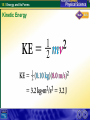* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 15.1 Energy and Its Forms
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
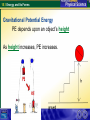
15.1 Energy and Its Forms Energy and Work How are energy and work related? Energy is the ability to do work. Work is a transfer of energy. http://phun.physics.virginia.edu/demos/double.html 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Energy and Work Work and energy are closely related. • Work is done when a force moves an object through a distance. • Energy is transferred by a force moving an object through a distance. • Work and energy are measured in joules (J). 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Energy and Work Energy has different forms. A. The sun gives off energy in the form of heat and light. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Energy and Work Energy has different forms. A. The sun gives off energy in the form of heat and light. B. Plants convert sunlight into food. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Energy and Work Energy has different forms. A. The sun gives off energy in the form of heat and light. B. Plants convert sunlight into food. C. People convert food energy into muscle movement. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Forms of Energy What are the major forms of energy? 1. Mechanical Energy a. Kinetic b. Potential 2. Thermal energy 3. Chemical Energy 4. Electrical Energy 5. Electromagnetic Energy 6. Nuclear Energy 15.1 Energy and Its Forms 1. Mechanical Energy • Energy associated with the motion and position of objects. • potential energy + kinetic energy. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms 2. Thermal Energy The total potential and kinetic energy of all the microscopic particles in an object. If atoms move faster, its thermal energy increases, and the object becomes warmer. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms 3. Chemical Energy Energy stored in chemical bonds. When bonds are broken, the released energy can do work. All chemical compounds store energy. Ex: use the chemical energy of burning wood to produce thermal energy for roasting marshmallows. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms 4. Electrical Energy Energy associated with electric charges. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms 5. Electromagnetic Energy A form of energy that travels through space in the form of waves. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms 5. Electromagnetic Energy More examples: A. Lightning bolts B. Galaxies contain billions of stars. The stars give off electromagnetic energy. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms 6.Nuclear Energy The energy stored in the nucleus of an atom • Nuclear fission releases energy by splitting nuclei apart. • Nuclear fusion releases energy when nuclei combine. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms 2 Types of Mechanical Energy: Kinetic Energy & Potential Energy Kinetic Energy: The energy of motion is called kinetic energy. The kinetic energy depends on mass and velocity. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Kinetic Energy Calculating Kinetic Energy A 0.10-kilogram bird is flying at a constant speed of 8.0 m/s. What is the bird’s kinetic energy? 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Kinetic Energy What information are you given? 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Kinetic Energy 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Kinetic Energy 1. A 70.0-kilogram man is walking at a speed of 2.0 m/s. What is his kinetic energy? Answer: 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Kinetic Energy 1. A 70.0-kilogram man is walking at a speed of 2.0 m/s. What is his kinetic energy? Answer: KE = (0.50)(70.0 kg)(2.0 m/s)2 = 140 J 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Kinetic Energy 2. A 1400-kilogram car is moving at a speed of 25 m/s. How much kinetic energy does the car have? Answer: 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Kinetic Energy 2. A 1400-kilogram car is moving at a speed of 25 m/s. How much kinetic energy does the car have? Answer: = (0.50)(1400 kg)(25 m/s)2 = 437,500 J 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Kinetic Energy 3. A 50.0-kilogram cheetah has a kinetic energy of 18,000 J. How fast is the cheetah running? (Hint: Rearrange the equation to solve for v.) Answer: 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Kinetic Energy 3. A 50.0-kilogram cheetah has a kinetic energy of 18,000 J. How fast is the cheetah running? (Hint: Rearrange the equation to solve for v.) Answer: 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Potential Energy Energy that is stored as a result of position or shape. 2 types: 1. Potential Energy 2. Gravitational Potential Energy An object’s gravitational potential energy depends on its mass, its height, and the acceleration due to gravity. