 1 R1 1 3 f R2 2RC Continuous variation of frequency is accomplished by varying simultaneously two capacitors. Change in frequency range accomplished by switching in different values for the two identical resistors R. Procedure 1. Connect the circuit as shown in Fig.(2), insert potentiometer of l k in the feedback arm. 2. Measure the frequency of oscillation (f o) and the amplitude of the output voltage. 3. Measure and draw the waveforms of points A, B, C and D. 4. Observe the effect of variation of the potentiometer on the frequency of oscillation. 5. Observe the effect of the variation of RE and RB on fo. 6. Break the feedback network and measure the gain by connecting the signal generator to point d. Jassim K. Hmood 3 3-2011 Electronics II Laboratory 7. Connect the circuit as shown in Fig.(3). 8. Measure the frequency and amplitude of oscillation. 9. Change the value of R and C their effect on the frequency and amplitude of oscillation. C C Amplifier C with 180 phase shift R R Vo R Fig.(1) : Schematic of phase shift (RC) Oscillator Vcc 8.2k -12V 390 10uF 0.01uF A 0.01uF B 560 0.01uF D C 560 680 Vo Q1 BCY71 10 47uF Fig.(2): RC phase shift oscillator Jassim K. Hmood 4 3-2011 Electronics II Laboratory Rf 2.2k +15V + 741 eo -15V R1 1k 220 0.1uF 0.1uF 220 Fig.(3): Wien bridge oscillator Discussion l. What are the general oscillation conditions in feedback amplifiers? 2. Drive an expression for the frequency of oscillation in both phase shift and wein bridge oscillators. 3. Compare between phase shift and wein bridge oscillators. 4. Comment on the wave forms at points A, B, C and D in figure. 5. Discuss the effect of changing RB and RE on fo. Jassim K. Hmood 5 3-2011