* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polymers - Yafi Zayyat
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
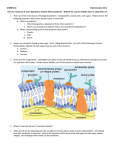
Polymers The word ‘polymer’ comes from the Greek words poly (meaning ‘many’) and meros (meaning ‘parts’). Yafi Zayyat What is a polymer? A substance that has a molecular structure consisting chiefly or entirely of a large number of similar units bonded together How is a Polymer formed? A polymer is formed by polymerization. Polymerization is the process in which monomers combine chemically to produce a polymer. What is a Monomer? A monomer is a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer. For example A + A + A + A -A-A-A-Ae.g- Ethene= Poly(ethene) How many types of polymerization are there? There are two types of polymerization: Addition Condensation Addition polymerization Addition polymerization is the formation of successive links between small units called monomer molecules containing a C=C double bond to form a a long chained macromelcule For example: Polyethene (sometimes called polythene) is a polymer made from ethene. Polymerization Polymer Condensation polymerization Condensation polymerization is the formation of successive links between small units called monomer molecules to form a long chained macromolecule ( polymer ) and a small molecule ( usually water). For example: Dicarboxylic acid + Diamines Nylon ( polyamide ) + water Types of condensation polymers What decides the properties of a polymer? Stronger attractive forces between chains = stronger, less flexible polymer. Chains able to slide past each other = flexible polymer . Drawing polymers – shorthand formulae Polymers contain thousands of molecules, so how can their structures be easily drawn? Part of the polymer molecule can be drawn A better way is to show a shorthand formula: The ‘n’ means that the polymer contains a very large number of the repeating unit shown in the brackets. Examples of polymers Polythene – plastic bags, bottles, bowls Very cheap and strong. Easily moulded. Polypropene – crates, ropes, carpets. Forms strong fibres. Has high elasticity. Polystyrene – radio cases, foam packaging. Cheap and easily moulded. Can be expanded into foam. Four types of organic polymers 1. CARBOHYDRATES – glucose, bread, pasta CARBO(C) – HYDRATE(H2O) 2. PROTEINS – muscle, meat, hair, nails 3. LIPIDS – fat, oil, butter 4. NUCLEIC ACIDS – DNA, RNA Carbohydrates Monomer- the simple sugars, Glucose, sucrose, fructose (and many others) Polymer - The complex carbohydrates. Starch and Cellulose are long chains of simple sugars Proteins Monomer- amino acids Polymer- polypeptide Nucleic Acid DNA (a nucleic acid) is a polymer DNA is made of monomers called nucleotides Longer chains make stronger polymers. • Critical length needed before strength increases. • Hydrocarbon polymers average of 100 repeating units necessary but only 40 for nylons. • Tensile strength measures the forces needed to snap a polymer. Review Polymers are made up of monomers Polymerization; Addition- produces only a polymer Condensation- produces a polymer and small moclecule usually water. Four types of organic polymers Proteins Carbohydrates Nucleic acids lipids