* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Demand-side and Supply
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
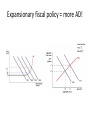
Demand-side and Supply-side Policies Different policies used by government to achieve macroeconomic stability Demand-side Policies • Focus on changing AD to achieve price stability, full employment and economic growth. These policies are put into effect to counter the short-term fluctuations in real GDP due to the actions of……. The Animal Spirits! Behavior of consumers and businesses are responsible for the ups and downs of the business cycle. Goals of Demand-side policies To bring AD to potential GDP or create economic growth by increasing potential GDP Discretionary Fiscal Policy • Fiscal Policy • Monetary Policy Stabilization Policies • Fiscal and monetary policies are designed to stabilize the fluctuations of the business cycle. Remember, economists (but not economics) are boring and like predictability! Government Finance • Balanced budget, Budget deficit, Budget surplus and debt……… • What’s the difference? Fiscal Policy • Fiscal policy are the decisions made by government concerning its taxes and expenditures in order to influence the level of AD. Fiscal policy can affect three of the four components of AD, those three are…….. Components of AD influenced by fiscal Policy Right you are! Fiscal policy can influence the level of spending by consumers, businesses and the government itself How can fiscal policy be so powerful? • The government can increase or decrease the tax rate on consumers • The government can increase or decrease the tax rate on businesses • The government can increase or decrease its own spending levels Suffering from a recessionary gap? Fiscal policy remedy! • Expansionary fiscal policy to the rescue…….Uhmmmm, what’s that again? Expansionary Fiscal Policy • If we are experiencing a recessionary gap due to insufficient AD, the following will help! • Increase government spending • Reduce taxes on consumers • Reduce taxes on businesses or • A combination of the above Expansionary fiscal policy = more AD! Different results at Different Stages • If we are in a deep recession (at the horizontal part of the Keynesian AS curve) expansionary fiscal policy will increase GDP without increasing the average price level • At other points of the Keynesian AS curve expansionary fiscal policy may or may not increase GDP but will increase the average price level Suffering from an inflationary gap? Fiscal policy remedy! • Contractionary fiscal policy to the rescue…….Uhmmmm, what’s that again? Contractionary Fiscal Policy • If we are experiencing an inflationary gap due to excessive AD, the following will help! • Decrease government spending • Increase taxes on consumers • Increase taxes on businesses or • A combination of the above Contractionary fiscal policy = less AD! Halftime! Time for some review questions Questions • What’s the difference between budget deficit and government debt? • What are the objectives of fiscal policy? • What’s the difference between expansionary and contractionary fiscal policy? • What will fix an inflationary gap? • What will fix a recessionary gap? Monetary Policy • Monetary policy is carried out by the central bank of each country. Central banks also control the money supply, determine interest rates and oversee the banking system Interest Rates • So what’s the relationship between interest rates and the demand for money? When interest rates are high, people hold less cash, when interest rates are low, people hold more cash. Comprende? Or is it Entiende? Changes to the money supply • So what happens to interest rates if the central bank increase the money supply? Interest rates increase, decrease or stay the same? • And if the central bank decreases the money supply? Interest rates increase, decrease or stay the same? Interest Rates and AD Why change the money supply? • As you have already seen, when the central bank increases the money supply, interest rates fall, and when interest rates fall, what happens to AD? Easy Money! Expansionary Monetary Policy • When the central bank increases the money supply, interest rates fall, and consumers and businesses are more likely to borrow. Increased borrowing means increased spending, which means increased AD which is the perfect medicine to fight a recessionary gap! Tight Money! Contractionary Monetary Policy • When the central bank decreases the money supply, interest rates rise, and consumers and businesses are less likely to borrow. Decreased borrowing means decreased spending, which means decreased AD which is the perfect medicine to fight an inflationary gap! So to summarize….. • During a deflationary gap, to increase AD the government may choose to increase spending or cut taxes (fiscal policy) or increase the money supply/lower interest rates (monetary policy) • During inflationary gap, to decrease AD the government may choose to decrease spending or raise taxes (fiscal policy) or decrease the money supply/raise interest rates (monetary policy) So which is better? Fiscal or Monetary? Strengths of fiscal policy In case of emergency… • Fiscal policy can be extremely effective during times of economic emergency, whether that is during a deep recessionary gap (see 1930s) or times of escalating inflation Fiscal Policy and long-term economic growth • Expansionary fiscal policy leads to investment and gains in research and development/new technology as well as infrastructure improvement and training/education. All of these can have the effect of shifting the AS curve to the right and create economic growth in the future. The many weaknesses of fiscal policy Timing • Fiscal policy comes with delays. Delays in recognizing the problem, delays in making the appropriate decision and delays until the policy has taken effect. By the time these “lags” are overcome, the problem could be worse, maybe been solved already….. The many weaknesses of fiscal policy Information • Fiscal policy decisions are based on statistical information compiled by government workers. Can these workers be trusted? Your teacher used to be one, so what do you think? The many weaknesses of fiscal policy Politics • Taxes are unpopular. Government might want to raise taxes to slow AD, but that is not going to be a popular move with voters • Government might want to cut spending, but many programs are protected by law, so this may not be easy to do either The many weaknesses of fiscal policy Crowding Out? • If the government begins to borrow more money, what will happen to interest rates? What effect will that have on private investment? Might that be a problem? The many weaknesses of fiscal policy Tax cuts don’t always lead to increased AD • Government may think reducing taxes will lead to increased spending, but if consumer confidence is low, people may just take that money and put it in the bank, rather than spend it…..government spending is more effective… The many weaknesses of fiscal policy Inability to “fine-tune” the economy • Fiscal policy can guide the economy to a certain point, but it is not very effective in reaching precise targets in terms of output, employment, or price levels. Strengths of Monetary Policy Strengths of Monetary Policy • Quick implementation • No political constraints • No crowding out effect • Better able to fine-tune the economy Weaknesses of Monetary Policy • Lags can exist due to problem recognition, and time for policy to take effect • Reliance on statistics compiled by government bureaucrats • May not be effective during severe recession (banks may not want to lend money, consumers and businesses may not want to take loans) What about stagflation? • Fiscal and monetary policy can correct economic problems that arise from a problem with AD, but what about a negative supply shock? Fiscal policy is unable to deal with instability arising from a leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve Pick one!!! • Keynesians believe most strongly in fiscal policy while other economists are wishywashy and prefer a combination of fiscal and monetary policy. Utilizing the strengths of each policy together is probably the wisest strategy. Opponents of Fiscal and Monetary Policy • Monetarists argue that demand-side policies only make matters worse. They believe government should focus on social priorities and change the money supply to match the rate at which economic growth is occurring. They also argue for policies that increase wage and price flexibility to allow the markets to more easily adapt to changing conditions.