* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Characteristics of Stars - Laconia School District
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
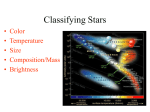
Characteristics of Stars By: Kendra, Paige, and Brandon Constellations • Constellations are an imaginary pattern of stars in the sky. The ancient observers found this out first. They imagined this though. The ancient observers saw that the stars made animals and people in the sky. Apparent Brightness • Apparent brightness is seen from Earth. The astronomers can measure apparent brightness fairly easy using electronic devices. Absolute Brightness • Absolute brightness is the brightness of the star that would have if it were at a standard distance from Earth. Spectrograph • A spectrograph is a device that breaks into colors and produces an image of resulting spectrum. Most large telescopes have spectrums. Light-Year • The distance that light travels in one year, about 9.5 million million kilometers. Parallax • A parallax is the apparent change in position of an object when you look at it from different places. For an example, image that you and a friend have gone to a movie. A man with a large hat sits down in front of you. Because you and your friend are sitting in in different places he covers half of the screen. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram • People say about 100 years ago, two scientists were working alone and made this discovery. Both Ejnar Hertzsprung in Denmark and Henry Norris Russell in the United States, they made these graphs to find out if the temperature and the absolute brightness of the stars related. This was called the Hertzsprung- Russell Diagram. Main Sequence • A main sequence is the diagonal on an H-R diagram that includes more than 90 percent of all stars. Key Concept #1. • How are stars classified? • Stars are classified by their color, temperatures, sizes, and brightness Key Concept #2. • How do astronomers measure distance to the stars? • Astronomers use a method called parallax. Because of the Earth's revolution about the sun, near stars seem to shift their position against the farther stars. The smaller the parallax shift, the farther away from earth the star is. This method is only accurate for stars within a few hundred light-years of Earth. When the stars are very far away, the parallax shift is too small to measure. Key Concept #3. • What is an H-R diagram and how do astronomers use it. • The H-R diagram can be thought of as a graph, with color (temperature) on the x-axis and luminosity on the y-axis. Since stars go through a definite "life cycle" which can be mapped on the H-R diagram, a star's location on the diagram can indicate both its mass and its relative age. Figure #1. • How many times larger is this than the sun, which has a diameter of 1.4 million kilometers? Figure #2. • Why do the closer street lights appear bigger than the more distant lights? • Because the brightness depends on the both its size and temperature. The closer you are to a light it seems better. Figure #3. • Why do nearby stars appear to change position between January and July? Look at the image to the right and figure it out. Reading checkpoint #1. • What is a spectrograph? • A device that breaks light into colors and produces an image of the resulting spectrum. Reading Checkpoint #2. • What is a star’s absolute brightness? • The brightness a star would have if it was standing a distance from Earth. Reading Checkpoint #3. • How is a parallax useful in astronomy? Reading Checkpoint #4. • What is the main sequence? • The main sequence is the diagonal region in the H-R diagram. Assessment #1. • Name three characteristics used to classify stars. • Size • Temperature • Brightness Assessment #2. • What is the difference between apparent brightness and absolute brightness? The difference between apparent brightness and absolute brightness is Assessment #4. • What is a light-year? • The distance that light travels in one year, about 9.5 million million kilometers. Assessment #5. • What is a parallax? • A parallax is the apparent change in position of an object when you look at it from different places Assessment #6. • Identify two ways in which astronomers can use the H-R diagram. • Astronomers can use the H-R diagram for classifying stars and to understand how stars change over time. THE ENDD :D Alright, we worked on this for 4 days. It took us a lot of time and a lot of effort, we also put a lot of effort into this twoo. So…really, we hope you liked it. Now you may clap :D. By: Brandon, Kendra, and Paige :D.