* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Network Topology
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
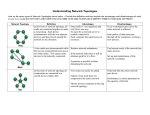
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 9 Computer Networks 1 Chapter Topics OSI network layers Network Topology Media access control Addressing and routing Network hardware Network standards 2 OSI Network Layers 3 OSI Network Layers Presentation Layer – ensures that data transmitted by one network node is correctly interpreted by the other network node. Session Layer – establishes and manages communication sessions. 4 OSI Network Layers Transport Layer – formats messages into packets suitable for transmission over the network. Network Layer – routes packet to their proper destination. Data Link Layer – interface between network software and hardware. 5 OSI Network Layers Physical Layer – the layer at which communication between devices actually takes place. 6 Mathieson’s Three Layers 7 Chapter Topics OSI network layers Network Topology Media access control Addressing and routing Network hardware Network standards 8 Network Topology Definition of Network Topology Point-to-Point transmission Shared Connections Store and Forward Physical Topology (star, bus, ring) Logical Topology 9 Network Topology Network topology refers to: The spatial organization of network devices. The physical routing of network cabling. The flow of message from one network node to another. 10 Network Topology Point-to-Point transmission – the line is laid over the shortest path and connected directly to both nodes. Used for small networks. Shared connections – smaller shared links are connected to larger shared links. Used for larger networks. 11 Network Topology 12 Network Topology Store and Forward - interconnected system of end nodes and transfer points used to route data among end nodes. 13 Network Topology 14 Network Topology Physical topology – refers to the physical placement of cables and device connections to those cables. Logical topology – refers to the path that messages traverse as they travel from node to node. 15 Network Topology Physical Topology Star Bus Ring 16 Network Topology Star Topology Uses a central node to which all other nodes are connected. The central node can be a transfer point. Advantage: simple wiring. Disadvantage: the failure of the hub disables the entire network. 17 Network Topology 18 Network Topology Bus Topology Connects each node to a common transmission line. Transmitted messages travel from a node across the common transmission line. Advantage: simple wiring and low susceptibility to failure. 19 Network Topology 20 Network Topology Ring Topology Connects each network node to two other nodes and the entire network forms a closed loop. Advantages: long maximum network length and low susceptibility to noise and distortion. 21 Network Topology Ring Topology Disadvantages: Susceptibility to failure and difficulty adding , deleting and moving nodes. 22 Network Topology 23 Network Topology 24 Network Topology 25 Chapter Topics OSI network layers Network Topology Media access control Addressing and routing Network hardware Network standards 26 Media Access Control Definition of a Collision Methods for dealing with Collisions Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection Token Passing 27 Media Access Control Collision – noise or interference in a message. Methods for dealing with collisions: Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) Token Passing 28 Media Access Control Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection – (Commonly used on bus network topologies) A node that wants to transmit listens (carrier sense) until no traffic is detected. The node then transmits its message. 29 Media Access Control Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection – The node listens during and immediately after its transmission. If abnormally high signal levels are heard, which is a collision detection, then the node ceases transmission. If a collision is detected, the node waits for a random time interval and then retransmits its message. 30 Media Access Control 31 Media Access Control Token Passing Used in ring network topologies. A token is passed from node to node. Only the node with the token can pass a message. Advantage: simplicity. Disadvantage: inefficient use of data transfer capacity. 32 Chapter Topics OSI network layers Network Topology Media access control Addressing and routing Network hardware Network standards 33 Addressing and Routing Definition of a Local Area Network Definition of a Wide Area Network Local Area Network Routing Wide Area Network Routing 34 Addressing and Routing Local Area Network – a network covering a floor or building. Wide Area Network – a network a network that spans large physical distances, such as multiple buildings, cities, regions, or continents. 35 Addressing and Routing Local Area Network Routing Each time a node is started, it sends a message announcing its presence and its address to the nearest hub. Each hub maintains a table of addresses and transmission lines or connections ports and uses that table to make routing decisions. 36 Addressing and Routing 37 Addressing and Routing 38 Addressing and Routing Wide Area Network Routing Each router knows: The addresses and physical locations of its own nodes Other nearby routers Groups of addresses that they control Default destination for messages to the addresses that it does not know 39 Chapter Topics OSI network layers Network Topology Media access control Addressing and routing Network hardware Network standards 40 Network Hardware Network Hardware Devices: Network interface units or network interface cards Hub Bridges Routers Switches 41 Network Hardware 42 Technology Focus Home Networks 43 TCP/IP 44 Chapter Topics OSI network layers Network Topology Media access control Addressing and routing Network hardware Network standards 45 Network Standards The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) has drafted a number of telecommunication and network standards – IEEE 803 standards. 46 Network Standards 47 Technology Focus - Ethernet 48 Technology Focus - Ethernet 49 Windows Commands ipconfig ipconfig /all net statistics workstation net use net view 50 Summary Network topology refers to the spatial organization of network devices, the physical routing of network cabling and the flow of messages from one network node to another. LANs are interconnected to form WANs. 51 Summary A media access control (MAC) protocol specifies rules for accessing a shared transmission medium. Network hardware devices include NIUs, hubs, bridges, routers, and switches. 52 Summary The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is an ISO conceptual model that divides network architecture into seven layers. TCP/IP is the core Internet protocol suite. The IEEE 802 standards cover many types of networks. 53