* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4. RLC series resonance
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Amateur radio repeater wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Atomic clock wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Equalization (audio) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
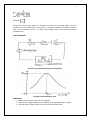
1 EXPERIMENT NO. 4 AIM: Study the Phenomenon of Resonance in RLC series circuit & obtain the Resonance Frequency. APPRATUS REQUIRED: Sl. No. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Equipments Single Phase AC Supply Variable Frequency Signal Generator AC Ammeter Inductor Capacitor Resistor Connecting Wires Type AC AC MI Specification 230 volts, 50 Hz 1 HZ –Mhz, (0-10)Volts, Sine Wave (0-10) mA 10, 20, 30 mH 10, 20, 30 nF 100 ohm PVC Insulated Quantity 1 no. 1 no. 1 no. 1 no. 1 no. 1 no. As per ckt. requirement THEORY: In a circuit, consisting of reactive components of opposite nature i.e., L & C, if we change the variables F, L or C there comes a situation when over all impedance(or Admittance) of the circuit becomes purely resistive (or conductive G). Such a condition is called “RESONANCE”. In Resonance condition, Output becomes much larger than the excitation. Let us consider the circuit shown in fig. (1) Applying the KVL we get: Where; & the magnitude of current Now, at Resonance, we have: Since, 2 Now, Z=R, as (XL=XC) Therefore, Variations of current with respect to frequency are shown in the Graph. When current is maximum, the ckt is said to be in resonance. So, in resonance condition Z should be minimum. Thus, in this condition current is in phase with voltage, Power Factor Becomes unity & impedance Z=R; CIRCUIT DIAGRAM Figure(1): Circuit Diagram for RLC Series Resonance Figure(2): Series Resonance curve PROCEDURE: 1. Make the connections as per the circuit diagram. 2. Switch on the supply keeping source frequency of the signal generator at lowest. 3. Take the value of frequency & current as per the observation table. 3 4. Increase the value of Frequency & take the reading still it current reaches its maximum value. 5. If the frequency is increased further, the current start decreasing again, take few more readings upto maximum frequency range of the available source. 6. Take at least 10-12 readings to cover the complete range, of variations of current around maximum value. 7. Now draw a graph between, Current & Frequency. OBSERVATION TABLE: Sl. No. Reading of Signal Generator Frequency in (KHz) Ammeter Reading I(mA) Frequency corresponding to maximum Current CALCULATIONS: 1. Resonance Frequency: Hz 2. Percentage Error in Resonance Frequency OBSERVATIONS: Value Given: R=_____________ohm, L=___________mH, C=_____________nF Applied Voltage=___________ Volts, Frequency=__________Hz (calculated)