* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 20.1 KEY CONCEPT Plant life began in the water and
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
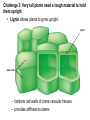
Section 20.1 KEY CONCEPT Plant life began in the water and became adapted to land. Where did life begin? What did life begin as? Land plants evolved from green algae. • Plants and green algae have many common traits. – both are photosynthetic eukaryotes – both have the same types of chlorophyll – both use starch as a storage product – both have cell walls with cellulose Land plants evolved from green algae. • Genetic analysis points to the common ancestor of all plants. – extinct green algae species –modern green algae common in lakes and ponds Land plants evolved from green algae. • Important plant characteristics likely originated in green algae – multicellular body allowing for specialization of cells and tissues – cell division that allows for chemical communication between cells – reproduction involving sperm swimming to egg Land plants evolved from green algae. • True plants evolved through natural selection. – Ancestral green algae lived in areas of shallow water. – Those that could survive longer dry periods were favored. – True plants have embryos that develop while attached to female parent. Land plants evolved from green algae. • True plants evolved through natural selection. Plants have adaptations that allow them to live on land. • Life in the ocean had plentiful water • Plants needed some adaptations to survive the dry environment of land Challenge 1: Land is dry compared to the ocean. • A cuticle allows plants to retain moisture. – waxy, waterproof layer – holds moisture in • Stomata are tiny holes in the cuticle. – can open and close – allow air to move in and out stoma Challenge 2: Sunlight comes from above so plants needs to be as tall as possible. • Plants develop vascular systems to transport materials around plant – brings water and mineral nutrients up from roots – disperses sugars from the leaves – allows plants to grow higher off the ground water and mineral nutrients sugars Challenge 3: Very tall plants need a tough material to hold them upright. • Lignin allows plants to grow upright. lignin plant cells – hardens cell walls of some vascular tissues – provides stiffness to stems Challenge 4: Plants need to reproduce without using water. • Pollen grains protect plant gametes. – pollen grains contain a cell that divides to form sperm • A seed is a storage device for a plant embryo. – seed coats protect embryos from drying wind and sunlight Plants evolve with other organisms in their environment. • Plants and other organisms can share a mutualistic relationship. – a mutualism is an interaction in which two species benefit – plant roots and certain fungi and bacteria (nitrogen fixation) – flowering plants and their animal pollinators Plants evolve with other organisms in their environment. • Plants have adaptations that prevent animals from eating them (Plant-herbivore interactions). – spines and thorns – defensive chemicals