* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Economics Mr. Bernstein AP Economics Mr. Bernstein
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
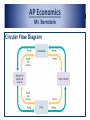
AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Micro Graphs Review May 2014 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein The Production Possibilities Curve 2 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Economic Growth • Concave due to “Law of increasing opportunity costs” 3 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Circular Flow Diagram 4 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Expanded Circular Flow Diagram 5 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Demand Curves • A Shift in Demand is different from movement along the Demand Curve!! 6 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Supply Curves • A Shift in Supply is different from movement along the Supply Curve!! 7 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Equilibrium • Price is the adjustment mechanism: falls when there is a surplus, rises when there is a shortage 8 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Simultaneous Shifts of Supply and Demand Curves • Example: Demand for Justin Beiber tickets decreases and Supply decreases • Equilibrium Price is ambiguous but Quantity change decreases (awww…) • Know all four possible combinations 9 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Elasticity along the Demand Curve • Consumers are less price sensitive on inexpensive items • TR begins to fall as prices rise and Elasticity grows 10 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Consumer Surplus and Producer Surplus • CS is the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good or service and what they actually have to pay • PS is the difference between what a producer must receive to sell a unit and the actual price they receive 11 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Deadweight Loss Example: The Effect of Taxes Dead Weight Loss P S1 S CS T T D D PS D Qt Q • Excise tax causes lower Q, efficiency loss Q 12 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Price Ceilings • Price ceiling is below equilibrium, creates shortage 13 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Price Floor • Price floor is above equilibrium; creates surplus 14 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Quotas (Quantity Controls) • Examples: limits, licenses; creates price “wedge” 15 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Firm’s Cost Curves: Swoosh, Smirk and Smile • The MC curve intersects the U-shaped AC and AVC curves at their minimum points 16 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Perfectly Competitive Firm $ • Produce at MR=MC • Profit = MR – ATC • In this case, zero economic profit… • This is long-run equilibrium… • Profit or loss if P > or < ATC MC ATC MR D.AR.P! Q* Output 17 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein The Short-Run Shut-Down Decision • Shut down when P < AVC $ MC P=ATC ATC AVC P=MR=d=AR Shut-down Price Q* Output 18 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Long Run Average Costs • U-shaped LRATC is a series of U-shaped SRATCs – one for each level of fixed costs 19 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Adjustment toward Long-Run Equil (Perf Comp) 20 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Classic Monopoly Graph • Q at MR=MC; lower Q and higher P than Perfect Competition; long-run economic profit exists due to barriers to entry 21 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Monopoly Reduces Societal Welfare 22 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Price Regulation Restores Consumer Surplus 23 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Monopolists will use Price Discrimination • Without competition, they take advantage of differing elasticities 24 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Game Theory • Each player competes to maximize individual payoffs and ignores the effects of his/her action on the payoffs received by the rival • But Oligopolies engage in tacit collusion, tit for tat 25 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Monopolistic Competition in the Long Run • Adjusts to normal profit, as in Perfect Competition • P*=ATC, tangent to ATC (not at minimum…) 26 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Factor Market: Labor • Value of W* = MRPL; (MC = W) Wage Market Labor Supply W* Market Labor Demand Q 27 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Imperfect Competition in the Labor Market • Hire where Wage MPRL = MFCL • Monopsony pays W* < MRPL Remember, whether Perfect or Imperfect Markets, firms hire where MRPL = MFCL MFCL Labor Supply W* MRPL E* Quantity of Labor (workers) 28 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Equilibrium in the Market for Land and Capital • Supply curve for Land is very steep (inelastic) 29 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Positive Externalities: MSB > MPB • Market underproduces Price, MSB vs. socially optimal outcome • Deadweight loss Popt • Policy to eliminate: Pmkt Subsidy Pcons S Subsidy MPB Qmkt Qopt MSB Qty 30 AP Economics Mr. Bernstein Negative Externalities: MSC > MPC Price, MSC • Market overproduces vs. socially optimal outcome • Deadweight loss • Policy to eliminate: Popt Per unit tax Pmkt • Lump-sum tax does Pfirm not affect MC so does not Qopt affect Q MSC MPC Tax D Qmkt Electricity 31