* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RF amplifier PA70E on RD70HVF1
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
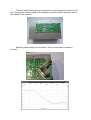
RF amplifier PA70E on RD70HVF1 by Peter SP2DMB www.sp2dmb.blogspot.com ver. 1.0 13.08.2014 www.sp2dmb.cba.pl [email protected] Shows a further my design. This time, a more simplified version of the power amplifier - PA70E (Economic). The minimum elements of maximum effect. Depending on input signal, the output power on 70MHz will inrange 40-50W. The amplifier can work CW, SSB and FM. The design is based on mosfet transistor manufacturing by MITSUBISHI RD70HVF1. Practice has shown that it is very resistant to destruction. NOTICE ! Don’t exceeds gate-source and temperature limit. The plate is one-sided, tinned with solder mask. Plate size: 52x131mm. Diagram is typical for this type of design. This project is modeled on the datasheet. The amplifier consists of several blocks: - RF VOX - if the problem is to control the amplifier, this circuit should be applied. When RF signal appears, two relays are energized: input and antenna relays. Delay from transmit to receive is regulate PR 4,7k - FAN - may be needed if the heat sink is too small. To reduce the fan current shall be connected resistor in series (or a few). Selected so that the performance of the fan enough to cool the heat sink. You can not use resistors, but will increase the noise produced by the fan. - PA - amplifier with RD70HVF1. - Bridge PWR – this circuit can be used to display output power. Display can be tilt meter or LED indicator. Maximum voltage from this circuit is regulate PR 4,7k. If the output voltage will be too small is needed additional D5. - LPF - simple LPF filter 70MHz MOSFETs have characteristics similar to the lamp. This feature allows to control in wide range (mW to watts). Tests done with transverter TS70 has produced more than 30W output power !!! And now the technical details. I used to build the heatsink with dimensions 165.5 x 100 x 35mm The first step is to make a rectangular hole to transistor. Cut out a green field with the mark “RD70HVF1”, to edges of the metallization. NOTE! Do not cut out the extreme edge of the plate !!! The bridge should be soldered to the ground and connected to the screw of transistor (source RD70HVF1). The drain current of the transistor is flowing by two bridges ! The next step is drilling and grooving holes for mounting plate, transistor and fan. The plate should be placed on the heatsink so that the power transistor was at the middle of the heatsink. Soldering always begin from the filters. This is comfortable to measure process. In the next step we are starting from relay antenna. Below pictures of the assembled amplifier: Before mount the transistor, set the slider PR 4,7k to ground. Connect 13.8V voltage to pin + PTT. Check the voltmeter adjustment range gate bias voltage of the transistor. The range is from 0 to approx. 2.7V (3V). Set the slider to the groun again. NOTE ! The image shows the transistor, but this one should be not mounted !!! If everything is fine, coat the bottom of transistor thermal grease and put this one to a hole in the plate. Screws transistor and bridges. Connect the voltage 13.8V to “+ PTT” and point marked “+” - the orange wire in the picture – Set PR 4,7k voltage on the gate in the range of 1.9 to 2.1V. We control and set the drain current at range 40-50 mA. Now time to test. To testing I used transverter TS70 and PA70E. To control the voltage, current and power consumed by the system I usem my construction MULTIMETER. Description of MULTIMETER can be found here: http://www.sp2dmb.cba.pl/projeng.html PA connect through 5A fuse. The first regulation: set TRX on SSB mode. Press PTT and see if anything disturbing happens. My set (TS70 + PA70E) have quiescent current about 0.34A (including 3 relays). We speak into the microphone. On the power meter should be immediately output power. Set TRX in RTTY mode (full carrier). Press the PTT and adjust the trimmers of amplifier to achieve maximum output power. My power meter showed 30W output power ! This amplifier works with my other transverters: TS70 and TH70 or other transverters. On the board there are two 2 pins marked “RX”. This pins should be connected to input circuit of transverter. When we are operating digital modes, may be needed to cool the heatsink fan. Long screws fixing the fan can be used to attach the entire PA. The fan has dimensions of 92 x 92mm. Speed control is performed using resistors with a capacity of at least 2W. We select the value of the resistors to enough cold the heatsink during testing of WSJT or FM. You can also build a regulated power supply to the fan on the LM317. On the board is a simple stripline detector for power output display . The level of the output voltage adjust PR 4,7k (5k). This voltage can be shown on milivoltmeter, LED (eg. 10mm diameter) or LED line. The output marked "RF". I hope that this description will encourage colleagues to build an amplifier. MITSUBISHI mosfet transistors are for me the best solution in this type construction. Link to the video on YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wb8vxSSwI8Q If you have any questions - email me: [email protected] I wish you success in building and much DX-s !!!! 73 – Peter SP2DMB Assembly diagram Elements: C3 = 1 x 100p/100V C12 = 1 x 10µ C20 = 1 x 22p/100V C21 = 1 x 25p C22 = 1 x 65p C26 = 1 x 2,2p C1,C23 = 2 x 47p/100V C17,C19 = 2 x 40p C2,C4 = 2 x 68p/100V C24,C25 = 2 x 56p/500V MICA C5,C8,C10,C14, C29,C30,C31 = 7 x 4,7n C6,C7,C11,C15, C16,C18,C32, C33,C34 = 9 x 100n C9,C13,C27 = 3 x 100µ L2 L4 L5 L6 L11 L3,L7 L8,L9,L10 = 1 x 10t/6,5mm/1,3mm = 1 x FB = 1 x 5t/6,5mm/diam 1mm CuE = 1 x 15uH = 1 x 15µH = 2 x VK200 =3x P,P,P = 3 x 4,7k PR Q1 Q2 = 1 x RD70HVF1 = 1 x BDP953 option D1 = 1 x 2,7V D5 = 1 x 1N4148 opt. D2,D3,D4,D6,D7 = 5 x 1N4148 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6,R7 = 1 x 120 = 1 x 820 = 1 x 8,2k = 1 x 2,2k = 1 x 150 = 2 x 270/2W opt. L1 = 1 x 2t/6,5mm/CuAg 1mm Rel1,Rel2 = 2 x 2 x Um FAN = 1 x option