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms REVIEW Major forms of energy 1. Mechanical Energy a. Kinetic b. Potential 2. Thermal energy 3. Chemical Energy 4. Electrical Energy 5. Electromagnetic Energy 6. Nuclear Energy 15.1 Energy and Its Forms REVIEW Mechanical Energy = Kinetic Energy + Potential Energy or ME = KE + PE KE is the energy of _____________ motion 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Potential Energy Potential Energy: energy stored as a result of position. 2 types of PE: 1. Gravitational PE 2. Elastic PE 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Question….. Assuming your mass is 50 kg, would you rather – 1. Fall off a 5 meter tower on the moon. Or 2. Fall off a 0.5 meter tall desk on earth with 20 kg (about 44 lbs) of rocks in your pockets. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Gravitational Potential Energy PE depends upon an object’s height As height increases, PE increases. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Gravitational Potential Energy PE depends upon an object’s mass As mass increases, PE increases. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Gravitational Potential Energy PE depends upon gravity As gravity increases, PE increases. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Summary: If height increases, then PE increases If mass increases, then PE increases If gravity increases, then PE increases Let’s put it all together in 1 equation!! 15.1 Energy and Its Forms • Mass = kilograms (kg) • Height = meters (m) • Gravity: g = 9.8 m/s2 The unit for gravitational potential energy = joules. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Gravitational Potential Energy 1. What is the potential energy of a 50 kilogram diver at the top of a 10 meter high diving board? PE = ? m = 50 kg g = 9.8 m/s2 h = 10 m PE = mgh = (50 kg)(9.8 m/s2)(10 m) = 4900 kg•m2/s2 = 4900 J 15.1 Energy and Its Forms 2. A car that is to be transported by ship is raised 7 m above the dock. If its mass is 1000 kg, what is the car’s gravitational potential energy? PE = ? m = 1000 kg g = 9.8 m/s2 h=7m PE = mgh = (1000 kg)(9.8 m/s2)(7 m) = 68,600 kg•m2/s2 = 68,600 J 15.1 Energy and Its Forms 3. A small airplane and a helicopter have the same mass. The airplane’s altitude is 3 times higher than the helicopter. How much more gravitational potential energy does the airplane have than the helicopter? a. b. c. d. 0.333 times as much 3 times as much 6 times as much 9 times as much 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Question….. Assuming your mass is 50 kg, would you rather – 1. Fall off a 5 meter tower on the moon. Or 2. Fall off a 0.5 meter tall desk on earth with 20 kg (about 44 lbs) of rocks in your pockets. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Moon Earth PE = ? m = 50 kg g = 1.6 m/s2 h=5m PE = ? m = 50 kg + 20 kg=70 kg g = 9.8 m/s2 h = 0.5 m PE = mgh PE = mgh = (50 kg)(1.6 m/s2)(5 m) = (70 kg)(9.8 m/s2)(0.5 m) = 400 J = 343 J 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Homework Due Wednesday March 25 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Potential Energy When this musician pulls the string of her cello to one side, the string is stretched and gains potential energy. The stored energy is converted into kinetic energy when the string is released and it vibrates. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Elastic Potential Energy The potential energy of an object that is stretched or compressed. Ex: shock absorber, spring, slingshot 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Assessment Questions 1. How are work and energy related? a. b. c. d. Energy is the rate of doing work. Work is a form of energy. Work is the transfer of energy. Energy is created by work. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Assessment Questions 1. How are work and energy related? a. b. c. d. Energy is the rate of doing work. Work is a form of energy. Work is the transfer of energy. Energy is created by work. ANS: C 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Assessment Questions 2. A moving object with a mass of 10 kg has 320 J of kinetic energy due to its motion. How fast is the object moving? a. b. c. d. 64 m/s 32 m/s 8 m/s 10 m/s 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Assessment Questions 2. A moving object with a mass of 10 kg has 320 J of kinetic energy due to its motion. How fast is the object moving? a. b. c. d. 64 m/s 32 m/s 8 m/s 10 m/s ANS: C 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Assessment Questions 3. Which of these is an example of elastic potential energy? a. b. c. d. a bow prepared to release an arrow a rubber ball thrown into the air a book about to fall from a table a truck pulling a trailer 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Assessment Questions 3. Which of these is an example of elastic potential energy? a. b. c. d. a bow prepared to release an arrow a rubber ball thrown into the air a book about to fall from a table a truck pulling a trailer ANS: A 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Assessment Questions 5. The energy stored in the bonds between atoms of a compound is called a. b. c. d. electromagnetic energy. chemical energy. atomic energy. thermal energy. 15.1 Energy and Its Forms Assessment Questions 5. The energy stored in the bonds between atoms of a compound is called a. b. c. d. electromagnetic energy. chemical energy. atomic energy. thermal energy. ANS: B