* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nursing diagnosis/objectives/interventions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
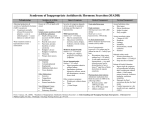
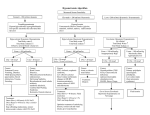
CRITICAL THINKING SUMMARY Student: _____Cheryl hamilton_________________________ Client Dx: _______Low sodium Levels________________________ Age: __8___ Allergies: __________None___________________________________ The MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS that brought the client to the hospital is: Hyponatremia/ Addison’s disease PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of diagnosed disease: (From text) Hyponatremia when there is abnormally low blood sodium levels (below 135 mEq/L). Results when there is too much water in the extracellular fluid for the amount of sodium present. Causes include excessive antidiuretic hormone secretions, burns, prolonged use of certain diuretics, wound drainage, vomiting, diarrhea, and renal disease. Addison’s Disease is the hyposecretion of adrenal cortex hormones (glucocorticoids and mineralcorticoids) SYMPTOMS typically seen with this diagnosis include (as identified in your text): Hyponatremia: stupor, coma, confusion, altered mental state, lethargy, N/V, abdominal cramps, tachycardia, weakness, muscle twitching Addison’s: weakness, GI disturbances, weight loss, emotional disturbances, bronze pigmentation of the skin, electrolyte imbalances such as hyponatremia and hyperkalemia, and hypotension CLIENT’S SYMPTOMS of the diagnosed disease include: Nausea Muscle weakness Fatigue Body aches NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT: Height (actual or estimated): _18.3 cm_______ Weight (actual or estimated): ____83.6 kg______ Estimate Ideal Body Weight (Male: 105lb + 6 lb/inch > 5’. Female: 100lb + 5lb/inch > 5’): ___70.76________ Does this client have characteristics of a well-nourished person? Yes __X___ No _____ Explain your answer. The patient exhibits no signs of malnutrition. She has no difficulty eating and has no complaints of nausea or vomiting that could potentially cause her to become malnourished. She weighs more than her ideal body. PSYCHOSOCIAL STAGE OF DEVELOPMENT What is the client’s developmental stage? Generativity vs. Stagnation Has he/she met the necessary accomplishments? Yes __X___ No _____ Explain. She has a son and works to support her child as well as herself. She talks about her accomplishments in life and feels successful for all she has accomplished. How is this illness affecting the client’s ability to meet these necessary accomplishments? Being in the hospital keeps her from working, this can potentially decrease her income for the month. She is unable to be with her child and is unable to care for him. NURSING DIAGNOSIS/OBJECTIVES/INTERVENTIONS Indicate below the 2 priority nursing diagnoses that are most relevant for your client. #1 NURSING DIAGNOSIS (problem r/t) Activity Intolerance r/t weakness and fatigue DEFINING CHARACTERISTICS (S/S) that support this diagnosis: Pt is feeling weak and fatigue which makes it difficult to do ADL’s OBJECTIVE/CLIENT OUTCOME for this diagnosis: Pt will demonstrate increased tolerance t activity NURSING INTERVENTIONS that will assist the client to resolve the above identified diagnosis: 1.gradually increase activity, allowing client to assist with positioning changes, transferring, and self care 2. assess pt for signs of activity intolerance and for daily appropriateness of activity 3.determine cause of intolerance and treat cause #2 NURSING DIAGNOSIS (problem r/t) Risk for electrolyte imbalance r/t hyponatremia DEFINING CHARACTERISTICS (S/S) that support this diagnosis: Sodium level 123 mEq/L OBJECTIVE/CLIENT OUTCOME for this diagnosis: Pt will maintain normal serum sodium levels NURSING INTERVENTIONS that will assist the client to resolve the above identified diagnosis: 1. monitor sodium levels 2. monitor for signs and symptoms of hyponatremia 3. administer prescribed electrolytes COMPLICATIONS: If this client’s condition were to worsen, what would be the most likely reason and why? The reason the pts sodium levels would continue to decrease would be if the problem causing the low sodium levels is not corrected and/or there is more water in the extracellular fluid and it continues to dilute the sodium. The loss of sodium could lead to a fluid volume depletion which signals release of ADH which signals the kidneys to retain water leading to blood sodium dilution. How would you know this is happening? They pt would exhibit signs of altered mental status, seizures, and eventually coma What will you do if this happens? Notify physician, administer prescribed medications, monitor pt for seizures/ implement seizure precautions, administer sodium chloride to raise sodium levels Analysis of Diagnostic Tests DIRECTIONS: 1. List all diagnostic and laboratory tests pertinent to the patient's medical diagnosis or medical treatments (i.e. medications) and provide the patient values for each test. Explain why they are pertinent for this patient. 2. List any screening diagnostic and laboratory tests that are not within normal limits. Explain why these tests are increased or decreased in relation to your patient's medical condition. Diagnostic/Lab Test Patient Values Neg. Study Analysis of Values No abnormalities Enlarged upper half of pituitary stalk 1.9mm stone in gallbladder There are no signs of a mass or infarction that could be impeding cortisol secretions cholelithiasis Admitting Na+ levels 123 mEq/L hyponatremia Admitting cortisol level 0.9 Low due to insufficient adrenal gland function resulting in decreased cortisol levels Abdominal CT Reason: adrenal insufficiency MRI Brain US RUQ Florinef Corticosteroids Hormones Fludrocortisone PO: 100 mcg/day Causes Na+ reabsorption and water retention by effect on distal tubule Sodium loss and hypotension associated with adrenocortical insufficiency Maintenance of sodium balance and BP in pts with adrenocortical insufficiency lovenox Anticoagulants Enoxaparin Sub Q: 1 mg/kg every 12hrs Antithrombotics Low molecular weight heparins Claritin Loratidine Antihistamines Administer deep into subq tissue Alternate injection sites Do not expel air bubble PO: 10 mg daily Loradamed Alavert allergy May be taken with or without water Potentiates the inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor Xa and thrombin Prevention of thrombus formation Blocks peripheral effects of histamine released during allergic reactions Prevention of venous thromboembolism, DVT, and PE Treatment of DVT with or without PE Prevention of ischemic complications from unstable angina Treatment of acute ST segmentelevation MI Relief of symptoms of seasonal allergies Management of hives Dizziness Headache HF Arrhythmias Edema HTN Hypokalemia Arthralgia Anorexia Nausea Monitor BP during therapy Dizziness Headache Insomnia Edema Constipation ↑ liver enzymes n/v urinary retention hyperkalemia bleeding anemia fever ↑ risk for bleeding when concurrent use of drugs that affect platelet function and coagulation Confusion Drowsiness Blurred vision Dry mouth GI upset Rash Wt gain Photosensitivity Assess allergic symptoms Monitor for fluid retention Monitor serum electrolytes Assess for signs of hemorrhage and bleeding Observe injection sites for hematomas, ecchymosis or inflammation Assess lung sounds Hydrocortisone Cortef Corticosteroids PO: 20-240 mg/day Cortenema IM,IV Hycort 1-2 mg/kg/dose bolus; 25-250 mg/day Suppress inflammation and the normal immune response Management of adrenocortical insufficiency Depression Euphoria Headache HTN Anorexia n/v peptic ulceration osteoporosis wt gain muscle wasting Teach pt side effects of prolonged steroid use: wt gain, hyperglycemia, etc.