* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Complementary Feeding - ManipurHealthServices
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
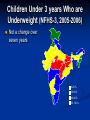
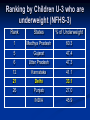
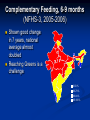
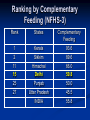
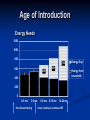
Complementary Feeding Children Under 3 years Who are Underweight (NFHS-3, 2005-2006) Not a change over seven years 0-29 % 30-39 % 40-49 % 50 -100 % Ranking by Children U-3 who are underweight (NFHS-3) Rank States % of Underweight 1 Madhya Pradesh 60.3 5 Gujarat 47.4 6 Uttar Pradesh 47.3 12 Karnataka 41.1 21 Delhi 33.1 26 Punjab 27.0 INDIA 45.9 Under-5 deaths preventable through universal coverage with individual preventive interventions Percent 0% 2% 4% 6% 8% 10% 12% 14% 16% 18% INDIA Breastfeeding Complementary feeding Clean delivery Hib vaccine Clean water, sanitation, hygiene Intervention Zinc Vitamin A Antenatal steroids Newborn temperature management Tetanus toxoid Antibiotics for PRM Measles vaccine Nivirapine and replacement feeding Insecticide-treated materials Antimalarial IPT in pregnancy Source: Jones et al. LANCET 2003;362:65-71 Complementary Feeding, 6-9 months (NFHS-3, 2005-2006) Shown good change in 7 years, national average almost doubled Reaching Greens is a challenge 0-59 % 60-79 % 80-94 % 95-100 % Ranking by Complementary Feeding (NFHS-3) Rank States Complementary Feeding 1 Kerala 93.6 2 Sikkim 89.6 11 Himachal 66.0 15 Delhi 59.8 25 Punjab 50.0 27 Uttar Pradesh 45.5 INDIA 55.8 Optimal Feeding Norms as per National Guidelines on Infant and Young Child Feeding Starting breastfeeding within one hour of birth Exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months Introducing appropriate and adequate complementary feeding after 6 months along with Continued breastfeeding for two years or beyond Definition of Complementary feeding The process of giving an infant other foods and liquids along with breast milk or non-human milk as breast milk alone is no longer sufficient to meet the nutritional requirements. These foods should complement rather than replace breastmilk. Appropriate Complementary Feeding Timely: Introduced when need for energy and nutrients exceeds that provided by BF Adequate: Should provide sufficient energy, protein, and micronutrients Properly Fed: Active feeding method and proper frequency according for age Safe: Should be hygienically prepared, stored and fed Timing of Complementary Feeding Soon after completing 6 months of age Breast milk sufficient to promote growth and development till 6 months Energy and nutrient gap appears after 6 months and widens thereafter Infant’s development and behavior makes him ready for other foods Holds objects (e.g. biscuit) and takes everything to mouth Chewing movements start Tendency to push solids out decreases Eruption of teeth and beginning of biting movements Age of Introduction Energy Needs 1200 1000 800 746 600 0 269 3-6 mo 6-9 mo 0 451 Energy from breastmilk 400 200 0 0-3 mo Excl. Breastfeeding 9-12 mo Energy Gap 12-24 mo Comp. feeding & continued BF Timing of Complementary Feeding Disadvantages of adding foods too soon Decrease the intake of breast milk resulting in a low nutrient diet Increase risk of illness esp. diarrhea Disadvantages of adding foods too late Growth and development slows down or stops Risk of deficiencies and malnutrition Importance of continued breastfeeding for 2 years and beyond 120 100 2 24 % daily needs provided by 500ml breast milk 80 45 63 60 95 98 40 20 76 55 37 5 0 Energy Protein Vit. A Vit. C Iron Gaps to be filled by complementary foods Energy and Nutrients from breastmilk Why Continue Breastfeeding? Vital source of energy (30-40%) and nutrients into 2nd yr of life Key source of Good quality proteins & essential fatty acids Micronutrients: 45% of Vitamin A 40% of calcium & riboflavin 95% of Vitamin C Fluids and nutrients during infection Associated with greater linear growth Linked to lower risk of chronic diseases & obesity Key Message-1 (Timely) Complementary feeding should begin soon after completing 6 months of age along with continued breastfeeding Adequacy (Quality) Staples: Cereals (Rice, wheat, maize, millets) and Legumes Fats (Vegetable oils/butter/ghee; 1g ~ 9 Kcal) and sugars to improve energy density and taste Foods of animal origin (Milk, curd, eggs, meat, fish) to provide good quality proteins, vitamin A and calcium. Vegetables and Fruits to provide micronutrents e.g. iron and vitamins. Supplements e.g. iron might be required. Other Attributes of Complementary Foods Right consistency Soft Easy to digest Inexpensive Locally available