* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monetary Policy and the Interest Rate
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Inflation targeting wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Okishio's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative easing wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
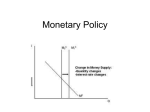
Inflation, Unemployment, and Stabilization Policies: Monetary Policy and the Interest Rate AP Economics Mr. Bordelon Monetary Policy and the Interest Rate Monetary Policy and the Interest Rate Use the money market model to explain how the Fed uses monetary policy to stabilize the economy in the short run. Remember, this is the nominal interest rate here. Fed increases MS through openmarket operations to buy T-bills from large commercial banks. The increase in MS causes nominal interest rates to decrease. Monetary Policy and the Interest Rate Fed decreases MS through open market operations, selling T-bills to large commercial banks. Decrease in MS causes nominal interest rates to increase. Monetary Policy and the Interest Rate The Fed adjusts the money supply to target a specific federal funds rate. If current federal funds rate is higher than target, Fed will increase MS so that rate decreases to target. If current federal funds rate is lower than target, Fed will decrease MS so that rate increases to target. Expansionary and Contractionary Monetary Policy Investment spending is sensitive to changes in the interest rate. When interest rates decrease, investment spending increases. Some types of consumption spending also increases when the interest rates decrease (car/truck buying, college educations, real estate). Investment spending and consumption spending are important components of AD. When interest rate decreases, AD should increase. Expansionary and Contractionary Monetary Policy Expansionary Monetary Policy Fed sees the economy is in a recessionary gap. Fed increases MS. Interest rate decreases. Investment and consumption increase. AD increases (shifts right). Real GDP increases, unemployment rate decreases, APL increases. Expansionary and Contractionary Monetary Policy Contractionary Monetary Policy Fed sees the economy is in an inflationary gap. Fed decreases MS. Interest rate increases. Investment and consumption decrease. AD decreases (shifts left). Real GDP decreases, unemployment rate increases, APL decreases. Question 1 Suppose the economy is currently suffering from a very high rate of inflation caused by aggregate demand that has increased beyond potential GDP. In a correctly labeled graph, show equilibrium in the money market. In a correctly labeled AD/AS graph, show the current short-run equilibrium in the macroeconomy. In response to this high inflation rate, should the Fed engage in expansionary or contractionary fiscal policy? In your graph from the first part, show the impact of this monetary policy in the money market and on the equilibrium interest rate. In your graph from the second part, show the impact of this monetary policy on real GDP and the price level.