* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dielectric loss
Strengthening mechanisms of materials wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Shape-memory alloy wikipedia , lookup
Viscoelasticity wikipedia , lookup
Tunable metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
X-ray crystallography wikipedia , lookup
Negative-index metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Nanochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Colloidal crystal wikipedia , lookup
History of metamaterials wikipedia , lookup
Curie temperature wikipedia , lookup
Crystal structure wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
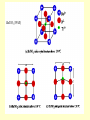
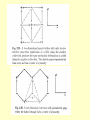
Ferroelectrics: •There is a class of materials which shows spontaneous polarization and for which the relation between P and E is non-linear. Such materials also exhibit Hysteresis. •These substances whose properties are similar to ferromagnetics in many respects are called Ferroelectrics. Spontaneous polarization is a function of temperature. Ps decreases with increase in temperature and vanishes at the curie temperature Tc. T < Tc At E = 0 Above Tc , the substance is in the paraelectric state in which the elementary dipoles of the various unit cells in the crystal are randomly oriented. Ferroelectric behavior T > Tc At E = 0 Paraelectric behavior Electric susceptibility In paraelectric state the substance is found to obey the Curie-Weiss Law C , T TC where C and Tc are constants known as and Curie Weiss temperature . χ Tc T To prove Curie-Weiss Law P E o We know that If Eloc P NEloc Polarization p2 and 3k T Where ( = 1/3) Np 2 P (E ) 3kT 0 Np 2 Np 2 P(1 ) E 3kT 0 3kT P E Np 2 Np 3k T 1 3k T 0 2 Np 2 2 Np 3k T 3k 0 P Np 2 C r 1 0 E 3k 0 (T Tc ) (T Tc ) C Curie-Weiss Law (T Tc ) 2 Np Where, Tc 3k 0 and Np 2 C 3k 0 χ Tc T Condition for spontaneous Polarization: Polarization of a dielectric material is given as In above equation, if 1 N 0 N E P N (1 ) 0 0 one gets non-vanishing solution for P even in absence of Ef(E=0). Thus there exists possibility of spontaneous polarization. Thus condition for spontaneous polarization is given as 1 N 0 0 N 0 1 Examples of ferroelectric materials: •There are mainly three types of crystal structures which exhibit ferroelectricity: 1. Rochelle salt structure or Rochelle salt, NaK(C4H4O6).4H2O:Sodium Potassium Tartrate KH2 PO4 (123K ) KD2 PO4 (213K ) RbH 2 PO4 (147K ) RbH 2 AsO4 (111K ) 2. Perovskite group consisting mainly of titnates and niobates BaTiO3 : Barium titanate 3. Dihydrogen phosphates and arsenates KH2PO4 : Potasium di phosphate (KDP) • The ferroelectricity can be explained by the domain theory. KH2 AsO4 (96) BaTiO3 (393K ) SrTiO3 (~ 0K ) KNbO3 (713K ) PbTiO3 (763K ) LiTaO3 (890K ) LiNbO3 (1470K ) BaTiO3 (393K ) Summary • • • • Spontaneous Polarization P & E are nonlinear. Ferroelectric state (Below Tc) shows Hysteresis. Para electric (above Tc) state having Linear relation in P & E. • Obey Curie – Weiss Law (Prove) • Condition of Spontaneous Polarization. Piezoelectricity: History • Piezoelectricity was discovered by Jacques and Pierre Curie in the 1880's during experiments on quartz. • The word piezo is Greek for "push". The effect known as piezoelectricity. • Electromechanical phenomena. How it appears • On a nanoscopic scale, piezoelectricity results from a nonuniform charge distribution within a crystal's unit cells. When such a crystal is mechanically deformed, the positive and negative charge centers displace by differing amounts. So while the overall crystal remains electrically neutral, the difference in charge center displacements results in an electric polarization within the crystal. Electric polarization due to mechanical input is perceived as piezoelectricity. Q: Are you getting any similarity with dielectric substances? PIEZOELECTRICITY •In some crystals, the application of an external stress induces a net dipole moment, such crystals are known as Piezoelectric crystals. •A stress applied to the crystal will change the electric polarization. Similarly, an electric field E applied to the crystal will cause the crystal to become strained (electrostriction). •All crystals in a ferroelectric state are also Piezoelectric. But vice verse is not true. E.g Quartz. • Crystals with no centre of symmetry exhibit Piezoelectricity. Ques: What is magnetic analog of Piezoelectricity? Magnetic analog of Piezoelectricity There is a magnetic analog where ferromagnetic material respond mechanically to magnetic fields. This effect, called magnetostriction, is responsible for the familiar hum of transformers and other AC devices containing iron cores. Little more on Piezoelectricity • Piezoelectricity is a coupling between a material's mechanical and electrical behaviors. • In the simplest of terms, when a piezoelectric material is squeezed, an electric charge collects on its surface. Conversely, when a piezoelectric material is subjected to a voltage drop, it mechanically deforms. • Many crystalline materials exhibit piezoelectric behavior. A few materials exhibit the phenomenon strongly enough to be used in applications that take advantage of their properties. • These include – – – – – quartz, Rochelle salt, lead titanate zirconate ceramics (e.g. PZT-4, PZT-5A, etc.), barium titanate, and polyvinylidene flouride (a polymer film). Applications • Applications where strongly-piezoelectric materials are used include buzzers inside pagers and cell phones. • Shakers inside ultrasonic cleaners, spark generators inside electronic igniters. • Strain sensors inside pressure gages. • Piezoelectric materials also make inexpensive but fantastically accurate "clocks". For example, – the element keeping track of time inside a quartz watch is literally a small piece of vibrating quartz. Its vibration period is stable to more than one part per million as a result of its piezoelectric properties.