Culturally acceptable Easily prepared at home Variety of Foods Start at 6 mo with small amounts of food; increase quantity with age, maintaining frequent breast feeding Increase food consistency & variety with age Can feed mashed & semi-solids (e.g. porridge) at 6 mo; Can feed finger foods by 8-9 mo By 12 mo, family foods can be eaten Combine foods (e.g. rice and legumes) to provide good mixture of amino acids Foods to Avoid Tea & coffee: interfere with iron absorption Aerated beverages: No nutritional value Too much sugary drinks & Fruit juices: cause decreased appetite for other nutritious foods and also may cause loose stools. Nuts: may cause choking Stomach size Adequacy (Frequency and Amount) 6-12 months Give at least one katori (150-200 mL) serving* at a time of Khichdi or dalia or sooji (semolina) with added oil/ghee Mashed roti/rice/bread mixed in thick dal or sweeetened undiluted milk Add cooked/pureed vegetables or meat also in the servings Sevian/dalia/halwa/kheer/biscuits prepared in milk or any cereal porridge cooked in milk Mashed boiled/fried potatoes Mashed banana/cheeko/ mango/ papaya *3 times per day if breastfed; 5 times per day if not breastfed Frequency and Amount (1-2 yrs) Offer food from the family pot Give at least 1½ katori (250 mL) serving* at a time of: Mashed roti/rice/bread mixed in thick dal with added ghee/oil or khichri with added oil/ghee. Add cooked vegetables/meat also in the servings Mashed roti/ rice /bread/biscuit mixed in sweetened undiluted milk Egg preparations/ soft meat pieces without bones - Sevian/dalia/halwa/kheer prepared in milk or any cereal porridge cooked in milk OR Fruits (banana/cheeko/apple/orange/mango/papaya) * 5 times per day. Amounts of foods to offer Age Texture Frequency Amount of each meal 6 months Soft porridge, well mashed vegetable, meat fruit 2 times per day plus frequent breastfeeds 2-3 tablespoonfuls 7-8 months Mashed foods 3 times per day plus frequent breastfeeds Increasing gradually to more than 3/4 of katori (150ml) 9-11 months Finely chopped or 3 meals plus 1 snack mashed foods, and foods between meals plus that baby can pick up breastfeeds a full katori (200ml) 12-24 months Family foods, chopped or mashed if necessary more than katori (250ml) 3 meals plus 2 snacks between meals plus breastfeeds Ensure Adequacy Growth Monitoring: Measure weight and length periodically and interpret by plotting in growth curves. Investigate causes of poor growth: Dietary history; evaluate for any illness. Counsel mother/caregivers on growth, feeding and caring practices Key Message-2 (Adequacy) Complementary foods should be of right consistency, energy dense and the variety to provide all nutrient demands of a growing child. Feeding Techniques Feed infants directly & assist older toddlers eat; be sensitive to hunger & satiety cues Feed patiently; encourage, but don’t force If child refuses, experiment with different food combinations, tastes, textures Minimize distractions during meals Talk to child during feeding; maintain eye contact Responsive feeding Suitable Feeding Situation Key Message-3 (Properly Fed) Child should be fed patiently giving adequate attention and time Safe Unhygienic feeding the risk of infectious illness (esp. diarrhea) compromising nutritional status Undermines the parents’ confidence leading to delay in CF Ensuring Food Hygiene Washing caregiver’s and child’s hands before preparing, handling and eating food Clean water and raw materials to cook food Storing foods safely: Keeping food covered and serving shortly after preparation Use clean utensils to prepare & serve food Use clean bowls & cups when feeding child No feeding bottles Key Message-4 (Safety) Foods should be prepared, stored and fed hygienically to the children. Feeding the child who is ill Encourage the child to drink and to eat with lots of patience Feed small amounts frequently Give foods that the child likes Give a variety of nutrient-rich foods Continue to breastfeed Feeding during Recovery Feed an extra meal Give an extra amount Use extra rich foods Feed with extra patience Give extra breastfeeds as often as child wants Key Message-5 (During Illness) Continue feeding during illness and increase during convalescence. Key Messages Complementary feeding should begin soon after completing 6 months of age along with continued breastfeeding Complementary foods should be of right consistency, energy dense and the variety to provide all nutrient demands of a growing child. Child should be fed patiently giving adequate attention and time Foods should be prepared, stored and fed hygienically to the children. Continue feeding during illness and increase during convalescence. Thank You