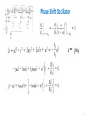* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Analog Sinusoidal Oscillator Part 2
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Cavity magnetron wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Atomic clock wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
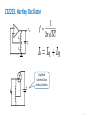
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
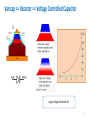
Crystal oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
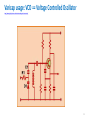
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
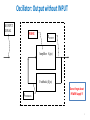
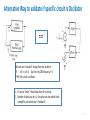
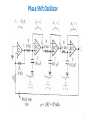
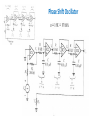
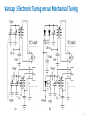
Electronic Instrumentation Analog Sinusoidal Oscillators Part 2 * In this presentation definitions and examples from Wikipedia, HowStaffWorks and some other sources were used Lecturer: Dr. Samuel Kosolapov Items to be defined/refreshed/discussed • Alternative Way to validate if specific circuit is Oscillator • Phase Shift Oscillator • Bubba Oscillator • Z1Z2Z3 Oscillators • Crystal Oscillators • VCO 2 Oscillator: Output without INPUT NO INPUT SIGNAL NOISE XOUTPUT Amplifier: A(jw) Feedback: b(jw) XFEEDBACK Do not forget about POWER Supply !!! 3 Alternative Way to validate if specific circuit is Oscillator == We have now “standard” Analog Electronic problem: IF Vin’ == Vin () (but for only ONE frequency !!!) THEN the circuit is oscillator 1. EE can be “smart”: Break loop when Zin is infinity. 2. Number of blocks can be > 2: It may be not clear which block is amplifier, and which one is “feedback” 4 Phase Shift Oscillator 5 Phase Shift Oscillator 6 Phase Shift Oscillator 7 Phase Shift Oscillator 8 Phase Shift Oscillator 9 Bubba Oscillator http://www.ti.com/lit/ml/sloa087/sloa087.pdf The RC sections each contribute 45° phase shift, The gain, A, must equal 4 for oscillation to occur. The test circuit oscillated at 1.76 kHz Rather than the ideal frequency of 1.72 kHz when the gain was 4.17 rather than the ideal gain of 4. 10 Three-point oscillator == Z1Z2Z3 Oscillator 11 Z1Z2Z3 Oscillator 12 Z1Z2Z3 Oscillator 13 Z1Z2Z3 Oscillator 14 Z1Z2Z3 Oscillator 15 Z1Z2Z3 Colpitts Oscillator. Example & Design Advantage: One transistor only is needed. RF up to 1 GHz can be achieved 16 Z1Z2Z3. Hartley Oscillator Simplified Common Drain Hartley Oscillator 17 Clapp Oscillator It was published by James Kilton Clapp in 1948 Oscillators of this kind were independently developed by several inventors, and one developed by Gouriet had been in operation at the BBC since 1938. Simplified Clapp Oscillator 18 Usage of Oscillator: (Simple) RF Transmitter Warning: Building RF transmitter without special permit is ILLEGAL 19 Crystal Oscillator Problem to be solved: Frequency Stability But: Crystals for f > 50 MHz are too THIN and mechanically fragile 20 Varicap == Varactor == Voltage Controlled Capacitor Usage: Voltage Controlled RLC 21 Varicap == Varactor == Voltage Controlled Capacitor Usage: Voltage Controlled LC 22 Varicap usage: VCO == Voltage Controlled Oscillator https://www.edgefx.in/varactor-diode-circuit-working-and-characteristics/ 23 Varicap : Electronic Tuning versus Mechanical Tuning 24 Control Questions • What have I learned ? 25 Literature to read 1. TBD 26