* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L4 series and parallel resistors
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Charlieplexing wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
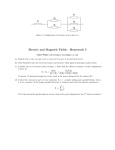
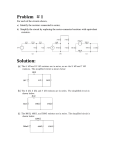
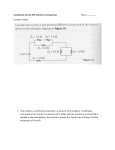
TITLE: Resistors in series and parallel and power measurement conductance OBJECTIVE: To verify the formulae for resistors in series and parallel. Calculate power from measurements of voltage and current EQUIPMENT: Variable voltage d.c. power supply, switch, resistors, circuit board. THEORY: When resistors are connected in series the total resistance of the circuit is given by the formulae: Rtot = R1 + R2 + R3 …… Ohms. When resistors are connected in parallel the total resistance of the circuit is given by the formulae: 1/Rtot = 1/R1 + 1/R2 +1/R3….. Ohms. The effect of current flowing through a resistor generates heat (electric to heat energy conversion) Power P = V∙I Watts (W) Resistance = V/I Ohms (Ω) PROCEDURE: Figure 1 A Ammeter Variable voltage d.c. supply Voltmeter V R Resistors in series: Figure 2 Resistors in series I R1 R2 R3 V1 V2 V3 V Rtot = V/I Replace R in the circuit shown in Figure 1 with three resistors in series as shown in Figure 2, Determine the nominal value of the resistors (RN) provided from their colour code. Set the supply voltage so that there is a 10 V across the three resistors. Measure the total current I flowing in the circuit with the ammeter and the voltage across each resistor. Place the results in Excel worksheet as shown below. Calculate the each and total resistance from Ohms Law. R R1 R2 R3 RSer Compare this to the theoretical formulae calculation to confirm formulae for resistors in series and calculate percentage error between values. Calculate power dissipated by each resistor and total resistance using current measurement and resistance voltage measurements RN (Ω) VR (V) IR(mA) Rexp (Ω) Err.(%) PR (mW) 10 Resistors in parallel: Figure 2 Resistors in parallel I I1 I2 V R2 R1 I3 R3 Rtot = V/I Replace R in the circuit shown in Figure 1 with three resistors in parallel as shown in Fig.3. Set the supply voltage so that there is a 3 volt p.d. across the parallel network of resistors. Measure the total current I flowing in the circuit and the currents flowing in each branch with the ammeter. Place the results in Excel worksheet. Calculate the each and total resistance from Ohms Law. Compare this to the theoretical formulae calculation to confirm formulae for resistors in parallel and calculate % error between values. Calculate power dissipated by each resistor and total network using the supply voltage and current measurements. Series - Parallel Circuit Repeat the experiment with a combination of 5 resistors connected as shown. Note: V= V1+V3, I=I1+I2= I3+I4 and V1=V2, V3= V4+V5, I4= I5 I1 I I2 R1 R3 I3 V3 V1 R2 R4 R5 V2 I4 V4 V5