* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download fakulti kejuruteraan elektrik
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Analog television wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
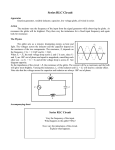
Faculty FACULTY OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Semakan :2 Nama Matapelajaran : MAKMAL KEJ. ELEKTRIK Tarikh Keluaran : Julai 2008 Pindaan Terakhir : 2005 Kod Matapelajaran : SEE 2742 No. Prosedur : PK-UTM-FKE-(O)-10 SEE 2742 FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRIK UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA KAMPUS SKUDAI JOHOR ELECTROTECHNIC LABORATORY SERIES AND PARALLEL RESONANCE CIRCUIT CHARACTERISTICS (Experiment 1) Disediakan oleh Nama Tandatangan Cop : : : : Disahkan oleh Nama Tandatangan Cop : : : : Tarikh : Tarikh : 1 FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRIK UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA ELECTROTECHNIC LABORATORY EXPERIMENT : 1-A TITLE 1. : MEASUREMENT OF SERIES RESONANCE CHARACTERISTICS Aims: i. ii. 2. Equipments: i. ii. iii. iv. v. 3. To investigate series resonance characteristics To identify resonant parameters Signal generator Volt meter Decade inductor (L) Decade capacitor (C) Decade resistor (R) Figure 1.0 shows a series resonance circuit connection. Figure 1.0 4. Equations for resonance circuit. i. Resonance occurs in the circuit when: Inductive reactance = Capacitive reactance. 2 ωo L = Therefore, 1 ωoC where, ωo = 2πf◦ fo = resonance frequency in Hz ii. Resonance frequency in terms of L and C , fo = iii. 2π LC Hz Selectivity factor, Q Q= iv. 1 ω0 L R or Q = 1 ω0C Resonance characteristics (a) Voltage supply, R, L, and C are constant, f varies, therefore Q= fo f 2 − f1 where, fo is the resonance frequency. (b) Voltage supply, R, L and f are constant, C varies, therefore Q= Co C 2 − C1 where, Co is the value of capacitance when resonance occurs 3 Figure 2.0 5. Procedure: i. Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 1.0. ii. Set the values of L = 5mH and C = 0.14 μF. iii. Set the value of R according to the signal generator model (OSC).You can use either of the signal generator listed below : No Type/Model of Signal Generator Set the value of R to : 1 Jupiter 500 35 ohm 2 Kenwood 50 ohm 3 Trio 50 ohm 4 Levell TG 152DM 0 ohm iv. Fixed the frequency at 10 kHz and set L = 4mH. Varies the value of C from 0.02 μF to 0.14 μF in step of 0.01 μF and record the voltage reading V2 as in the Table 1.0. Voltage V1 has to be adjusted so that the value is fixed at 0.5 volt. 4 EXPERIMENT TITLE 1. : MEASUREMENT OF PARALLEL RESONANCE CHARACTERISTICS Aims: iii. iv. 2. To investigate parallel resonance characteristics To identify resonant parameters. Equipments: vi. vii. viii. ix. x. 3. :1-B Signal generator Volt meter Decade inductor (L) Decade capacitor (C) Decade resistor (R) Figure 3.0 shows a parallel resonance circuit connection. I1 10 Ω A I2 A Osc f = (3 – 10) kHz 10 kΩ Figure 3.0 5. Equations for resonance circuit. v. Resonance occurs in the circuit when: Inductive reactance = Capacitive reactance. Therefore, ωo L = 1 ωoC where, ωo = 2πf◦ fo = resonance frequency in Hz 5 5 mH 100 nF vi. Resonance frequency in terms of L and C , 1 fo = Hz 2π LC vii. Selectivity factor, Q Q = ω o CR or Q = viii. R ωo L Resonance characteristics (b) Voltage supply, R, L, and C are constant, f varies, therefore Q= fo f 2 − f1 where, fo is the resonance frequency. (b) Voltage supply, R, L and f are constant, C varies, therefore Co C 2 − C1 where, Co is the value of capacitance when resonance occurs Q= Figure 4.0 6 5. Procedure: i. Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 4.0. ii. Set the values of L = 5mH and C = 100 nF. iii. Select the sinusoidal waveform from the signal generator output. Set the amplitude so that the reading of ammeter I1 is constant at 1mA. Record the reading of ammeter I1 and I2 for the frequencies range between 3 kHz to 10 kHz as in Table 2.0. 7