* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Reproductive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
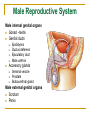
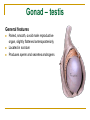
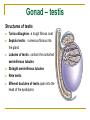
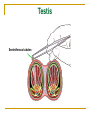
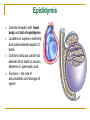
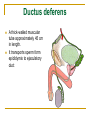
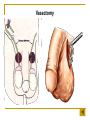
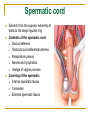
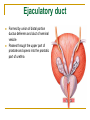
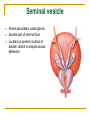
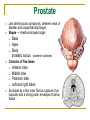
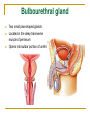
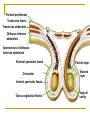
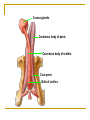
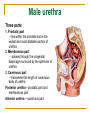
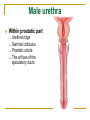
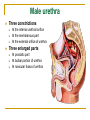
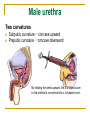
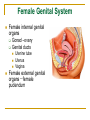
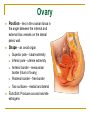
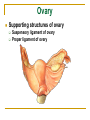
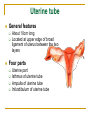
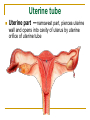
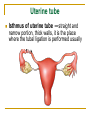
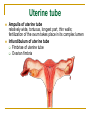
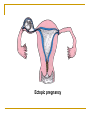
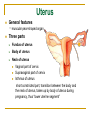
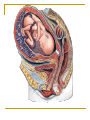
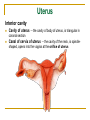
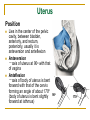
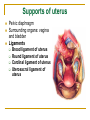
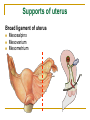
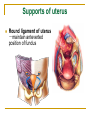
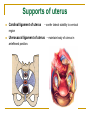
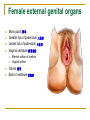
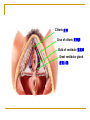
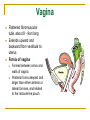
The Reproductive System SHANDONG UNIVERSITY Liu Zhiyu The Reproductive System Composition Internal genital organ Gonads (sex glands) -manufacture the sex cells an secrete the sex hormones. Genital ducts - transport the sex cells from the site of production into site fertilization Accessory glands -secrete the fluid External genital organ Male Reprodutive System Male Reproductive System Male internal genital organs Gonad –testis Genital ducts Epididymis Ductus deferens Ejaculatory duct Male urethra Accessory glands Seminal vesicle Prostate Bulbourethral gland Male external genital organs Scrotum Penis Male internal genital organs Gonad – testis General features Paired, smooth, ovoid male reproductive organ, slightly flattened anteroposteriorly Located in scrotum Produces sperm and secretes androgens Gonad – testis Structures of testis Tunica albuginea : a tough fibrous coat Septula testis : numerous fibrous into the gland Lobules of testis : contain the contorted seminiferous tubules Striaght seminiferous tubules Rete testis Efferent ductules of testis open into the head of the epididymis Testis Seminiferous tubules Epididymis Comma-shaped, with head, body and tail of epididymis Located on superior extremity and posterolateral aspect of testis Contains tortuous canal that extends from testis to ductus deferens in spermatic cord Function – the site of accumulation and storage of sperm Ductus deferens A thick-walled muscular tube approximately 45 cm in length. It transports sperm form epididymis to ejaculatory duct Ductus deferens 1. Testicular part - extends form the tail of epididymis to the superior extremity of testis 2. Spermatic part - extends form superior extremity of testis to the superficial inguinal ring, the place where the vasectomy is performed 3. Inguinal part - extends form superficial to deep inguinal rings 4. Pelvic part - crosses the obturator neurovascular bundle and the ureter to reach the base of bladder, where it expands to form the ampulla ductus deferentis Vasectomy Spermatic cord Extends from the superior extremity of testis to the deep inguinal ring Contents of the spermatic cord Ductus deferens Testicular and deferential arteries Pampiniform plexus Nerves and lymphatics Vestige of vagina process Covering of the spermatic Internal spermatic fascia Cremaster External spermatic fascia Ejaculatory duct Formed by union of distal portion ductus deferens and duct of seminal vesicle Passes through the upper part of prostate and opens into the prostatic part of urethra Seminal vesicle Paired sacculated, coiled glands Secrete part of seminal fluid Located on posterior surface of bladder, lateral to ampulla ductus deferentis Prostate Lies behind pubic symphysis, between neck of bladder and urogenital diaphragm Shape — chestnut-shaped organ Contains of five lobes Base Apex Body: prostatic sulcus (posterior surfaces) Anterior lobe Middle lobe Posterior lobe Left and right lobes Enclosed by a thin inner fibrous capsule (true capsule) and a strong outer envelope of pelvic fascia Bulbourethral gland Two small pea-shaped glands Located in the deep transverse muscle of perineum Opens into bulbar portion of urethra Male External genital organs Scrotum Pouch of thin skin lying below the root of the penis Divided into two haves by septum of scrotum, contains testes and their ducts Walls Skin Dartos coat Deep to skin A connective