* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ColdOrFlu
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Swine influenza wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
IS IT THE COLD OR THE FLU?
It is the time of year where sickness seems to be showing up everywhere. We
wonder if we should send our children to school or not and if it is the flu or just a
cold. Below is a list of the differences between the cold, the flu and Pertussis. The
best way to avoid getting sick is to use good hand hygiene and to use proper
technique for coughing and sneezing. Remember, that if your child has a fever,
he/she needs to be kept home until the fever breaks. As always, any questions
please contact me at 262-238-7932.
Best wishes for a safe new year!
Deanne Landvatter, RN, BSN
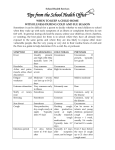
Rapid Reference: Flu versus Cold versus Pertussis
(source: City of Milwaukee Health Department)
Symptom
Fever
Headache
Aches and pains,
muscle aches, chest
discomfort
Fatigue and
weakness
Extreme exhaustion
Stuffy or runny nose
Sneezing
Sore throat
C
O
U
G
H
Character
Severity
Influenza ("Flu")
Usually present & high
(102-104°F or 3940°C); typically lasts 34 days
Very common
Cold (Viral URI)
Pertussis
Uncommon
Uncommon If present,
typically low-grade
Uncommon
Uncommon
Common, Often severe
Slight to Moderate
Uncommon
Mild
Mild to moderate
Extremely Rare
Rare
Moderate - severe; can
last up to 14-21 days
Very common early in
illness
Common, early in the
disease
Common, early in the
Sometimes
Common
disease
Sometimes
Common
Uncommon
Variable character; fits
Hacking cough, often
/ paroxysms and
Non-productive ("dry") productive; nocturnal
nocturnal cough are
cough is typical;
cough rare; usually
common; generally not
nocturnal cough rare
responds to cough
responsive to cough
medications
medications
Variable; can be mild
Moderate
Mild to Moderate
in adults and very
Sometimes
Common
Duration
Paroxysms
Infectious Period
severe in infants and
young children
Persistent cough,
Typically 3-7 days;
almost always >1week,
Typically 3-7 days
occasionally to 14 days
usually 2-6 weeks,
sometimes 10+ weeks
Uncommon
Rare
Common
From start of catarrhal
Variable; typically 4-7
1-2 d before symptom
phase (before cough) to
days after symptom
onset to 5-10 days after
21 days after cough
onset; can be longer
onset*
*or until taking 5 days of appropriate anti-pertussis antibiotics, or until a nasopharyngeal
pertussis PCR is negative, whichever occurs first