* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter review
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
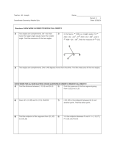
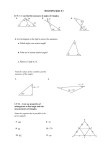
Name: ________________ Date: __________________ Class: _________________ Chapter 1 Review: The Chapter 1 test will cover sections 1.2-1.8. You must know all vocabulary terms from section 1.2-1.5. You must also know the midpoint and distance formula, as well as how to find the perimeter and area of squares, rectangles and triangles. This review packet is due on the day of your quiz. Use your notes and class website to review. You must show work for each problem in order to get credit. You may complete your work in the packet. Geometry A, your quiz is on Monday, October 12th. Geometry B, your quiz is on Tuesday, October 13th. I will give you an answer key on Friday. Section 1.2: Points, Lines and Planes Skill 1: Name points, lines, and planes. Skill 2: Name segments and rays. Example: Use the figure below for Exercises 1–8. Note that coplanar with V. pierces the plane at N. It is not 1. Name two segments shown in the figure. 2. What is the intersection of and ? 3. Name three collinear points. 4. What are two other ways to name plane V? 5. Are points R, N, M, and X coplanar? 6. Name two rays shown in the figure. 7. Name the pair of opposite rays with endpoint N. Skill 3: Find intersections between lines and planes Example: Use the figure at the right for Exercises 21–29. Name the intersection of each pair of planes or lines. 1. Planes ABP and BCD 2. and 3. Planes ADR and DCQ 4. Planes BCD and BCQ 5. and Skill 4: Understand the difference between collinear and coplanar. Questions to consider: 1. Can three points be both collinear and coplanar? Explain. 2. Can two points be non-collinear? Explain. Section 1.3: Measuring Segments Skill 1: Measure segment lengths using the ruler postulate. Example: Use the ruler postulate to find the length of each segment. 1. AB 2. BC Skill 2: Find the measure of segments using the segment addition postulate (and algebra skills). Use the segment addition postulate to find the length of each segment. 1. If PQ = 20 and QR = 22, then PR = . 2. If PR = 25 and PQ = 12, then QR = . Skill 3: Compare segment lengths and determine if they are congruent. Example: Skill 4: Use information regarding segments being congruent to find segment lengths. Example: Skill 5:Use information regarding midpoint to find segment lengths. Example: ̅̅̅̅̅ T is the midpoint of 𝑆𝑈. a. If ST = 2x + 3 and SU=26, find the measure of TU. b. If ST = x + 3 and TU = 4x 6, find the measure of SU. Section 1.4: Measuring Angles Skill 1: Correctly name angles. -If the vertex of an angle is not shared with any other angle, you may name an angle by the letter of the vertex. -If the vertex is shared, use three points on the angle to identify an angle. The center point must be the vertex, and the other two points must be on each side of the angle. -You may also name angles by numbers if indicated. Example: What are two other names for ∠1? Skill 2: Measure angles using a protractor and identify angles. Example: Find the measure of each angle and identify it as acute, right, obtuse or straight 1. MLN 2. NLO 3. MLP Skill 3: Use information about angles being congruent to find missing angle values. Skill 4: Use the angle addition postulate (and algebra skills) to find missing angle measures. Example: 1. 2. Section 1.5: Exploring Angle Pairs Skill 1: Identify and be able to draw all types of angle pairs: supplementary angles, complementary angles, adjacent angles, linear pair, and vertical angles. Example: Draw an example of each angle pair mentioned above: Supplementary angles Complementary angles Adjacent angles Linear pair Vertical angles Name an angle or angles in the diagram described by each of the following. a. Complementary to BOC b. Forms a linear pair with DOE c. Is a vertical angle to DOE? Skill 2: Find missing angle measurements using algebra and understanding of angle pairs. Supplementary ∠1 and ∠2 are supplementary. Show your work: angles ∠1 = 43𝑜 . Find the measure of ∠2. Complementary ∠1 and ∠2 are complementary. angles ∠1 = 6𝑥 + 7 and ∠2 = 4𝑥 + 13. Find the value of each angle. Show your work: Linear pair ∠1 and ∠2 form a linear pair. ∠1 = 7x - 46 and ∠2 = 3𝑥 + 6 . Find the measure of each angle. Show your work: Vertical angles ∠1 and ∠2 are vertical angles. ∠1 = 𝑥 + 16 and ∠2 = 4x+5. Find the measure of each angle Show your work: Putting it together: Find the measures of ∠𝑞 and ∠𝐵𝐸𝐶 Skill 3: Use information about an angle bisector to find missing angle measurements. Example Skill 4: Evaluate diagrams to assess the validity of information and to find missing information. Section 1. 7: Midpoint and Distance in the Coordinate Plane. Skill 1: Find the midpoint given two coordinates. Example: Find the midpoint of the two coordinates: 1. A(6, 7), B(4, 3) 2. A(1, 5), B(2, 3) Skill 2: Find an endpoint given one of the endpoints and midpoint. Example: The coordinates of point Y are (-10, 5) given. The midpoint of XY is (3, 5). Find the coordinates of point X. Skill 3: Use the distance formula to find the distance between points. Example: Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, round to the nearest tenth. 1. A(6, 7), B(1, 7) 2. C(5, 5), D(5, 3) Section 1.8: Perimeter, Circumference and Area. Skill 1: Find the perimeter of rectangles, triangles and irregular shapes. Example: Find the perimeter: 1. Skill 2: Find perimeter of above shapes in the coordinate plane by counting units and using the distance formula. Example: Find the perimeter of the shape. 1. R(1, 2), S(1, 2), T(4, 2) Skill 3: Find the area of rectangles, triangles and other irregular shapes that can be broken down into triangles and rectangles. Example: Find the area of the shape. Skill 4: Find the circumference of a circle. Remember, c = 𝝅𝒅 = 𝟐𝝅𝒓 Example: find the circumference of the circle. Use an estimate of 𝝅 to find your answer. Round to the nearest hundredth. Skill 5: Find the area of a circle. , A = 𝝅𝒓𝟐 Example: Find the area of a circle. Leave your answer in terms of 𝝅.