* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GRADE 10 SA2 PHYSICS revision worksheet-2
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Dispersion staining wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Image intensifier wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Schneider Kreuznach wikipedia , lookup
Refractive index wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Reflecting telescope wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
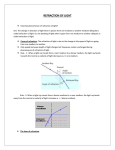
BUDS PUBLIC SCHOOL, DUBAI NAME: REVISION WORKSHEET -2 PHYSICS GRADE-10 LIGHT- REFLECTIONS AND REFRACTION 1. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of a three times magnified (i) real image, (ii) virtual image of an object kept in front of a converging lens. Mark the position of object, F, 2F, O and position of image clearly in the diagram. B. An object of size 5 cm is kept at a distance of 25 cm from the optical centre of converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Calculate the distance of the image from the lens and size of the image 2. (a) Draw a ray diagram showing the path of a ray of light when it enters with oblique incidence (i) from air into water (ii) from water into air (b) Under what condition in an arrangement of two plane mirrors, incident ray and reflected ray will always be parallel to each other, whatever may be the angle of incident. Show the same with the help of diagram. 3. (a) What is refraction of light? Give an expression to relate the absolute refractive index of a medium with speed of light in vacuum. (b) The refractive index of water and glass with respect to air are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 x 108 ms-1, then find the speed of light in (i) air, (ii) water. 4. (a) It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 20cm. (i) At what should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? (ii) Will the image be bigger or smaller than the object? (iii) Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (b) One half of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm covered with a black paper. (i) Will the lens produce a complete image of the object? (ii) Show the formation of image of an object placed at 2F1 of such covered lens with the help of a ray diagram. (iii) How will the intensity of image formed by half-covered lens compare with non-covered lens? 5. How can you distinguish between a plane mirror, a convex mirror and a concave mirror, just by looking at the image formed by them. (b) The lens prescribed by the doctor has a power equal to +2.0 D. What does it mean? (c) What would be the approximate focal length of a spherical lens preferred to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary? 6. (a) A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as well as real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall be the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images? (b) Light enters from air to glass having refractive index 1.50. What is the speed of light in glass? [The speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 ms-1] 7. (a) “A ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab immersed in any medium emerges parallel to itself.” Draw labelled ray diagram to justify the statement. (b) Mention the types of mirrors used as (i) rear view mirrors, (ii) shaving mirrors. List two reasons to justify your answer in each case. 8.(a) An object of height 6 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 5 cm. Use lens formula of determine the position, size and nature of the image if the distance of the object from the lens is 10 cm. 9.(a) An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 20 cm. Find the position and nature of the image. (b) Define refractive index. Light enters from air to diamond having refractive index 2.42. Find the speed of light in the diamond. The speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 ms-1,. 10. When light from free space bends towards normal, on hitting a surface, then what should be its refractive index (µ)? Is it µ >1, µ < 1, or µ=1/2? Justify your answer. 11. (a) While performing the experiment with glass slab, what should be the range of incident angle ? (b) Give reason for your answer. 12. Three students measured the focal length of a convex lens using parallel rays from a distant object. All of them measured the distance between the lens and the inverted image on the screen. Student A saw a sharp image on the screen and labelled the distance as 1f .Student B saw a slightly larger blurred image on the screen and labelled the distance as 2f .Student C saw a slightly smaller blurred image on the screen and labelled the distance as 3f. The relation between the three measurements would most likely: (b)f1 ˂ f2 and f3 (a)f1=f2=f3 (c) f3˂ f2˂ f1 (d) f1 ˃ f2 and f1=f3 13. Your school laboratory has one large window. To find the focal length of a concave mirror using one of the walls as the screen, the experiment may be performed. (a) near the wall opposite to the window. (b) on the same wall as the window. (c) on the wall adjacent to the window. (d) only on the table as per the laboratory arrangement 14. Refraction cannot cause bending as light moves from one surface to another if the incident and refraction angles i and r are related as: (a) i ≠ r = 0 (b) i =r = 90 (c) i = r = 0 (d) i = 90 ,r= 0 15. When the two opposite surfaces of the slab are not parallel, the emergent angle e and incident angle i are related as: (a) e= I (b) e> I (c) e< i (d) Depends on the medium index *********************************