* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AVOP-ELEKTRO-MEL-003
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
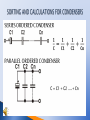
Tutorial: Mechanic - electrician Topic: Technical training II. class Passive components – condenser Prepared by: Melichařík Lubomír Projekt Anglicky v odborných předmětech, CZ.1.07/1.3.09/04.0002 je spolufinancován Evropským sociálním fondem a státním rozpočtem České republiky. Condenser Condenser -passive electro technical component -used in electrical circuits for temporary storage of electrical charge – electric energy -the basic property for the evaluation of the condenser is its electrical capacity -technically the condenser is determined by the maximum allowed voltage, dielectric type and design of the terminals. Electrotechnical schematic symbol: Schematic symbol of the condenser-ceramic, rolls Schematic symbol of electrolytic condensers Schematic symbols of variable – tuning condenser Schematic symbol the adjustable condenser – capacitive trimmer The principle of a condenser -consists of two conductive plates (electrodes) separated by a dielectric -on each of the plates is fed electric charges of opposite polarity Basic properties of a condenser -capacity -maximum allowed voltage -quality factor -other properties such as price, weight, durability, thermal stability, shape… Capacity of a condenser Capacity depends on the area of the plates, the mutual distance between the plates themselves and the dielectric permittivity between the plates (applies to the plate condenser): The plate condenser with a capacitance C can store and electric charge: Q = CU ( Charge × Voltage) Q = It (Current × Time) The unit of capacity is the farad in the system SI is: Symbols for condensers: -for colour coded electronic components we use the international code EIA-RS-279, and the type of condenser should also be considered to determine the values and tolerances to identify performance, the maximum voltage, and for ceramic condensers the thermal parameters. Types of condenser Electrolytic axial electrolytic radial large value electrolytic Roll condensers capacitive trimmers tuning condenser Calculate the resulting capacity of these series ordered condensers. Name the types of condensers. Calculate the resulting capacity of these parallel ordered condensers. Václav Malina Adrian Schommers Poznáváme elektroniku I. Elektronika tajemství zbavená. ISBN 3-92608-32-5