* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download scala tympani - cloudfront.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
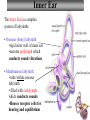
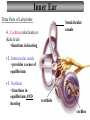
Auditory processing disorder wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
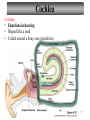
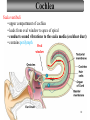
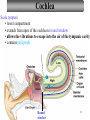
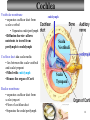
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
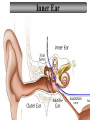
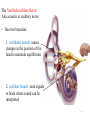
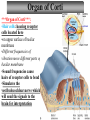
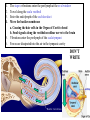
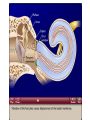
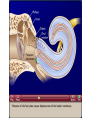
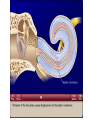
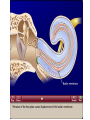
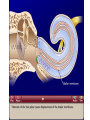
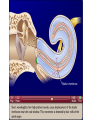
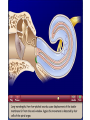
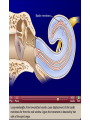
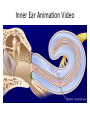
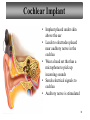
Tape in Notebook 5 mins • 50: 12.3 Clinical Application Smell and Taste Disorders • 54: Lab 31 Smell and Taste Lab • 55: Hearing Case Study: No More Loud Music (Read/Highlight/Questions) • 56: External Ear Picture (color-coded--Functions) • 56: Now Hear This: Don’t Remove Earwax (Read/Highlight/Questions) • 58: Middle Ear Picture (color-coded---Functions) • 60: All About Ear Infections (ONLY Highlight) • 62: Inner Ear Picture (color-coded---Functions) 1 Sponge: Set up Cornell Notes on pg. 63 Topic: 12.5: Major Parts of the Inner Ear Essential Questions: Picture Bubble Map of Inner Ear: • Cochlea • Semicircular canals • Osseous Labyrinth • Membranous Labyrinth • Vestibule • Vestibulocochlear Nerve 12.5: Major Parts of the Inner Ear 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules QUIZ: On MONDAY Labeling the parts of the external, middle, and inner ear Extra Credit: • IB Art Show @ mall • Little Mermaid • Tonight 6pm • Sat 2pm Inner Ear 3 Inner Ear 4 Inner Ear The Inner Ear is a complex system of labyrinths • Osseous (bony) labyrinth •rigid outer wall of inner ear •secretes perilymph which conducts sound vibrations • Membranous labyrinth • tube within osseous labyrinth • filled with endolymph which conducts sounds •Houses receptor cells for hearing and equilibrium 5 Inner Ear Three Parts of Labyrinths: Semicircular canals •1. Cochlea (coke/le/ah) or (Kok/le/ah) •functions in hearing • 2. Semicircular canals • provides a sense of equilibrium • 3. Vestibule • functions in equilibrium AND hearing vestibule 6 cochlea The Vestibulocochlear Nerve: Aka acoustic or auditory nerve • Has two branches: 1. vestibular branch: senses changes in the position of the head to maintain equilibrium 2. cochlear branch: send signals to brain where sound can be interpreted 7 Cochlea Pg. 62 • Leave a little room for info about cochlea Organ Scala Scala Cochlear Vestibular Basilar Vestibuli Tympani Duct Membrane Membrane of Corti 8 Cochlea Cochlea • Functions in hearing • Shaped like a snail • Coiled around a bony core (modiolus) 9 Cochlea Scala vestibuli • upper compartment of cochlea • leads from oval window to apex of spiral • conducts sound vibrations to the scala media (cochlear duct) • contains perilymph Oval window 10 Cochlea Scala tympani • lower compartment • extends from apex of the cochlea to round window • allows the vibrations to escape into the air of the tympanic cavity • contains perilymph Round window 11 Cochlea Vestibular membrane • separates cochlear duct from scala vestibuli • Separates endo/perilymph •Diffusion barrier- allows nutrients to travel from perilymph to endolymph Cochlear duct aka scala media • lies between the scala vestibuli and scala tympani •Filled with endolymph •Houses the organ of Corti Basilar membrane • separates cochlear duct from scala tympani •Floor of cochlear duct •Separates the endo/perilymph endolymph Scala Vestibuli Scala Tympani 12 Organ of Corti ***Organ of Corti***: •Hair cells: hearing receptor cells located here •on upper surface of basilar membrane •Different frequencies of vibration move different parts of basilar membrane •Sound frequencies cause hairs of receptor cells to bend •Simulates the vestibulocochlear nerve which will send the signals to the brain for interpretation 13 Pg. 62 Label this diagram of the Ear *Quiz on Mon. Tympanic Membrane Cochlea Incus Tympanic Cavity Auricle Stapes Round Window Malleus Auditory Tube Semicircular Canals Vestibulocochlear Nerve External Acoustic Meatus14 Pg. 62 Incus stapes malleus Auricle Tympanic membrane Label this diagram of the Ear *Quiz on Mon. Semicircular canals cochlea Vestibulocochlear nerve Round window External acoustic meatus Auditory tube Tympanic cavity Tympanic Membrane Cochlea Incus Tympanic Cavity Auricle Stapes Round Window Malleus Auditory Tube Semicircular Canals Vestibulocochlear Nerve External Acoustic Meatus15 Sponge: Set up Cornell Notes on pg. 65 Topic: 12.5: How Sound Travels Through the Inner Ear Essential Questions: • NONE. 12.5: How Sound Travels Through the Inner Ear 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Ear Labeling Quiz Time 13. 14. 15pts 15. 17 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The stapes vibrations enter the perilymph at the oval window Travel along the scala vestibuli Enter the endolymph of the cochlear duct Move the basilar membrane a. Causing the hair cells in the Organ of Corti to bend b. Send signals along the vestibulocochlear nerve to the brain Vibrations enter the perilymph of the scala tympani Forces are dissipated into the air in the tympanic cavity DON’T WRITE 1. Sound waves vibrate the tympanic membrane 2. The tympanic membrane vibrates the auditory ossicles 3. The vibrations enter the perilymph (fluid in the scala vestibule and scala tympani) at the oval window 4. Travel along the scala vestibule (top compartment of cochlea) 5. Enter the endolymph (fluid in the cochlear duct) of the cochlear duct 6. These vibrations move the basilar membrane a. Frequencies cause organ of corti to bend against the tectorial membrane b. Vesicles in hair cells release neurotransmitters c. Neurotransmitters stimulates the ends of nearby sensory nerve fibers d. Impulse travels along the cochlear branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve e. To the medulla oblongata f. Through the midbrain g. To the thalamus h. Into auditory cortices of the temporal lobes of the cerebrum (BRAIN) where they are interpreted 7. Vibrations enter the perilymph of the scala tympani 8. Forces are dissipated into the air in the tympanic cavity by movement of the round window Inner Ear Animation Video 29 Cochlear Implant • Implant placed under skin above the ear • Leads to electrodes placed near auditory nerve in the cochlea • Wear a head set that has a microphone to pick up incoming sounds • Sends electrical signals to cochlea • Auditory nerve is stimulated 30 Cochlear Implants 3m7s 31 8 mo. Old Deaf Baby with Cochlear Implants 49s http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HTzTt1VnHRM 32 Bionic Ears Start at (4m42s) 4m10s 33 Clinical Application 12.4: Getting a Cochlear Implant