* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Dietary fiber wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Calorie restriction wikipedia , lookup
Childhood obesity in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
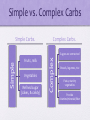
Nutrition What is nutrition? • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TTh93TuU Eck • Food; nourishment What are nutrients? • A substance that provides nourishment, essential for growth and the maintenance of life. 6 Classes of Nutrients • Carbs • Fats • Proteins • Vitamins • Minerals • Water Carbohydrates • 1 gram = 4 calories • Energy giving nutrients that include • Sugars, starches, and fiber • Sugars: simplest form of carbohydrates • Starches: more complex & can be broken down into sugar. • Fiber: complex carb that provides help for a healthy digestion. Fiber • Soluble – dissolves in water to help trap cholesterol. • Insoluble – does not dissolve in water, but helps with digestion. Starches • Complex and must be broken down by the body into sugar. • Plant foods (potatoes, beans, peas, rice, corn, wheat) Simple vs. Complex Carbs Simple Carbs. Complex Carbs. Fruits, milk Vegetables Refined sugar (cakes, & candy) Complex Simple Sugars are connected Breads, legumes, rice Pasta, starchy vegetables Provide vitamins/minerals/fiber Fats • 1 gram = 9 calories • 25-35% should be of your diet • Long term energy sources • 3 types • Saturated Fats, Unsaturated fats, and Trans Fats FATS SATURATED FATS UNSATURATED FATS TRANS FAT • SOLID @ ROOM TEMP. • COME FROM FOODS SUCH AS MEAT & MILK. • TOO MUCH LEADS TO: - OBESITY, HIGH CHOLESTEROL, & INCREASE RISK OF HEART DISEASE. • LIQUID @ ROOM TEMP. • COME FROM FOODS SUCH AS OILS & FISH. • UNHEALTHY SUBSTANCE MADE THROUGH THE CHEMICAL PROCESS OF HYDROGENATION OF OILS. • FOOD IN FRIED FOODS, COMMERICAL BAKED GOODS, PROCESSED FOODS, & MARGINE. Fats Use • Body use it for • Energy, insulation, padding for organs, carry fat soluble vitamins, hormones, growth, skin. Cholesterol • Found in all animal tissues (you and the animal products you eat) • LDL = bad cholesterol • HDL = good cholesterol Proteins • 1 gram = 4 calories • 3 types: • Essential amino acids – 9 amino acids the body can’t produce on it’s on • Complete proteins – contain all essential amino acids • Incomplete proteins – do not contain the essential amino acids Use of Protein • Protein in the body used for • • • • • Body building Build & repair tissue Hormones, enzymes, antibodies Energy Excess stores as fat Metabolism • Sum of the chemical processes that take place in your body to keep you alive & active. • Requires energy from carbs., fats, and proteins Calories • How energy in food is measured • FYI: it takes ~ 3500 calories below your calorie needs to lose a pound of body fat. And ~ 3500 calories above your calorie needs to gain a pound of body fat. Calories Needed Boys Average Calorie Needs Each Day • 11-14 years : 2500 calories • 15-18 years: 3000 calories Girls Average Calorie Needs Each Day • 11-14 years: 2200 Calories • 15-18 years: 2200 Calories