* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study questions - (canvas.brown.edu).
Survey
Document related concepts
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Retinal waves wikipedia , lookup
Retinitis pigmentosa wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
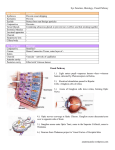
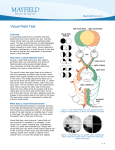
VISUAL SYSTEM I. TRUE or FALSE. Circle the correct letter. T F 1. Axons of retinal ganglion cells synapse in the striate cortex. T F 2. Light depolarizes photoreceptors, bipolars and ganglion cells to produce the sensation of vision. T F 3. The lens is the main refracting element of the eye. T F 4. Photopic vision refers to vision mediated by the eye in relatively bright, daylight conditions. T F 5. The antagonistic surrounds of ganglion-cell receptive fields are largely attributable to the lateral inhibitory circuitry involving the horizontal cells. T F 6. In the cat retina, ganglion cells of the X-cell class have smaller receptive fields and more tonic (sustained) light responses that do Y cells. T F 7. The ON and OFF channels of the retina can be traced to two different classes of bipolar cells with opposing responses to the photoreceptor transmitter. T F 8. In humans, retinal ganglion cells lying in the temporal hemiretina send their axons to the contralateral hemisphere by decussating at the optic chiasm. II. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Circle every correct answer. There may be more than one correct answer per question. 1. Visual acuity is degraded by each of the following a. b. c. d. damage to the fovea of the retina eliminating the air/cornea interface by immersing the eye in water dilating the pupil with topical application of drugs distorting the shape of the eyeball 2. The visual field defect produced by transection of the optic chiasm in humans is called a. b. c. d. homonymous superior quadrantanopia bitemporal hemianopia binasal hemianopia bilateral homonymous hemianopia 3. The layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus serve to segregate afferents a. b. c. d. from the cortex from those of arising from the retina from different ganglion cell classes from different eyes from the two optic tracts 4. Axons of retinal ganglion cells synapse in a. b. c. d. e. medial geniculate nucleus lateral geniculate nucleus superior colliculus inferior colliculus visual cortex 5. The optic disc of the retina corresponds to the a. b. c. d. e. fovea pupil blind spot shadow of the lens visual axis IV. Label the indicated structure or region in the eye. V. In the space provided beside each pair of visual fields, write the numbers of the lesion or the combination of lesions which produce the defect. (OS = left eye; OD = right eye). VISUAL SYSTEM I. True/False 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. F F F T T 6. T 7. T 8. F II. Multiple choice 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. IV. Ocular Anatomy V. Field defects. A. 2 B. 3 C. 1 + 3 D. 1 + 2 E. 2 + 3 a,b,c,d b b,c b,c c III. Matching 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. S D N J A 6. L 7. R 8. Q 9. O 10. H