* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
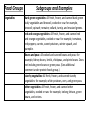
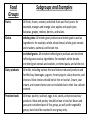
Nutrition Healthy Diet, Nutrients & Hydration THE FACTS • The amount and kinds of food you eat affect your health and wellness. • Poor nutrition increases risks for numerous diseases. • Proper nutrition enhances the quality of life. • Applying good nutrition principles is challenging. Science of Nutrition Examines food, level of nutrients and other chemicals in foods, and how they are used in the body. Diet: Total intake of food and beverages consumed. Healthy Diet • A healthy balanced diet is one that includes all the food groups. – Fruits – Vegetables – Grains – Proteins – Dairy (Sketch the MyPlate diagram on your output page) Healthy Diet: what you can do? • Increase vegetable and fruit intake. • Consume at least half of all grains as whole grains. • Increase intake of fat-free or low-fat milk and milk products, such as milk, yogurt, cheese, or fortified soy beverages. • Choose a variety of protein foods, which include seafood, lean meat and poultry, eggs, beans and peas, soy products, and unsalted nuts and seeds. • Use oils to replace solid fats where possible. • Choose foods that provide more potassium, dietary fiber, calcium, and vitamin D. These foods include vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and milk and milk products. Nutrients • Nutrients are the essential substances that we get from our food. They are what the body needs to perform its daily functions properly. Proteins Carbohydrates Fats Vitamins Minerals Water Proteins o o o o Assist in growth Repair body cells Found in animal products Proteins are made of amino acids Carbohydrates (Carbs) • 2 types – simple (sugars) and complex (starches) • Provide the main source of energy for the human body • Found in breads, cereals, rice and potatoes Fats Unsaturated Fats • Come from fish and plant products • Healthier of the fats Saturated Fats • Come from dairy products, solid vegetable fat, meat and poultry • Hardens at room temperature • “bad” fats Vitamins • Needed daily • 13 different vitamins • Control chemical processes in the body Minerals • Needed for growth and maintenance • Involved in many of the body’s activities • Iron, calcium and potassium are all minerals Water • • • • Regulates body temperature Helps eliminate waste Necessary for cells and organs to function normally At least 8 glasses per day Calories • A calorie is a unit of energy. Calories refer to energy consumption through eating and drinking and energy usage through physical activity. • The number of calories foods contain tells us how much potential energy they posses. Below are the calorific values of the three main components of the food we eat: • 1 gram of carbohydrates contains 4 calories • 1 gram of protein contains 4 calories • 1 gram of fat contains 9 calories Calories and You • Kids come in all sizes and each person's body burns energy (calories) at different rates, so there isn't one perfect number of calories that a kid should eat. But there is a recommended range for most school-age kids: 1,600 to 2,500 per day. • When they reach puberty, girls need more calories than before but they tend to need fewer calories than boys. As boys enter puberty, they will need as many as 2,500 to 3,000 calories per day. But whether they are girls or boys, kids who are active and move around a lot will need more calories than kids who don't. Hydration • Hydration: Students need to drink 8 tall glasses of water daily in addition to consuming other fluids like soda or juice. • Pre-hydrate: drink plenty of water beginning the day before any significant activity. • Hydrate: get drinks during activity. • Post hydrate: after the activity drink plenty of water. If possible, also drink a watered down sports drink (like Gatorade or Powerade) to help restore electrolytes. Poor Hydration • Stay away from caffeinated and high sugar beverages, both are known to dehydrate your cells. • By not consuming enough water daily (even with a lack of activity) your blood thickens and you feel fatigued. • Not drinking enough water and exercising outdoors can cause signs of heat illness. • The following two slides are informational… Food Groups Vegetables Subgroups and Examples dark-green vegetables: All fresh, frozen, and canned dark-green leafy vegetables and broccoli, cooked or raw: for example, broccoli; spinach; romaine; collard, turnip, and mustard greens. red and orange vegetables: All fresh, frozen, and canned red and orange vegetables, cooked or raw: for example, tomatoes, red peppers, carrots, sweet potatoes, winter squash, and pumpkin. Beans and peas: All cooked and canned beans and peas: for example, kidney beans, lentils, chickpeas, and pinto beans. Does not include green beans or green peas. (See additional comment under protein foods group.) starchy vegetables: All fresh, frozen, and canned starchy vegetables: for example, white potatoes, corn, and green peas. other vegetables: All fresh, frozen, and canned other vegetables, cooked or raw: for example, iceberg lettuce, green beans, and onions. Food Groups Subgroups and Examples Fruits All fresh, frozen, canned, and dried fruits and fruit juices: for example, oranges and orange juice, apples and apple juice, bananas, grapes, melons, berries, and raisins. Grains whole grains: All whole-grain products and whole grains used as ingredients: for example, whole-wheat bread, whole-grain cereals and crackers, oatmeal, and brown rice. enriched grains: All enriched refined-grain products and enriched refined grains used as ingredients: for example, white breads, enriched grain cereals and crackers, enriched pasta, and white rice. Dairy products All milks, including lactose-free and lactose-reduced products and fortified soy beverages; yogurts; frozen yogurts; dairy desserts; and cheeses. Most choices should be fat-free or low-fat. Cream, sour cream, and cream cheese are not included due to their low calcium content. Proteins foods All meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, nuts, seeds, and processed soy products. Meat and poultry should be lean or low-fat. Beans and peas are considered part of this group, as well as the vegetable group, but should be counted in one group only.