tissue layer that contains many smooth muscle fibers Contracts in response to cold, pulling the testes closer to the body and wrinkling the skin Parietal peritoneum Transverse fascia Trasversus abdominis Obliquus internus abdominis Aponeurosis of obliquus externus abdominis External spermatic fascia Cremaster Parietal layer Visceral layer Internal spermatic fascia Tunica vaginalis of testis Vaginal cavity Penis Consists of the root, body and glans penis Contains Two cavernous body of penis A cavernous body of urethra Skin-thin and loose Prepuce of penis Frenulum of prepuce Corona glandis Cavernous body of penis Cavernous body of urethra Crus penis Bulb of urethra Male urethra Three parts 1. Prostatic part -lies within the prostate and is the widest and most dilatable portion of urethra. 2. Membranous part - passes through the urogenital diaphragm surround by the sphincter of urethra 3. Cavernous part -transverse the length of cavernous body of urethra Posterior urethra-prostatic part and membranous part Anterior urethra –-cavernous part Male urethra Within prostatic part Urethral ridge Seminal colliculus Prostatic utricle The orifices of the ejaculatory ducts Male urethra Three constrictions At the internal urethral orifice At the membranous part At the external orifice of urethra Three enlarged parts At prostatic part At bulbar portion of urethra At navicular fossa of urethra Male urethra Two curvatures Subpubic curvature -concave upward Prepubic curvature -concave downward By holding the penis upward, the S-shaped curve to the urethra is converted into a J-shaped curve. Female Reproductive System Female Genital System Female internal genital organs Gonad –ovary Genital ducts Uterine tube Uterus Vagina Female external genital organs-female pudendum Female internal genital organs Ovary Position-lies in the ovarian fossa in the angle between the internal and external iliac vessels on the lateral pelvic wall. Shape-an ovoid organ Superior pole-tubal extremity Inferior pole-uterine extremity Anterior border-mesovarian border (hilum of ovary) Posterior border-free border Two surfaces-medial and lateral Function: Produce ova and secrete estrogens Ovary Supporting structures of ovary Suspensory ligament of ovary Proper ligament of ovary Uterine tube General features About 10cm long Located at upper edge of broad ligament of uterus between the two layers Four parts Uterine part Isthmus of uterine tube Ampulla of uterine tube Infundibulum of uterine tube Uterine tube Uterine part -narrowest part, pierces uterine wall and opens into cavity of uterus by uterine orifice of uterine tube Uterine tube Isthmus of uterine tube -straight and narrow portion, thick walls, it is the place where the tubal ligation is performed usually Uterine tube Ampulla of uterine tube relatively wide, tortuous, longest part, thin walls; fertilization of the ovum takes place in its complex lumen Infundibulum of uterine tube Fimbriae of uterine tube Ovarian fimbria Ectopic pregnancy Uterus General features -muscular pear-shaped organ Three parts Fundus of uterus Body of uterus Neck of uterus Vaginal part of cervix Supravaginal part of cervix Isthmus of uterus short constricted part, transition between the body and the neck of uterus, taken up by body of uterus during pregnancy, thus “lower uterine segment” Uterus Interior cavity Cavity of uterus -the cavity of body of uterus, is triangular in coronal section Canal of cervix of uterus -the cavity of the neck, is spindleshaped, opens into the vagina at the orifice of uterus Uterus Position Lies in the center of the pelvic cavity, between bladder, anteriorly, and rectum, posteriorly, usually it is anteversion and anteflexion Anteversion -axis of uterus at 90o with that of vagina Anteflexion -axis of body of uterus is bent forward with that of the cervix forming an angle of about 170o (body of uterus is bent slightly forward at isthmus) 90o 170o Supports of uterus Pelvic diaphragm Surrounding organs: vagina and bladder Ligaments Broad ligament of uterus Round ligament of uterus Cardinal ligament of uterus Uterosacral ligament of uterus Supports of uterus Broad ligament of uterus Mesosalpinx Mesovarium Mesometrium Supports of uterus Round ligament of uterus -maintain anteverted position of fundus Supports of uterus Cardinal ligament of uterus -confer lateral stability to cervical region Uterosacral ligament of uterus -maintain body of uterus in anteflexed position. Female external genital organs Mons pubis 阴阜 Greater lips of pudendum 大阴唇 Lesser lips of pudendum 小阴唇 Vaginal vestibule 阴道前庭 Eternal orifice of urethra Vaginal orifice Clitoris 阴蒂 Bulb of vestibule 前庭球 Clitoris 阴蒂 Crus of clitoris 阴蒂脚 Bulb of vestibule 前庭球 Great vestibular gland 前庭大腺 Vagina Flattened fibromuscular tube, about 8~9cm long Extends upward and backward from vestibule to uterus Fornix of vagina Formed between cervix and walls of vagina Posterior fornix deepest and larger than either anterior or lateral fornices, and related to the rectouterine pouch