* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Community Interactions
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
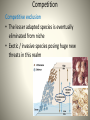
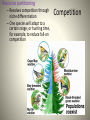
Community Interactions Community = all biotica within a defined area Interactions • • • • • • *Predation *Competition Mutualism Commensalism Herbivory Parasitism *considered to be defining interactions within ecosystems; research growing in other areas Predation • Predator/prey • Often cyclic Predation • Predators have many adaptations for locating and killing prey • Can you name 3 of each? • Prey also have many adaptations to avoid being eaten • Name 5 Competition • Species compete for same niche Interspecific – Species competition keeps both populations in check – Hard to determine in wild, as would have to eliminate one species to see how other population reacts – Easier in lab Competition Competitive exclusion • The lesser adapted species is eventually eliminated from niche • Exotic / invasive species posing huge new threats in this realm Resource partitioning – Resolves competition through niche differentiation – One species will adapt to a certain range, or hunting time, for example, to reduce full-on competition Competition Competition http://www.ib.bioninja.com.au/options/option-g-ecology-and-conser/g1community-ecology.html Competition Character displacement – Species evolve slightly different eating habits, beak shape, etc, to differentiate within habitat – Allopatric populations (geographically separate) can be seen to have more similar characteristics than sympatric (overlapping) populations Herbivory • Herbivores eating producers Parasitism • Ecto – external • Endo – internal • Parasitoidism – lay eggs for young to feed Disease • Interaction because disease is caused by living pathogens • Related to parasitism • Pathogens: – Fungi – Bacteria – Viruses (sort of, but not really alive) – Protists – Prions (proteins) Mutualism Win-win Commensalism • Win/eh • debated