* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RNSG 1144 SPRING 2016 Study Guide Rev
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
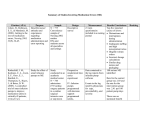
LAREDO COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE NURSING PROGRAM RNSG 1144 Concepts of Adult Health Study Guide (To Accompany Course Syllabus) Chapter Objectives Ch 29 1. Accurately assess body temperature, pulse, respirations, oxygen saturation, and blood pressure. Course Student Learning Outcomes 1,3,4,6,7 2. Explain the physiology of normal regulation of blood pressure, pulse, oxygen saturation, and respirations. 1,2,3,4,6,7 3. Describe the factors that cause variations in body temperature, pulse, oxygen saturation, respirations and blood pressure. 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 4. Describe the cultural and ethnic variations with blood pressure assessment. 1,2,3,4,6,7 5. Identify ranges of acceptable vital sign values for an adult. 1,2,3,4,6,7 6. Accurately record and report vital sign measurements. 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 7. Appropriately delegate measurement of vital signs to nursing assistive personnel. 1. Discuss the nurse’s role and responsibilities in 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 Ch 31: Medication Administration(pages medication administration. 565-639) 2. Describe the physiological mechanisms of medication action. 3. Discuss factors that influence medication actions. 4. Discuss methods used to educate patients about 1,2,3,4,5,6 1,6 1,4,6 1,2,3,4,5,6 prescribed medications. 5. Describe factors to consider when choosing routes of medication administration. Revised Spring 2016 1,3,4,5,6,7 6. Calculate prescribed medication doses correctly. 1,4,5 7. Discuss factors to include in assessing a patient’s needs for response to medication therapy. 1,4,5,6,7 8. Identify the six rights of medication administration and apply them in laboratory setting. 9. Correctly and safely prepare and administer parenteral medications in the laboratory setting. Ch 41 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance (pages 904-905, 906-913) CH 44 Parenteral Nutrition pp. 10211024 Ch 48 Wound Care -(pages 1176-1231) Revised Spring 2016 1,3,4,5,6,7 1,3,4,5,6,7 10. Identify the nurse’s role and responsibilities in medication administration. 1,2,3,4,5,6 1. Apply the nursing process when caring for patients with fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base imbalances. 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 2. Discuss purpose and procedure for initiation and maintenance of intravenous therapy. 1,3,4,5,6,7 3. Describe how to measure and record fluid intake and output. 1,4,6 4. Explain how to change intravenous solutions and tubing and discontinue an infusion. 1,3,4,5,6 5. Describe potential complications of intravenous therapy and what to do if they occur. 1,3,4,5,6 6. Discuss the procedure for initiating a blood transfusion and interventions to manage a transfusion reaction. 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 7. Calculate an intravenous flow rate. 1,4,5 8. Explain the purpose, initiation and maintenance of central venous devices. 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 9. Discuss the nurse’s role and responsibilities with parenteral nutrition. 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 1. Discuss the risk factors that contribute to 1,2,3,4,6 pressure ulcer formation. 2. Describe the pressure ulcer staging system. 3. Discuss the normal process of wound healing. 1,4,6 Ch 45 Urinary Elimination (PP10611084) 4. Describe the differences of wound healing by primary and secondary intention. 5. Describe complications of wound healing. 6. Explain the factors that impede or promote wound healing. 7. List nursing diagnoses associated with impaired skin integrity. 8. List appropriate nursing interventions for a patient with impaired skin integrity. 1,4,6 9. Identify the nurse’s role and responsibilities of wound care management. 1,2,3,4,5,6 1. Compare and contrast common alterations in urinary elimination. 2. Identify nursing diagnoses appropriate for patients with alterations in urinary elimination. 3. Obtain urine specimens correctly from an indwelling urinary catheter. 4. Insert and remove a urinary catheter correctly in both male and female clients. 6. Irrigate a urinary catheter correctly. 7. Discuss nursing measures to reduce urinary tract infection of a client with an indwelling urinary catheter. 1,2,6 8. Obtain and record urinary output. Ch 44 Nutrition (1018-1039) Chapter40 Oxygenation(pp.844878) Revised Spring 2016 1. Describe the procedure for initiating, maintaining, and removing nasogastric tubes. 2. Discuss patient teaching in relation to patient’s expectations. 3. Explain the nurse’s role and responsibilities in the management of nasogastric tubes with and without suction. 4. Discuss the nurse’s role and responsibilities in the management of enteral feedings. 1. Identify the clinical outcomes occurring as a result of hyperventilation, hypoventilation, and hypoxemia. 2. Assess for the risk factors affecting a patient’s oxygenation. 3. Assess for the physical manifestations that occur with alterations in oxygenation. 1,4,6 1,4,6 1,2,3,4,5,6, 1,2,3,4,5,6 1,2,4,6,7 1,3,4,6,7 1,3,4,6,7 1,3,4,6,7 1,2,3,4,6 1,2,6 1,3,4,6 1,3,4,6 1,3,4,6,7 1,3,4,6,7 1,2,3,4,6 1,3,4,6 1,3,4,6 4. Provide/simulate oral, nasal and tracheostomy airway care in the laboratory setting. 5. Identify the nurse’s role and responsibilities in the management of a client’s oxygenation’s needs. Revised Spring 2016 1,3,4,6,7 1,2,3,4,5,6