* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Food allergies and intolerances - here
Overeaters Anonymous wikipedia , lookup
Coeliac disease wikipedia , lookup
Food safety wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Food studies wikipedia , lookup
Gluten-free diet wikipedia , lookup
Food politics wikipedia , lookup
Food coloring wikipedia , lookup
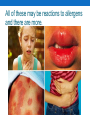
Food allergies and intolerances – module 1 Introduction to allergens and intolerances Welcome • Welcome to University of West London and the one day course on Food allergens and intolerances. • Timing of the course • Test and certificate • While you are here…… What this course is all about • To provide information and understanding about the 14 allergens identified in EU No. 1169 2011 which comes into force in December 2014. • The information applies to all hospitality and catering operations, and all staff working in the businesses. All staff need to be aware of allergen hazards, and how to reduce risk of harm. • Offering a full understanding of allergies and intolerances and how to manage these hazards in the business. • The course is divided into 4 areas with some Key Points and Revision at the end. Module 1 - Introduction 1. The risks that everyday foods can bring to your customers 2. What is an allergen? 3. What is an allergic reaction and its symptoms? 4. What is an intolerant? 5. What is food intolerance and its symptoms? 6. Understanding the responsibilities to your customer 14 foods or ingredients have been identified by EU Legislation as allergens • How many can you name? Analise • 5 year old Analise’s parents knew she reacted to some foods and avoided the main allergens. • They informed her new school of problems and provided her with an ‘allergen free’ lunchbox. • First day had a severe reaction due to sitting near a child eating a nut product. Jonathan • On a school trip where children were staying in a hostel with food provided. • Party leaders chose a vegetable pasta dish as suitable for everyone. • The vegetables were fried in an oil with some sesame content. • He had a severe and rapid reaction. Emily • 18 months old out on a riverside walk with her parents. Stopped at pub for lunch. • Barbeque pork sate was being cooked in the garden near to their table. • Rapid and severe reaction including difficulty with breathing. • She had never had a reaction to food before. All of these may be reactions to allergens and there are more. Dangers of allergens • Some people can have rapid and frightening reactions to certain ingredients and food. The reaction can prove to be fatal if not treated quickly. • This is not a common occurrence but very serious for the allergic person. • The allergy foods do not affect everyone. Good communication between the food provider and customer is essential. Reactions (Jonathan) • The party leader had checked there were no nuts in the dish being served • In the kitchen they had run out of the usual vegetable oil but the person doing the cooking saw another bottle of oil and used it. • It was an oil from various sources including sesame. • His reaction was rapid. Medication was applied quickly – otherwise he could have died. The 14 Allergens stated on 1169/2011. The identified allergens • An allergen a substance that can cause certain people to become seriously ill when they have contact with it. • People can react to all kinds of things including pollen, insect bites or stings and latex or rubber. Here we are only concerned with food allergens. The 14 Allergens stated on 1169/2011. Not always obvious • People who know that they have an allergy to certain foods or ingredients will avoid them but allergy ingredients can be hidden such as in Jonathan’s pasta dish. • Worcestershire sauce contains fish extracts, egg often listed on food labels as ‘emulsifier’ wheat flour used to keep black pepper free running. • Other examples……………………………………… • May contain • Not suitable for…. Allergen ingredient not in the food but may be present – why? The risks • Concerns because the risk of with a particular allergen is so great. A seafood restaurant cannot avoid shrimp contamination a Thai restaurant serving Satay dishes cannot avoid peanut contamination. • A "sensible" allergy sufferer is likely not to go to a restaurant specialising in dishes containing the allergen, but typically young people in groups do sometimes take risks. • You must always give the safest, most truthful advice at all times. Can you change an allergen in food? • There are some allergens that when cooked can become harmless to some sufferers but this is never certain so best not to take the risk. • When a customer says they are allergic to any food or ingredient do not serve it raw, processed or cooked. • If in doubt, never think that it will be all right. Don’t serve it! Tomato allergy • A medical professional told a woman with a tomato allergy it was all right to use bottled, processed bolognaise sauce to cook for her children. • However sauces vary between brands. She opened a glass jar with chunky tomato pieces, breathed the air from the jar and died in hospital four days later. This was a severe allergic reaction and clearly shows the importance of always giving accurate information. What is an Allergy? • Everyone has defence systems to protect from illness - the immune system. Immunity from illness is achieved either by having already had the disease or by vaccination which has saved many lives around the world. • Immunity is when the body has experienced the disease or a small sample by vaccination. The immune system fights it off and ‘remembers’ it for the future. Illness either does not occur or will be in a minor form. • A person with an allergy has come across the allergen but the body has not remembered it correctly so does not react properly and fights against itself; in the most severe cases shutting the whole body down and killing the person. • This type of reaction is called an anaphylactic shock. Reasons for allergy are still not fully understood but suggestions include: Some people in infancy experienced contact with peanut crumbs through the skin, because of skin being broken (as with eczema) triggering the wrong information in the immune system. Increased use of nuts and nut oils in processed foods