* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Persian Wars 2016
Pontic Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
List of oracular statements from Delphi wikipedia , lookup
First Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
Ionian Revolt wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Eurymedon wikipedia , lookup
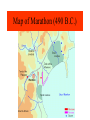
The Persian Wars Maps and Pictures Cyrus conquers Lydia Persian Rule • How did the Persians rule the cities? – They appointed local aristocrats as tyrants under the supervision of the Persian satraps. • When was the Ionian revolt and what was the result? – 499-494 BC – The Persians squashed the revolt. The Empire of Darius (490 BC) Persian Empire 490 B.C. Darius invades Greece • Why did King Darius I attack Athens? – To punish it for sending a [small] fleet to assist the Ionian rebels. • What was the result of his invasion (what, where, when, by whom)? – He was defeated at Marathon in 490 BC by the Athenian hoplites under Miltiades. • What was Sparta’s role in the Ionian revolt and the battle of Marathon? – None. Persian War Events Miltiades Athenian victor at Marathon Map of Marathon (490 B.C.) Greek Hoplite The Greek Phalanx Persian Warrior Dariac The Plain of Marathon Today The Battle of Marathon Burial Mound at Marathon Xerxes Invades Greece • How and when did Xerxes respond to his father’s defeat? – He attacked Greece in 480 BC. • Why did he take this action? – He believed it was necessary to subjugate the free Greeks of the Greek mainland in order to secure his control over western Asia Minor. • How did his invasion route differ from Darius’ route? – Darius’ army sailed directly across the Aegean Sea while Xerxes led his army along the coast with the fleet sailing along side it to provision it. Xerxes’ Invasion Route Xerxes Xerxes’ Canal at Athos Thermopylae • What happened at Thermopylae and when? – In 480 BC the Spartan king Leonidas sacrificed himself and 300 of his men to delay the Persians. Though they were all killed, their valiant effort inspired the Greeks. • What happened to Athens after Thermopylae? – The Athenians evacuated their city and took refuge on the island of Salamis. Xerxes destroyed Athens. King Leonidas (Spartan king at Thermopylae) The Battle of Thermopylae Thermopylae Today Thermopylae – the Anopaea Persian Arrowheads from Thermopylae The Spartans’ Last Stand Plaque Memorializing the Spartan’s Last Stand at Thermopylae ‘Go tell the Spartans, stranger passing by, that here, obedient to their laws, we lie.’ - Poet Simonides (c. 556-469 BC) Themistocles Athenian victor at Salamis • What was Themistocles’ advice and how was his plan funded? – He advised the Athenians to build a large navy with the silver discovered at Laurium in southern Attica. • What happened at Salamis? – The Athenians and their allies defeated the Persian fleet in the bay of Salamis. The Battle of Salamis Greek Trireme Air View of Salamis Today Pausanius Spartan victor at Plataea • What happened at Plataea and when? – In 479 BC the Greeks, under Spartan leadership, defeated the Persian army. • What subsequent actions did Athens take after the defeat of the Persians? – The Athenian fleet liberated the Greek cities along the coast of Asia Minor. The Battle of Plataea Plataea Today The legacy of the Persian wars • The battles inspired the Greeks for many years. • In Europe, they later came to represent the triumph of free Greek states (western freedom) over Asia (eastern despotism). • This saved Greek culture, the source of Western civilization. That’s all folks