* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9 (Part A)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
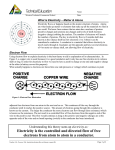
Chapter 9. Principles of Electricity for Electrotherapy (Part A) Basics of Electricity Electricity Defined - ____ definitions 1. A property of certain fundamental particles of all _____________ that have a __________ ____________ associated with them, manifested by an ___________________________ of, or __________________ of, _________________ on an atom or body 2. A form of ____________________ associated with the existence and __________________ of ________________ charge, manifested by the ___________________________ of, or __________________ of, _________________ on an atom or body; exhibits ___________________ (electromagnetic), chemical, mechanical (electrokinetic), and ________________________ properties 3. A form of energy that exhibits __________________, chemical, mechanical, and _________________ effects; formed from the interaction of positive (+) and negative (−) _________________ 4. The physical phenomena associated with the existence and ____________________ of electrical charge, either ________________ charges (electrostatics) or _______________ streams of charge (current) Electricity (1) Static Electricity •Static electricity is ____________________ electricity. –One body _________________ electrons; the other ________________electrons. –Stored in an insulated conductor in which the charges are in a state of tension –State of tension = (2) Current Electricity •A stream of loose ______________________ passing along a _____________________ •Current passes in two ways –_________________ current (DC) –_________________ current (AC) DC Current •Steady _________________ flow of electrons •Example: •Also called _________________ current AC Current •Flow of electrons that rhythmically _________________ direction •Two terminals of generator (source) alternatively change from _________________ to _________________ DC and AC Current Modulation Most common = 1 Physics of Electricity •Matter – •Element – •Atom – –________________________ part of an element –Composed of _________________, _________________, _________________, and other smaller substances •Molecule –Two or more atoms held together in –May be same (____) or different (_____) •Proton – – •Neutron – – •Electron – – •Electrical charge –Net sum of charges of _________________ and ____________________ •Difference between number of _________________ and ________________ •In normal state: •Chemical, mechanical, solar, or thermal force causes _________________ to be _______________ or ___________________ from the atom, and it becomes __________________ or __________________ charged •Ion •Atom or molecule that has _____________ or _______________ one or more ________________ •Is either _________________ or ___________________ charged •Electrolyte •Substance that contains ____________ •Able to ______________ electricity Current Flow •Flow of ___________________ _________________ from one point to another –Higher concentration of _________________ to an area lacking _______________ •Flows from ___________________ pole to ________________ pole 2 Conductor •Substance that can ____________________ _________________ ________________ •Must have ____________ electrons that can be pushed along • •_______________ with minerals or electrolytes is a good conductor. –Good electrical conductors also good ___________ conductors. •Electrical conductors don't allow electricity to flow ___________ –They oppose the flow of electricity, called ____________________ Conduction Insulator •Nonconductor •________________ the flow of electrons. •Has no free ___________________ to bump •Examples – Semiconductor •Substances whose conductivity is ________ at _______ temperatures •Increases when small amounts of other _________________ are added – •__________________ flow of electricity •Examples – Partial conductor •Substance that allows some flow of electricity under certain conditions •Examples – Quantifying Electricity •Coulomb –The basic unit of ____________________ –Produced by 6.28 × 1018 displaced electrons (6,280 quadtrillion) •Voltage (V) –Force created by __________________________ of extra _________________ at one point in circuit, usually corresponding to _________________ of electrons at another point in circuit –If two points are __________________, difference in _____________ population causes __________________ to move from area of _________________ concentration to area of _____________ –Volt (V) is unit of ______________ –Force required to push a current of 1 amp (A) through a resistance of 1 ohm (Ω) •Voltage sources –From ___________________ battery or generator 3 –Voltage from a _____________________ is called electromagnetic force (emf) –Commercial emf either 110 or 220 V –High-power transmission lines are 20,000 V •Ampere (A) –Unit of ________________ _________ –Equal to the passage of one coulomb per second — that is 6.28 × 1018 electrons passing per second –Electromedical work requires much less (milliamperes, mA). –Some therapeutic devices use 0.1 to 1 mA, others use 500 to 1500 mA •Ohm (Ω) –Unit of ____________________ or opposition to the flow of _________ –Equal to resistance of a column of mercury 1 mm2 in cross section and 106 cm high at 0°C –Resistance •Opposition to flow of ____________ in a _______ •Caused by the _______________ •Determined by: – – – – –Impedance •Opposition (resistance) to flow of _________________ in a _______ Review Elements of current flow: •Force = •Flow = •Resistance = Current = Force / Resistance Water/Electricity Analogy: Water through a pipe similar to electricity through a conductor •Volume –Water: –Electricity: •Rate of flow –Water: –Electricity: •Resistance to flow –Water: –Electricity: 4 –Owing to characteristics of the pipe or conductor •Pipe: narrow or wide, long or short, rough or smooth •The composition and size of the conductor determine its resistance •Requirements for flow –Water • • •Closed system of pipes to carry the water in (if you want to control flow) •Water flows by displacing _____________ •_________________ or _____________________ to help direct flow •Different sizes of pipe to provide resistance and help control volume of flow –Electricity • • •Closed system (circuit) of _________________ •Electricity flows by displacing ___________________, which must be accepted by something else; must have a complete circuit. •Different sizes of resistors to provide resistance and control volume of flow Electrical Equipment Generator •A tale of two devices: –A device that _________________ various forms of energy into _________ electricity –A medical device that converts an input electrical current (AC or DC) into various output currents (AC, DC, or pulsed) Terminal (pole) •Output device of a battery or generator •Attached by wires to ___________________ •Positive –Terminal from which current _________________ generator •Negative –Terminal into which current ________________ to generator •Electrical circuit –System of ___________________ that allows __________________ to move between __________ of a generator –Closed circuit • • –Open circuit • 5 Medical Devices •Muscle stimulator (neuromuscular electrical stimulation, NEMS) –A therapeutic device that delivers current to the body to cause ______________ and ______________ nerve ______________________________ –Causes _______________ _____________________ •Nerve stimulator (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulator; TENS) –Therapeutic device that delivers current to the body to cause _________________ nerve ____________________________________ –Stimulate sensory nerves to ___________________ ____________ –Muscle contraction __________ occur, but this is not the purpose of (or necessary for) TENS stimulation. Safety Devices •Circuit breaker –Safety device that protects equipment and structures from ______________ current –Manufactured to respond to specific amounts of current flow (such as 10 A, 30 A, etc) –When current exceeds the specified rating of the breaker, it ___________________ •Ground-fault interrupter (GFI) – –Senses very small ______________-_____________ currents that might flow through the body of a person standing on damp ground while touching a hot AC line wire. –Acts in a little as 0.025 sec to the circuit breaker –Typical trip in homes is at ____ mA –Used chiefly for wall-outlet circuits into which potentially dangerous appliances might be plugged 6