* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Always on HA - TechNet Gallery
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Tandem Computers wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
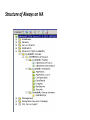
Always on HA • SQL Server Always ON feature is the new comprehensive high availability and disaster recovery solution which increases application availability. Always ON provides availability at either the application database or instance level. • Features Multiple database failover Multiple secondaries (conceptwise similar to a Mirror in Database Mirroring), at the max 4 secondaries are allowed Data movement can be synchronous and asynchronous For additional data protection there is support for two synchronous secondaries. Manual, Automatic and Forced Failover Flexible policy for failover Automated Page Repair Active Secondary Readable secondary Secondary backup Automatic redirection of application using virtual name SSMS for SQL 2012 Structure of Always on HA • An availability group is a collection of databases which behave as a single unit. During a Failover, even if one of the databases fails then it affects all the databases and hence the whole Availability Group will fail. Structure of Always on HA Structure of Always on HA AG Listener: Availability Group Listener provides client connectivity to the database of given Available Group. Listener is a virtual network name to which client connects to the database in the Availability Groups. A Listener enables a client to connect to an availability replica without knowing the name of the physical instance of SQL Server to which the client is connecting. Availability Replica Roles: The Availability Replicas are the database replicas which can reside in the Availability groups. For a single database there can exist a maximum of 4 replicas. When one replica is made Primary the other replicas are considered as Secondary and can be used as database back up. One availability group can own one replica at a time. Data Synchronization mode: The Data Synchronization mode is the mode of data replication between the Primary & Secondary Replicas. The data replication can be in Synchronous and Asynchronous Mode. Synchronous commit: In Synchronous Commit mode, when a transaction/data hits the primary replica then it is reflected in the Secondary replica as well in same time interval. The Secondary replica then sends a Check point and only then the Transaction is committed in both the Primary & Secondary Replicas. Output is in synchronous with input which means it occurs at the same time. The Synchronous commit data replication is applicable for maximum of two replicas. Asynchronous commit: In Asynchronous Commit mode, when a transaction/data hits the primary replica then it is reflected in the Secondary replica as well in same time interval. The transaction is committed as soon as the Primary replica sends a check point. The Synchronous commit data replication is applicable for maximum of four replicas. Connection Mode in Secondary: The connection mode is set for the Secondary replicas present in the Availability Groups. Allow all connections, Allow only Read-Only connections, Disallow all connections are the different types of connections. The Client connectivity towards the Secondary replicas is determined by the type of Connection Mode. Failover Modes: Always ON feature in SQL Server 2012 gives a choice of two types of Failovers. This feature operates on Automatic and Manual Failover. Automatic Failover: An Automatic Failover causes a Synchronized available Secondary Replica to transit to a Primary Role without Data Loss after a Failover in the Primary Replica and the Primary Replica transits to a Secondary Role. The Primary & Secondary Replicas should mandatorily be in Synchronized commit mode. Manual Failover: Manual Failover can also be called as Planned Manual Failover. If the Failover is done on the Secondary replica forcefully, then it becomes a Manual Failover. In this Scenario the Secondary replica on which the Failover has been performed performs Primary role and the Primary replica performs a Secondary Role. The Primary & Secondary Replicas should mandatorily be in Synchronized commit mode. Always ON Architecture Availability Group Failover: The Client connects to the Primary replica SQL – AG1 through Availability Group Listener. The SQL – AG1 is Primary and SQL – AG2 & SQL – AG3 Servers are Secondary. When a failover is initiated the SQL – AG1 notifies the database administrator and SQL – AG1 goes offline. And then the client disconnects from the AG1. The Availability Group Listener moves to the next available replica SQL – AG2 [refer above fig]. The Client is automatically connected to the SQL- AG2 availability group through Availability Group Listener. At this point the SQL – AG1 becomes Secondary & SQL – AG2 becomes the Primary replica. The SQL – AG3 remains secondary and the Synchronization among all the Replicas resumes. SQL Server 2012 Always ON feature offers High Availability & Disaster Recovery The Availability Groups enhances the capability of database mirroring. Multiple database coordination during Failovers and Simplified application connectivity. Synchronous and Asynchronous data movement along primary and secondary replicas. Automatic & manual failover modes with configurable failover trigger levels. Ability to read from Secondary replicas and can be used as Back up. Availability Dashboard for monitoring the health of Availability Groups.