* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download semi-conductors-16
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Carbon nanotubes in photovoltaics wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Negative-feedback amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
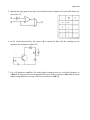
Page 1 of 6 CBSE CLASS 12 PHYSICS – Semiconductor Physics: Test Name: School: Max. Score: 35 Duration: 60 min Batch: 1. In a transistor, the doping level is slightly increased. How will affect the (a) collector current and (b) base current? (2) 2. How will the collector current change if the base is widened? (1) 3. Sn, C, Si and Ge are in the same group (14th). Yet only Si and Ge are considered semiconductors. Explain. (2) 4. Zener diodes have high dopant densities. What effect does it have on the (a) depletion layer and (b) junction field? Draw the circuit for a Zener diode as an voltage regulator. (2) Page 2 of 6 5. Identify the logic gates in the logic circuit shown below. Complete the truth table below for the circuit. (3) 6. In the circuit shown below, the resistor R1 is increased. How will the readings on the ammeter and voltmeter change? (2) 7. For a CE-transistor amplifier, the audio signal voltage across the collected resistance of 2 kΩ is 2 V. Suppose the current amplification factor of the transistor is 100, find the input signal voltage and base current, if the base resistance is 1 kΩ. (2) Page 3 of 6 8. Construct AND, OR and NOT gates using NAND gates only. (3) 9. The figure shows the I – V characteristics of a PN diode. Determine the dc and ac resistances of the diode when it operates at 0.3 V. (2) Page 4 of 6 10. A semiconductor has equal electron and hole concentration of 2 x 108 m-3. On doping with a certain impurity, the hole concentration increases to 4 x 1010 m-3. (2) (a) What type of semiconductor is obtained by this type of doping? (b) Calculate the electron concentration after doping. (c) How does the energy gap change as a result of this doping? 11. A semiconductor has electron and hole concentrations as 0.45 x 1012 m-3 and 5 x 1020 m-3 respectively. Determine its conductivity if: hole mobility = 0.048 m2V-1s-1; electron mobility = 0.135 m2V-1s-1; electron charge = 1.6 x 10-19 C. (2) Page 5 of 6 12. What is an amplifier? Explain the action of a NPN transistor amplifier in the CE mode. Does an amplifier violate energy conservation? Draw the frequency response curve of (a) practical transistor amplifier and (b) ideal amplifier. Two amplifiers are connected one after the other in series (cascaded). The first amplifier has a voltage gain of 10 and the second has a voltage gain of 20. If the input signal is 0.01 volt, calculate the output ac signal. (6) Page 6 of 6 13. A square wave (-1 V to +1 V) is applied across a PN junction diode. Draw the output waveform across the diode assuming the diode to be ideal. (1) 14. In the circuit below, a source of 2 V is connected. Determine the currents that may be drawn from the source. 15. Suggest suitable materials for solar cells. (1) 16. Identify the type of transistor shown in the figure below. Is the transistor properly biased? (2)