* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.3 - Fairfield Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
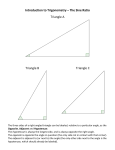
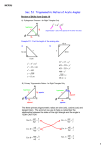
Pre -Lesson 8.3: Trigonometry Name ___________________________per_____date____ Objective: To use the sine, cosine, and tangent ratios to determine side lengths and angle measures in right triangles Big Ideas: We will explore concepts related to right triangles. How do you find a side length or angle measure in a right triangle? How do trigonometric ratios relate to similar triangles? Warm-up: Getting Ready for Trigonometry! TRIGONOMETRY trigon = triangle metron = measure Trigonometry = the relationship of the measures in triangles! reference angle – the angle being referred to ( ) hypotenuse – the side opposite the right angle opposite side – the side directly across from the reference angle adjacent side – the side next to the reference angle that is not the hypotenuse a. State the sides of the triangles below that are opposite the given angle ( ), adjacent and the hypotenuse. 1. 2. Opposite side = Opposite side = Adjacent side = Adjacent side = Hypotenuse = Hypotenuse = 3. 4. Opposite side = Opposite side = Adjacent side = Adjacent side = Hypotenuse = Hypotenuse = Label the sides of the triangles below with O for Opposite, A for Adjacent, and H for Hypotenuse. Scale : 0 1 2 3 4 Trigonometry Activity: Below you are given three different triangles. Each pair of triangles is similar. Find answers for each of the following questions. 1. Which postulate(s) allow you to conclude that these triangles are similar? Can there be more than one reason with the given information? 2. In each triangle, find the ratios of the following sides. Round each answer to the nearest thousandth. Triangle 1 Triangle 2 Triangle 3 DE to DF = KJ to KL = MN to MO = EF to DF = JL to KL = NO to MO = DE to EF = KJ to JL = MN to NO = 3. What do you notice?! 4. Find the ratios from the chart you created in the Table of Trigonometric Ratios that you were given. What do you notice now? 5. In your calculator, plug in the following and round to the nearest ten-thousandth. Compare your answers with those from the “Table of Trigonometric Ratios”. a. sin 48 d. cos 37 b. cos 72 e. sin 68 c. tan 81 f. tan 24 6. What if we knew the ratio and wanted to find the angle measure? a. sin B 0.4848 mB b. cos A 0.7431 mA c. tan W 0.5317 mW d. sin A 0.5150 mA e. cos L 0.6157 mL f. tan M 19.0811 mM 7. Using the triangle below, label the sides of the triangle “opposite”, “hypotenuse”, and “adjacent” from angle F. How do the side ratios compare to the Trigonometric Ratios table? If necessary, use your data from the activity to help you Triangle 1 DE to DF = EF to DF = DE to EF = 8. What do you think tan 45 1.0000 means? Why? Scale : 0 1 2 3 4 Pre-8.3 Geometry HOMEWORK Name ___________________________per_____date____ B. Label the sides of the triangles below with H for Hypotenuse, O for Opposite, and A for Adjacent with respect to the given acute angle. 1. Your Answer should look like this: 2. Your Answer should look like this: 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. E. Find the length of the hypotenuse, opposite and adjacent sides, using the named reference angle. 1. Use 30∘ as a reference angle. Opposite side = Adjacent side = Hypotenuse = 2. Use 50∘ as a reference angle. Opposite side = Adjacent side = Hypotenuse = 3. Use 53.1∘ as a reference angle. Opposite side = Adjacent side = Hypotenuse = F. Use the given acute angle as a reference angle and find the length of the hypotenuse, opposite and adjacent sides in terms of x and y.