affecting unborn babies and those in infancy Allergies can develop through life - much is still unknown. Generally there are no cures for allergies just avoidance of the allergens, medication to reduce the symptoms with hope that the body itself will change and so “correct” the immune system. Anaphylactic shock • The symptoms are severe, frightening and deadly if not treated. People at risk of anaphylactic shock will carry an adrenaline pen. (Called an EpiPen - it contains epinephrine, (adrenaline). • Adrenaline is used in heart failure to keep a person alive. The same applies here. • During an anaphylactic shock the blood pressure drops very low, and this will cause death. There is urgent need for adrenaline from the EpiPen, and urgent hospital treatment. How do they feel? • It may start with just an itchy throat and a tingling on the • • • • lips then the swelling and red rash, called uritica. The soft tissue of nose, throat and lips swell which can restrict airways Sufferers feel a sense of impending doom –that they feel that they are going to die. Very frightening alarming for sufferer and those around them. This all happens very quickly. Managing Allergies • Not all reactions are as severe as described, but they will make people very ill, and sometimes it can take time, even hours after the person has left the restaurant. • Food allergies are increasing and especially in children, it is estimated that close to 7 per cent of all children suffer from at least one allergy. • Medical science is still working on the reasons why there is an increase in allergies. • Now more awareness of allergy. Diagnosis is better so ability to identify more allergy sufferers and manage the dangers. Just to confuse matters! • Not everyone with a reaction to certain foods has a true ALLERGY. • Sometimes it is an INTOLERANCE which causes a different kind of reaction. What is an Intolerant? • An intolerant causes a different type of reaction in digestive system • It sometimes goes wrong and the digestive system fails to process food properly, illness results because the foods are not being broken down properly. • Worse - nutrition is not being taken from the food which can result in serious illness rather like starving to death but not feeling hungry. • The body’s reacts with symptoms such as, diarrhoea, wind and severe cramps so a different type of reaction to allergy. More about intolerants • Intolerants, tend to be grouped together with Allergens when providing food for customers. Both must be totally excluded from the guest’s meal. • Both allergens and intolerants must be considered as hazards! • Two kinds intolerances will be considered one caused by milk - lactose intolerance, and the second caused by gluten, found in flour, called coeliac disease. Intolerances – Lactose intolerance • Lactose intolerance - inability to digest the sugar in milk and milk products. • About 10,000 years ago domestication of cattle began so that we could drink their milk. Gradually, evolution favoured those people who continued to drink milk and consume milk products such as cheese. • Most people continue to produce the enzyme lactase, enjoying eating cheese and drinking milk. Yet some people still do not produce lactase so become ill when they have any milk product.. Apart from milk itself how many products are made from or contain milk? Intolerances - Coeliac Disease • Gluten - two combined proteins in flour, that react with the digestive system to cause inflammation, swelling, discomfort and diarrhoea. The intestine fails to absorb vital nutrients from the food. • Coeliac disease is complex because food is absorbed by the villi, small protrusions on the inside wall of the intestine. These villi are shrunk by the reaction and cannot absorb food in the normal way. • Person starts to suffer from malnutrition, so must avoid all food that contains gluten even in small amounts. Difficulties with Coeliac disease • With gluten in all common flours a wide range of foods must be avoided, bread, all pastries, pasta. • All these foods can be prepared from alternative, gluten free flour. It is important to recognise which are gluten free foods and food containing gluten. • It is essential that these foods are properly labelled and stored separately so that no confusion occurs. The food provider’s responsibility • As a food professional it is your responsibility, to know all the foods and ingredients in your kitchen that contain milk and gluten, so you can safely serve your customers suffering with either coeliac disease or lactose intolerance. • The letters GF beside a menu item means that it is gluten free? Allergies and Intolerances • Knowing the differences between allergies and intolerances it will help you to understand and communicate with your customer. • These fairly common diseases related to food show that it is vital for you to communicate well with your customer and a little understanding will go a long way. Key Points and Revision 1. Allergies can be fatal; therefore a person with an allergy must never come into contact with the particular allergen. 2. An anaphylactic shock is where a person’s body literally closes down, going towards death. 3. Allergens are the food items that cause an allergic reaction, many of which may be small ingredients in processed foods; these are known as "hidden allergens". 4. Allergies are the result of a failure of the immune system, which normally protects the body from disease and infection. The immune is turned against the body by having the wrong reaction to the allergen. 5. An intolerance is a fault of the digestive system, which causes serious discomfort, and in certain cases malnutrition. Key Points and Revision cont. 6. Allergens and intolerants must be equally treated as hazards and therefore extreme care must be taken when preparing food for any guest with either intolerance or an allergy. 7. The slightest contamination of a sufferer’s meal will have the most serious of consequences. 8. More children are being diagnosed with allergies each year. Therefore those working with the young need to ensure the strictest allergen control in daily working practice. 9. The final and important point is that if you feel that it is not safe to serve a customer you must politely tell them so. Remember stay safe – stay legal