* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download major terrestrial ecosystems
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
List of ecoregions in North America (CEC) wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
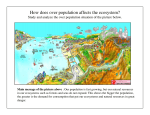
Name: ___________________________________ Date: ____________________________________ SNC1D MAJOR TERRESTRIAL ECOSYSTEMS - There isn’t an unlimited number of ecosystems on the planet—there are actually only a few that are the major land ecosystems The most important factor in determining the makeup of a terrestrial ecosystem is the climate—both precipitation and temperature Biome:__________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Tundra Biome - Basically, it’s a cold desert The low temperatures and short growing season put limits on the kinds of plants that can survive There is little light so photosynthesis is reduced and plants grow slower Lots of areas have ________________________ In the summer, the soil closest to the surface thaws and roots can grow but because the soil is so cold, the process of decomposition is slow and nutrients are cycled slowly Notable species in the tundra—_____________________ and the _________________ Boreal Forest Biome - Rainfall and warm summers support growth of trees ___________________ are the main trees—they can survive the harsh winter and keep their need-shaped leaves As conifer needles (e.g. pine needle, evergreens) decompose they release __________ into the soil, making the soil slightly acidic—the acidic soil limits the types of plants that can grow Grassland Biome - Moderate rainfall—it can support growth of grass but not of most trees Summers are hot and dry—the perfect conditions for fires—the fires keep up the grassland because they stop the growth of trees High summer temperatures encourage decomposition to release nutrients back into the soil making it one of the most fertile Notable species in the grassland—______________ Temperate Deciduous Forest Biome - Dominated by ______________________________—leafy trees like oak and maple Growing season is longer and temperatures don’t reach the extreme lows of the boreal biome so decomposition rates are faster Name: ___________________________________ Date: ____________________________________ SNC1D MAJOR AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS - There are 2 major categories of aquatic ecosystems: ___________________ and ________________ Freshwater Ecosystems - These ecosystems can be either moving water like rivers or stationary bodies of water like lakes. Rivers and streams of unique in that they are always flushed with a fresh supply of water Lakes and ponds are classified according to the amount of nutrients found in them: o _______________________—bodies of water that are low in nutrients Even with plenty of light, there aren’t enough nutrients to make lots of plants grow o _________________________—bodies of water that are high in nutrients Plants and algae grow very quickly and can support lots of different consumers Marine Ecosystems - - - Most of the water that evaporates and falls as rain or snow comes from oceans Much (not all) of the ocean can’t support photosynthetic life—the open ocean has very little nutrients, and there is no light in the deep water so photosynthesis is impossible o BUT shallow waters near the shore have lots of nutrients and support lots of greenery. ______________________ grow in warm shallow oceans and are very sensitive to changes in ___________________________, ___________________ and _______________________ ____________________ are bodies of water where fresh water and salt water mix— these areas are usually very high in nutrients and often support valuable shellfish ______________________: the area between low-tide line and high-tide line o Part-time terrestrial and part-time aquatic ecosystems o Common species that live in these areas: seaweeds, sea stars, urchins