* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 21
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
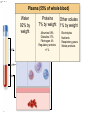
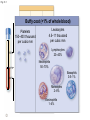
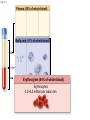
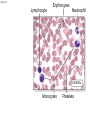
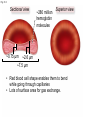
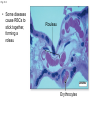
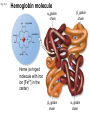
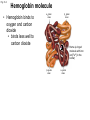
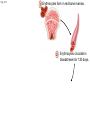
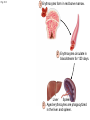
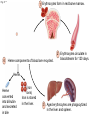
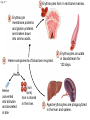
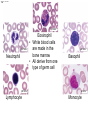
Click to edit Master title style CHAPTER 21 BLOOD 1 Fig. 21.1 Plasma (55% of whole blood) Water 92% by weight Whole blood 1 Withdraw blood into a syringe and place it into a glass centrifuge tube. Proteins Other solutes 7% by weight 1% by weight Albumins 58% Globulins 37% Fibrinogen 4% Regulatory proteins <1% Electrolytes Nutrients Respiratory gases Waste products Buffy coat (<1% of whole blood) Leukocytes Platelets 4.5–11 thousand 150–400 thousand per cubic mm 55% per cubic mm <1% Neutrophils 50–70% Lymphocytes 20–40% Centrifuge 44% Monocytes 2–8% Eosinophils Basophils 1–4% 0.5–1% Erythrocytes (44% of whole blood) Erythrocytes 4.2–6.2 million per cubic mm Formed elements 2 Place the tube into a centrifuge and 3 Components of blood separate during centrifugation to reveal plasma, buffy coat, and erythrocytes. spin for about 10 minutes. Fig. 21.1 Plasma (55% of whole blood) Water 92% by weight 55% <1% 44% Proteins 7% by weight Other solutes 1% by weight Albumins 58% Globulins 37% Fibrinogen 4% Regulatory proteins <1% Electrolytes Nutrients Respiratory gases Waste products Buffy Coat 4 Fig. 21.1 Buffy coat (<1% of whole blood) Platelets 150–400 thousand per cubic mm Leukocytes 4.5–11 thousand per cubic mm Lymphocytes 20–40% 55% <1% Neutrophils 50–70% Basophils 0.5–1% 44% Monocytes 2–8% Eosinophils 1–4% Fig. 21.1 Plasma (55% of whole blood) Buffy coat (<1% of whole blood) 55% <1% 44% Erythrocytes (44% of whole blood) Erythrocytes 4.2–6.2 million per cubic mm Fig. 21.2 Lymphocyte Erythrocytes Neutrophil LM 640x Monocytes Platelets Fig. 21.3 Sectional view ~0.75 µm ~280 million hemoglobin molecules Superior view ~2.6 µm ~7.5 µm • Red blood cell shape enables them to bend while going through capillaries • Lots of surface area for gas exchange. Fig. 21.3 • Some diseases cause RBCs to stick together, forming a roleau Rouleau LM 250x Erythrocytes Fig. 21.4 Hemoglobin molecule α2 globin chain H3C β1 globin chain CH2CH2COOH N CH2CH2COOH H2C=CH N Fe N H3C CH3 N H2C=CH CH3 Heme (a ringed molecule with iron ion [Fe2+] in the center) β2 globin chain α1 globin chain Fig. 21.4 Hemoglobin molecule • Hemoglobin binds to oxygen and carbon dioxide • binds less well to carbon dioxide α2 globin chain β1 globin chain Heme (a ringed molecule with iron ion [Fe2+] in the center) β2 globin chain α1 globin chain Fig. 21.5 1 Erythrocytes form in red bone marrow. Fig. 21.5 1 Erythrocytes form in red bone marrow. 2 Erythrocytes circulate in bloodstream for 120 days. Fig. 21.5 1 Erythrocytes form in red bone marrow. 2 Erythrocytes circulate in bloodstream for 120 days. Liver Spleen 3 Aged erythrocytes are phagocytized in the liver and spleen. Fig. 21.5 4 1 Erythrocytes form in red bone marrow. Heme components of blood are recycled. 2 Erythrocytes circulate in bloodstream for 120 days. Heme Heme converted into bilirubin. and secreted in bile (iron ions) Iron is stored in the liver. 3 Aged erythrocytes are phagocytized in the liver and spleen. Fig. 21.5 1 Erythrocytes form in red bone marrow. 5 Erythrocyte membrane proteins and globin proteins are broken down into amino acids. 4 Heme components of blood are recycled. 2 Erythrocytes circulate in bloodstream for 120 days. Heme Heme converted into bilirubin. and secreted in bile (iron ions) Iron is stored in the liver. 3 Aged erythrocytes are phagocytized in the liver and spleen. Table 21.3a LM 1600x LM 1600x Neutrophil LM 1600x Lymphocyte Eosinophil • White blood cells are made in the bone marrow • All derive from one type of germ cell LM 1600x Basophil LM 400x Monocyte Fig. 21.9 Platelets Fibrin Erythrocytes SEM 5000x • Platelets stick to injured blood vessel, create pile of platelets, begin clotting process • Fibrin collects over platelets and trapped erythrocytes, creates clot or scab