* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BI Session-SQL_Server_Analysis_Services
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
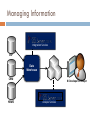
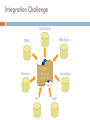
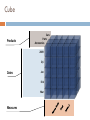
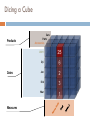
SQL Server Analysis Services ……………………………………………………………………………………… Khalid Abu Qtaish Sr. BI Consultant / Solution Designer KhalidBI.wordpress.com [email protected] Analysis Services Agenda Introduction ETL OLAP Terms Storage Modes Queries (MDX) Tools Live Demo Q&A SQL Server 2008 R2 BI Platform Introduction Analysis Services provides access to large data sets Running SQL queries against a 100 million row table just doesn’t work When your data sets get large, you need a better way of handling the load Online analytical processing (OLAP) provides all your answers with speed! Analysis services is an OLAP implementation Integration & Structure Managing Information Integration Services ERP Data Warehouse CRM HRMS BI Developer or Analyst Analysis Services ETL The Extract, Transform and Load (ETL) process is vital to the OLAP results If you input junk, you get junk back out! All data that enters the OLAP database must be valid or your results could be exponentially wrong! Make sure that all possible means are employed when ensuring only valid data is entered into the system and that it is entered only once! Common issue is data inserted more than once which causes invalid results ETL ETL Integration Challenge Call Center Web Apps CRM Finance Inventory Data Warehouse HR ERP Source Systems Process real-time transactions Optimized for data modifications Normalized Limited decision support Commonly called: Online transaction processing (OLTP) systems Operational systems HR Finance Inventory Data Warehouse Provides data for business analysis Grouped in subject-specific stores called Data Marts Optimized for rapid ad-hoc information retrieval Integrates heterogeneous source systems Consistent historical data store Star Schema Star Schema Benefits Simple, not-so-normalized model High-performance queries Especially with Star Join Query Optimization Mature and widely supported Low-maintenance OLAP Terms Data Source View Diagrams of star schemas – state cube, perf cube Dimensions Describe business entities Contain attributes that provide context to numerical data Present data organised into hierarchies Fact Table Fundamentals Collection of measurements associated with a specific business process Specific column types Foreign keys to dimensions Measures – numeric and additive Metadata and lineage Consistent granularity – the most atomic level by which the facts can be defined Cube (UDM) Unified Dimensional Model Combination of measures (from facts) and dimensions as one conceptual model Rich data model enhanced by Calculations Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Actions Perspectives Translations Partitions Formally, cube is called a UDM Cube Products Cars Parts Accessories 2009 Q1 Dates Jan Feb Mar Measures Dicing a Cube Products Cars Parts Accessories 2009 Q1 Dates Jan Feb Mar Measures Conceptual Terms Hierarchies Benefits View of data at different levels of summarization Path to drill down or drill up Implementation Denormalized star schema dimension Normalized snowflake dimension Self-referencing relationship Dimension Relationships Define interaction between dimensions and measure groups Relationship types Regular Reference Fact (Degenerate) Many-to-many Data mining Measure Group Group of measures with same dimensionality Analogous to a fact table Cube can contain more than one measure group E.g. Sales, Inventory, Finance Defined by dimension relationships Calculations Expressions evaluated at query time for values that cannot be stored in fact table Types of calculations Calculated members Named sets Scoped assignments Calculations are defined using MDX Time and Date Dimensions Calendar dates and hours of day, with separate attributes for time-folded analysis (values by hour for the past week, for example) • • • Date by Month (Year, Quarter, Month, Date) Date by Week (Year, Week, Date) Time (Hours, in 12 hour or 24 hour format) Period Calculations A dimension that contains dynamic, time-based calculations • Month-to-date • Quarter-to-date • Year-to-date • Prior Period • Year-to-date, Prior Year • Percentage change Parent-Child Hierarchy A dimension that contains a parent attribute A parent attribute describes a self-referencing relationship, or a self-join, within a dimension table Common examples Organizational charts General Ledger structures Bill of Materials Parent-Child Hierarchy Example Brian Amy Stacia Shu Stephen Syed Michael José Peter Slowly Changing Dimensions Maintain historical context as dimension data changes Three common ways (there are more): Type 1: Overwrite the existing dimension record Type 2: Insert a new ‘versioned’ dimension record Type 3: Track limited history with attributes Key Performance Indicators (KPI) KPIs are used to show very simply whether a target is being accomplished Components include the Goal, Value, Status, and Trend Example: Sales and Quality targets Analysis Services allows you to build MDX expressions off of Cube data to build KPIs KPI values can be queried from client applications Allows for visual display of meaningful data Actions Actions Allows client application users to be able to interact with what the data means Example: Browse to a customer or product via URL Types of Actions: CommandLine, DataSet, Drillthrough, Html, Custom, Report, URL Define and assign to objects in the Cube Perspectives Perspectives work similar to views in a relational database Shows different users the data they need to see for a particular role they may be in Used to reduce complexity of cube data Not meant to be security mechanism for data Storage Modes Data in an Analysis Services database is stored differently than a relational database Partition Optimized storage provides the OLAP query performance MOLAP – multidimensional OLAP (fact data and aggregations are stored in special format) ROLAP – Relational OLAP (fact data and aggregations remain in relational database) HOLAP – Hybrid OLAP (fact data is relational, aggregations are stored in special format) Dimension (dimension attributes only) MOLAP – stored in special format ROLAP – stay in relational format Querying Cubes SQL is not used in OLAP databases MDX (multidimensional queries) is used for querying cubes DMX (Data Mining queries) is used for querying data mining models MDX Queries Multidimensional Expressions (MDX) are used to query multidimensional data Some common terms are: Cell – the space at an intersection of a measure and attribute Tuple – a unique cell based on a set of attribute members Set – an order set of tuples with same dimensionality T-SQL & MDX I need to determine which month had the highest sales, then look at the products and customers that made that month so good Calculated Members and Named Sets Calculated Members are used when you need to determine something at query time Can be query or session scoped Value are only stored in memory not on disk Named Sets are basically predefined MDX queries that can be reused in other queries Used to group dimension members Partitioning Mechanism to break up large cube into manageable chunks Partitions can be added, processed, deleted independently Update to last month’s data does not affect prior months’ partitions Sliding window scenario easy to implement E.g. 24 month window Partitions can have different storage settings add June 2006 partition and delete June 2004 What could go wrong? Cubes really are simple things to build and utilize As simple as they are, it is easy to create a cube that has the wrong data Always validate that the data that is displayed in the Cube is valid and accurate Never hurts to be overly aggressive when testing Cube data Tools Business Intelligence Development Studio BI Studio is just Visual Studio with project templates installed Project templates provide item templates and wizards New 2008 Wizards are much easier to use and more powerful Context sensitive functionality keeps toolbars and menus trimmed to what elements you need based on what you are looking at Because it is Visual Studio it is fully customizable 3rd party add-ons can make it even more powerful Designing an Analysis Services Database BI Studio will be used to create new AS Databases Steps include: Define data source Define data view Create a new cube Define fact tables Define dimensions (data and time) Define measures Aggregate/Run the cube SSAS 2008 R2 New Features Develop solutions quickly with the new, streamlined Cube Designer Take advantage of enhanced Dimension and Aggregation Designers Create attribute relationships easily by using the new Attribute Relationship Designer Avoid common design problems by using best practice Enable high-performance “what if” scenarios by using MOLAP enabled write-back Take advantage of enhanced data mining structures and improved Time Series support Monitor and optimize analytical solutions by using Analysis Live Demo SQL Server Analysis Services Q&A SQL Server Analysis Services