* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Protectionism wikipedia , lookup
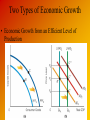
Ch. 17: Economic Growth: Resources, Technology, and Ideas Del Mar College John Daly ©2003 South-Western Publishing, A Division of Thomson Learning What is Economic Growth? • Absolute Real Economic Growth is an increase in Real GDP from one period to the next. • Per Capita Real Economic Growth is an increase from one period to the next in per capita Real GDP, which is Real GDP divided by population Do Economic Growth Rates Matter? • If a country has a 3 percent annual growth rate, Real GDP will take 24 years to double; If a country has a 4 percent annual growth rate, Real GDP will take 18 years to double. Two Types of Economic Growth • Economic Growth from an Inefficient Level of Production Two Types of Economic Growth • Economic Growth from an Efficient Level of Production Economic Growth and the Price Level • Economic Growth can occur with a falling price level, rising price level, or stable price level. • In recent decades, the US economy has witnessed economic growth with a rising price level. What Causes Economic Growth? • Natural Resources: Countries rich in natural resources are not guaranteed economic growth and countries poor in natural resources may grow. It is still more likely for a country with natural resources to grow. • Labor: It is possible to produce more output, but whether or not the average productivity of labor rises, falls or stays constant depends on how productive the additional workers are relative to existing workers. One way to achieve increased productivity is through education, training, and experience. What Causes Economic Growth? • Capital: To produce more capital goods, which are not directly consumable, present consumption must be reduced. As the saving rate increases, capital formation increases, and so does economic growth. • Technological Advances: Technological advances usually come as a result of companies and a country investing in research and development (R & D). Investment and Per Capita Real Economic Growth for Selected Countries Free Trade As Technology • There is really no difference between a machine that can turn wheat into cars and free trade between countries. • This is exactly what happens when we trade American wheat for Japanese cars. Property Rights Structure • Per Capita Real economic growth first appeared in areas that had developed a system of institutions and property rights that encouraged individuals to direct their energies to effective economic projects. • Individuals will invest more, take more risks, and work harder when the property rights structure allows them to keep more of the monetary rewards of their investing, risk taking, and labor. Economic Freedom • Some economists believe that economic freedom leads to economic growth. • The data show that economic freedom and Real GDP per capita are correlated. • Some economists believe there is a “cause and effect” relationship. Policies to Promote Economic Growth • When the economy is situated below its PPF, demand inducing expansionary monetary or fiscal policy is often advocated. • There are supply-side policies too. • These factors include natural resources, labor, increases in human capital, increases in physical capital investment, technological advances, and property rights structures. • Any policies that promote these factors promote economic growth. Tax Policy • Some propose cutting taxes on such activities as working and saving in order to increase the productive capacity of the economy. • Others argue that if the tax is lowered on income placed in saving accounts, the return from saving will increase and thus the amount of saving will rise. Regulator Policy • Some say that some government regulations increase the cost of production for business and consequently reduce output. • Economists who believe the benefits do not warrant the costs often argue for some form of deregulation. What About Industrial Policy? • Industrial policy is a deliberate government policy of aiding those industries that are most likely to succeed in the world marketplace. • Government needs to work with business firms in the private sector to help them compete in the world marketplace. • Critics maintain industrial policy does not always turn out the way its proponents would have for 3 reasons: government may favor industries with more political influence; officials who design policy don’t know what will be industries of the future; officials are likely to hamper growth if they aid certain industries. Worries about Future Economic Growth What are the Costs of Growth? • More pollution, more factories, more crowded cities, more emphasis on material goods, more stress, more psychological problems, more suicides, more drug abuse, and so on. • But is there direct evidence of these costs? What is the relationship between economic growth and availability of resources? • Continued economic growth leads to continued population growth and threatens survival of the human race by stripping us of our resources • Based on unrealistic assumptions, oversights, or flimsy evidence? Q&A • “Economic Growth refers to an increase in GDP.” Comment. • Country A has witnessed both economic growth and a rising price level during the past two decades. What does this imply about the LRAS and AD curves? • How can capital investment promote economic growth Two Worries About Future Economic Growth • Some individuals argue that more economic growth comes with more pollution, more factories, more crowded cities, more emphasis on material goods and getting ahead, more rushing around, more psychological problems, more people using drugs, more suicides, and so on. • Some people believe continued economic and population growth threatens the survival of the human race because this growth will hasten the time when the world runs out of resources. New Growth Theory • Technology is a central part of the economic system. • The amount and quality of technology that is developed depends on the amount of resources we devote to it. • If one person is trying to advance technology, his or her chances of success are much smaller than if hundreds or thousands of persons are trying. • The theory also places emphasis on the process of discovering and formulating ideas. Discovery, Ideas, and Institutions • If the process of discovering ideas is important to economic growth, then it behooves us to figure out ways to promote the discovery process. • Employee flexibility is becoming a larger part of the US economy. Expanding Our Horizons • “Economic Growth occurs whenever people take resources and rearrange them in ways that are more valuable.” • If we believe ideas are important to economic growth, then we need to have ideas as to how to generate more ideas: these are meta-ideas. Q&A • What are two worries about future economic growth? • If technology is endogenous, what are the implications for economic growth? • According to new growth theory, what countries will be the countries that grow the fastest in the next century?