* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Charge - Cremona School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
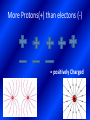
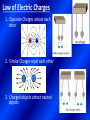
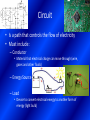
Electrical Energy can be transferred and stored Static Electricity Static Electricity Is created when there are unequal numbers of protons and electrons in atoms Protons : have a positive charge Electron: have a negative charge Can create attractive and repulsive forces Equal Protons(+) and electrons (-) = Neutral Charge More Protons(+) than electons (-) = positively Charged More Electrons (-) than Protons(+) = Negative Charge Built up a static Charge -Means stationary or not moving Static electricity does not flow but rather it may jump from one object to another in the form of electrical discharge. Charge Separation Resulting shock referred to as Electrical Discharge Law of Electric Charges 1. Opposite Charges attract each other 2. Similar Charges repel each other 3. Charged objects attract neutral objects Van De Graaff Generator Current Electricity • The steady flow of particles is called electrical current • Requires: – Energy Source – Completed path or Circuit Amperes • Rate at which an electrical current flows – Often called “amp” (A) – Most electrical devices at home have a current of less than 15 A Circuit • Is a path that controls the flow of electricity • Must include: – Conductor • Material that electrical charge can move through (wire, gases and other fluids) – Energy Source – Load • Device to convert electrical energy to another form of energy (light bulb) Voltage • Is the measure of how much electrical energy each charged particle carries • The higher the voltage is, the greater the potential energy of each particle • Volt (V) • Measured with a Voltmeter