* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Meiosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
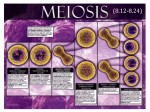
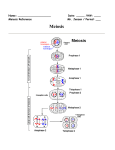
Meiosis Meiosis – process of reduction division in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in ½ by the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell. -Meiosis refers to sexual reproduction in which genetic info from 2 parents is combined to make genetically different offspring. -Meiosis occurs in sex cells (gametes). Meiosis – has 2 divisions (Meiosis I & Meiosis II = 4 daughter cells) A. Chromosome Number -In organisms that reproduce sexually, half of the genetic material comes from the mother & half comes from the father. -These 2 sets of chromosomes from each parent are homologous chromosomes – chromosomes that each have a matching chromosome from the opposite-sex parent. -Cells that contain both sets of chromosomes are diploid or 2N, meaning “two sets”. In humans 2N = 46 chromosomes in a cell. -Cells that contain a single set of chromosomes are haploid or N, meaning, “one set”. In humans N = 23 chromosomes. B. The Phases of Meiosis *Meiosis involves 2 divisions : Meiosis I & Meiosis II -By the end of meiosis II, the diploid cell has become 4 haploid cells. In meiosis I : 1. Each chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosome to form a tetrad - structure containing 4 chromatids. 2. Homologous chromosomes begin crossing-over exchange of portions of their chromatids. -Crossing-over creates genetic variation among organisms. 3. Homologous chromosomes separate & form 2 cells that are ready to divide again. Tetrads & Cross-over Meiosis I In Meiosis II : 1. The 2nd meiotic division starts. 2. Chromosomes line up in center of cell, separate, & form 4 daughter cells that are genetically different from the parent cell. Summarization of Meiosis Interphase I – cells undergo DNA replication, forming duplicate chromosomes. Meiosis I – Stage one of division - Has 4 phases : Prophase I – Each chromosome pairs with its matching homologous chromosome to form a tetrad. Metaphase I – Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. Anaphase I – Fibers pull the homologous chromosomes to opposite poles of cell. Telophase I & Cytokinesis – Nuclear membranes form. Cell separates into 2 cells. Meiosis II – Stage two of division – Has 4 phases : Prophase II – Meiosis I results in 2 haploid (N) daughter cells, each with ½ the number of chromosomes as the original cell. Metaphase II – Chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. Anaphase II – Sister chromatids separate & move to opposite poles. Telophase II & Cytokinesis – Result is 4 haploid (N) daughter cells. C. Gamete Formation *Meiosis is also called : Gametogenesis – the process by which gametes develop in the gonads (production of gametes). Gametes – haploid (N) sex cells. Sperm – male sex cells & Eggs – female sex cells Gonads – specialized organs used for reproduction. In males they’re testes, which produce sperm & in females they’re ovaries, which produce eggs or ova. -Males undergo spermatogenesis – formation of sperm in the testes. The end result is 4 good sperm cells. -Females undergo oogenesis - formation of eggs in the ovaries. The end result is 1 good egg & 3 polar bodies that aren’t used. *Fertilization restores the diploid (2N) # of chromosomes. Gametogenesis in males & females