* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11.2 Notes
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
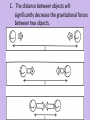
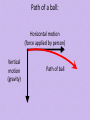
Bellringer/11.2 Notes Recall that weight is defined as a measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object. Use knowledge you have about gravity to answer the questions in the following situations: 1. Elvis is a student whose mass is 70 kg. On Earth’s surface, Elvis weighs about 690 N. Suppose Elvis could stand on the surface of the following bodies in the solar systems. Match Elvis’ weight with the letter of the appropriate body. (Note that Earth has a mass of 6.0 x 1024 kg.) Planet a. Jupiter (m = 1.9 x 1027 kg) b. Venus (m = 4.9 x 1024 kg) c. Neptune (m = 1.0 x 1026 kg) d. Mercury (m = 3.3 x 1023 kg) e. Earth’s moon (m = 7.4 x 1022 kg) 2. Elvis’ weight 780 N 113 N 260 N 1800 N 620 N Suppose Elvis is in orbit around Venus at a distance twice as far from the planet’s center as the surface of Venus is. Would you expect his weight to be greater than, less than, or equal to his weight on the surface of the planet? Section 2 Gravity I. Law of Universal Gravity A. The gravitational force exerted by objects is related to: 1. Distance between the objects 2. Size of their masses B. Gravitational force increase as mass increases Since the moon is smaller than Earth, the gravitational force placed on objects on the moon is much less. C. The distance between objects will significantly decrease the gravitational forces between two objects. II. Free Fall and Weight A. In the absence of air resistance, all objects fall at the same rate: B. On Earth, free-fall acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8m/s2. 1. Force of gravity on an object = weight. Example: My weight in Newtons 72.5 kg x 9.8 m/s2 = 710 N C. Mass and weight are not equal. On the moon, gravity is about 1.6 m/s2. 1. Even on Earth, the gravitational force can change On Earth at sea level g = 9.8 m/s2 Weight = 72.5 kg x 9.8 m/s2 = 710 N (159.6 pounds) On Earth atop a high mountain g = 9.78 m/s2 Weight = 72.5 kg x 9.78 m/s2 = 709.5 N (159.5 pounds) D. Terminal Velocity – Air resistance = Gravity Unbalanced + Acceleration Unbalanced + Acceleration Unbalanced + Acceleration Balanced 0 Acceleration E. Free fall only occurs when gravity is the only force acting on an object (in space). III. Projectile Motion and Gravity A. Projectile Motion – curved path an object takes due to: 1. Horizontal motion 2. Vertical motion Path of a ball: Horizontal motion (force applied by person) Vertical motion (gravity) Path of ball