* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Theorem 3.9
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
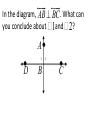
Geometry 3.6 Big Idea: Prove Theorems About Perpendicular Lines Theorem 3.8 If two lines intersect to form a linear pair of congruent angles, then the lines are ┴ . Theorem 3.9 If two lines are perpendicular, then they intersect to form 4 right angles . In the diagram, AB ^ BC. What can you conclude about Ð1and Ð2? A 1 D B 2 C Theorem 3.10 If 2 sides of 2 adjacent acute angles are ┴ , then the angles are complementary. In the diagram, AB ^ BC. Find the value of x. 51 3x Theorem 3.11 Perpendicular Transversal Theorem If a transversal is ┴ to one of 2 parallel lines, then it is ┴ to the other line. Theorem 3.12 Lines ┴ to a Transversal Theorem In a plane, if 2 lines are ┴ to the same line, then they are parallel to each other. Distance from a Line The shortest distance from a point to a line is the length of a ┴ segment from the point to the line. Distance from a Line The distance between any two ║ lines is the length of any ┴ segment joining the 2 lines.