* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classical versus Keynesian Economics
Nouriel Roubini wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
2008–09 Keynesian resurgence wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Keynesian Revolution wikipedia , lookup
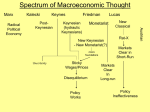
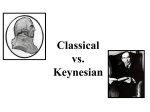
Macroeconomic Theories Classical vs. Keynesian Economics Reading • Read Keynesian Handout CLASSICAL Economists Classical economists were the 1st school of economic thought starting in 1776 Adam Smith was the founder and they believed: – – – – Markets are naturally self regulating No government intervention necessary Recessions are temporary Great Depression challenged Classical View KEYNESIAN VIEW 1. Economy is inherently unstable • not self regulating 2. Recessions can be long & permanent 3. Major government intervention necessary • Became popular after Great Depression (think FDR) 4. Support welfare and government assistance 5. Stagflation challenged Keynesian view John Keynes: Founder of Keynesian Economics 1883-1946 Economic Schools of Thought Classical Economics |----------------------------| 1800 1929 Keynesian Economics |----------------------------| 1936 1979 NeoClassical Economics |--------------------------------| 1980 2008 Housing Bubble Great Depression? Prices were not flexible! What Now? Now What? Keynesian Economics did not help here! How to Fix U.S. Economy? USA Economy LRAS1 Price Level E1 -------- P1 --------- Y1 AD1 Real GDP SRAS1 Let Prices & Wages Adjust? (60 minutes video: Buy American) • Free Trade • Protectionist => policies to reduce trade Keynesian vs. Classicial AS/AD Model “Keynesian Gov’t Intervention LRAS1 Price Level Y1 AD2 AD1 LRAS1 Price Level P1 --------- E1 Real GDP -------- -------- P1 --------- E1 SRAS1 AS/AD Model “Classical Self Regulation” Y1 End Result: Same Real GDP & Employment Keynesian leads to more debt & higher price level AD1 Real GDP SRAS1 SRAS2 End Day 1 Theory – Period Challenged Classical Theory - Great Depression (1929) Keynesian Economics- Stagflation (late 1970’s) Neo-Classical Theory Great Recession (2008) Review: Classical vs. Keynesian Economy is too slow => GDP “Do Nothing=> let prices adjust” or Help now! => use expansionary Fiscal Policy Keynesian vs. Classical • Keynesian economists felt recessions could be long/permanent – More AD was needed to “fix” economy => so cut taxes & ↑ Gov’t Spending • Classical economists felt recessions would “self regulate” because prices would fall which would lead to more jobs – SRAS shifts right whenever prices adjust lower Worksheet #2 Keynesian vs. Classicial “Keynesian Gov’t Intervention LRAS1 Price Level Y1 AD2 AD1 Y2 Real GDP LRAS1 Price Level P1 --------- E1 -------- -------- P2 -------------- E2 P1 --------- E1 SRAS1 “Classical Self Regulation” P2 -------------- AD1 Y1 Y2 End Result: Same Real GDP & Employment Keynesian leads to more debt & higher price level Real GDP SRAS1 SRAS2 Supply & Demand Free Response Computers Economists often Disagree • Are tax cuts good or bad? • Do Large Deficits always raise interest rates? • Will taxing “rich” people significantly lower GDP? The answer to most economic questions is: IT DEPENDS!