* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10-The Adrenal gland- Aldosterone 01-02-2016
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
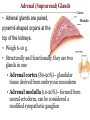
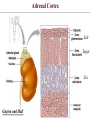
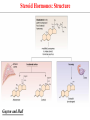
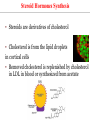
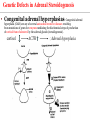
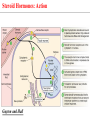
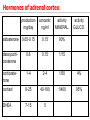
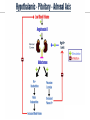
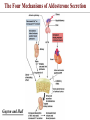
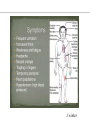
Endocrine Physiology The Adrenal Gland 1 Dr.Mouaadh abdelkarim Assistant Professor of Physiology Department of Physiology 2nd floor Email: [email protected] Tel: 0114671606 Adrenal (Suprarenal) Glands • Adrenal glands are paired, Cortex Medulla pyramid-shaped organs at the top of the kidneys. • Weigh 6-10 g. • Structurally and functionally, they are two glands in one • Adrenal cortex (80-90%)– glandular tissue derived from embryonic mesoderm • Adrenal medulla (10-20%)– formed from neural ectoderm, can be considered a modified sympathetic ganglion Adrenal Cortex • Synthesizes and releases steroid hormones (corticosteroids) • Different corticosteroids are produced in each of the three layers: • Zona glomerulosa – mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone) • Zona fasciculata – glucocorticoids +Androgens (mainly cortisol and corticosterone) • Zona reticularis – gonadocorticoids + glucocorticoids (mainly dehydroepiandrosterone DHEA) Adrenal Gland Guyton and Hall Adrenal Cortex Salt Sugar Sex Guyton and Hall HPA Axis Guyton and Hall Steroid Hormones: Structure Guyton and Hall Steroid Hormones Synthesis • Steroids are derivatives of cholesterol • Cholesterol is from the lipid droplets in cortical cells • Removed cholesterol is replenished by cholesterol in LDL in blood or synthesized from acetate Steroid Hormones Synthesis (Cont.) • Steroid hormones are synthesized and secreted on demand (not stored) • The first and rate-limiting step in the synthesis of all steroid hormones is conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone by the enzyme cholesterol dismolase (cholesterol side chain cleavage enzyme (SCC)) • Newly synthesized steroid hormones are rapidly secreted from the cell • Following secretion, all steroids bind to some extent to plasma proteins: CBG (corticosteroid binding globulin) and albumin Steroidogenesis: Steroidogenesis entails processes by which cholesterol is converted to biologically active steroid hormones Genetic Defects in Adrenal Steroidogenesis • Congenital adrenal hyperplasias: Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) are any of several autosomal recessive diseases resulting from mutations of genes for enzymes mediating the biochemical steps of production of cortisol from cholesterol by the adrenal glands (steroidogenesis). cortisol ACTH ِAdrenal hyperplasia Congenital adrenal hyperplasias • 21-hydroxylase (P450c21) deficiency: cortisol, corticosterone, and aldosterone deficiency *ACTH Adrenal hypertrophy and high amounts of androgen * Virilization of female (masculanization) Steroid Hormones: Action Guyton and Hall Hormones of adrenal cortex production mg/day concentr. ng/ml activity MINERAL. activity GLUCO. aldosterone 0.05-0.15 0.15 90% deoxycorticosterone 0.6 0.15 1/15 corticosterone 1-4 2-4 1/50 4% cortisol 8-25 40-180 1/400 95% DHEA 7-15 5 1- Cortisol is at 1000 fold higher concentrations than aldosterone 2- Corticosterone >>>>aldosterone 3- Cortisol binds well to the mineralocorticoid receptor Mineralocorticoids: Aldosterone • A steroid hormone. • Essential for life. • Synthesized in zona glomerulosa • Responsible for regulating Na+ reabsorption in the distal tubule and the cortical collecting duct • Target cells are called “principal (P) cell”. • It also affects Na+ reabsorption by sweat, salivary and intestinal cells. * Stimulates synthesis of more Na/K-ATPase pumps. Mineralocorticoids: Aldosterone • Aldosterone secretion is stimulated by: • Decreasing blood volume or pressure (reninangeotensin system). • Rising blood levels of K+ • Low blood Na+ • ACTH Aldosterone synthesis • Voltage-sensitive calcium channels open and the intracellular calcium concentration increases—activating calcium calmodulin kinase. • Calcium channel blockers inhibit aldosterone synthesis. • Aldosterone levels fluctuate diurnally— highest concentration being at 8 AM, lowest at 11 PM, in parallel to cortisol rhythms. The Four Mechanisms of Aldosterone Secretion • Renin-angiotensin mechanism – kidneys release renin, which stimulates angiotensin II that in turn stimulates aldosterone release • Plasma concentration of potassium and sodium– directly influences the zona glomerulosa cells • ACTH – causes small increases of aldosterone during stress • Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) – inhibits activity of the zona glomerulosa The Four Mechanisms of Aldosterone Secretion Guyton and Hall Actions of Aldosterone Stimulates sodium reabsorption by distal tubule and collecting duct of the nephron and promotes potassium and hydrogen ion excretion • Increases transcription of Na/K pump • Increases the expression of apical Na channels and an Na/K/Cl cotransporter • Expands ECF volume • Aldosterone binds to the mineralocorticoid receptor in target cells and affects transcriptional changes typical of steroid hormone action. • The kidney is the major site of mineralocorticoid activity. Aldosterone: Role in diseases • Complete failure to secrete aldosterone leads to death (dehydration, low blood volume). • Hyperaldosterone states: Contribute to hypertension associated with increased blood volume. Overproduction of aldosterone • primary causes, ie. Conn’s syndrome • adenoma, nodular hyperplasia of zona glomerulosa • secondary • cirrhosis, ascites, nephrotic syndrome • symptoms, signs • headache, hypokalemia causing muscle weakness, hypernatremia, hypervolemia, nocturnal polyuria, hand cramping J winker Overproduction of aldosterone • treatment • surgical for adenoma • Spironolactone Thank you شكرا على حسن اإلستماع