* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DC Analysis
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
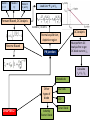
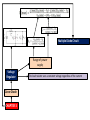
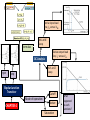
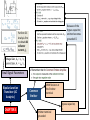
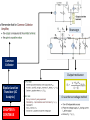
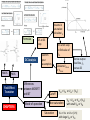
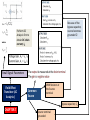
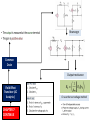
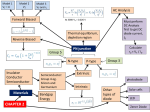
Model 1 V = 0 Model 2 V Model 3 V and rf Load Line ID vs VD Forward Biased, DC Analysis At 300K VT = 0.026 V Thermal equilibrium, depletion region Reverse Biased PN junction AC Analysis Must perform DC Analysis first to get DC diode current, ID Calculate rd = VT / ID photodiode Other types of diode CHAPTER 2 Schottky Barrier Diode Solar cells LED Zener Diode Multiple Diode Circuit Range of power supply Voltage Regulator Zener Diode CHAPTER 3 The load resistor sees a constant voltage regardless of the current Derive input load line, IB versus VBE Formulas KVL at BE Loop DC Analysis npn Derive output load line, IC versus VCE KVL at CE Loop pnp Bipolar Junction Transistor Cutoff Mode of operation CHAPTER 4 Active Saturation What happened to each junctions? Fixed Bias Biasing Circuit Collector to Base Feedback Resistor Voltage Divider Biasing Circuit Bipolar Junction Transistor (Biasing) CHAPTER 4 CONTINUE DC Analysis Voltage transfer characteristic, VO versus VI Because of the bypass capacitor, emitter becomes grounded Perform DC Analysis first to obtain DC collector current, IC Small Signal Parameters Bipolar Junction Transistor (AC Analysis ) CHAPTER 5 Common Emitter With Resistor at the Emitter terminal Emitter terminal grounded Bypass capacitor, CE Rearrange Common Collector Output resistance Bipolar Junction Transistor (AC Analysis ) CHAPTER 5CONTINUE Or use the test voltage method Assume in saturation: calculate ID Formulas KVL at GS Loop DC Analysis NMOS Confirm your assumption PMOS Field Effect Transistor CHAPTER 6 Differences between MOSFET and BJT Mode of operation Cutoff KVL at DS Loop to find value of VDS Calculate VDS sat or VSD sat VGS < VTN or VSG < |VTP| Non saturation Saturation Derive output load line, ID versus DS VGS > VTN or VSG >|VTP| with small VDS or VSD VGS > VTN or VSG >|VTP| with large VDS or VSD Because of the bypass capacitor, source becomes grounded Perform DC Analysis first to obtain DC drain current, ID Small Signal Parameters Field Effect Transistor (AC Analysis ) Common Source With Resistor at the Source terminal Bypass capacitor, CS CHAPTER 7 Source terminal grounded Rearrange Common Drain Output resistance Field Effect Transistor (AC Analysis ) CHAPTER 7CONTINUE Or use the test voltage method IDQ Answering the questions • There are 5 questions. Answer all. • Organize your thoughts. When it is organized, so will your workflow. – Messy work will make the lecturers feel annoyed as they have to look for your answers – bear in mind that lecturer handling one section = 50-60 students – each paper has 5 questions – TOTAL – 250 to 300 questions to mark • Don’t leave a question blank – just write down anything you know that might be related • Study smart, pray and tawakal.