* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classical vs. Keynesian Economists
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Gross domestic product wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Stagflation wikipedia , lookup
Keynesian Revolution wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
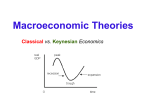
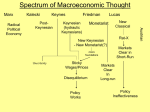
Macroeconomic Theories Classical, Keynesian & Supply Side Economics Economy is at Full Employment when AS turns Vertical AS Price Level Classical Range Intermediate Range Keynesian Range AD Real GDP Economic Schools of Thought Classical Economics |----------------------------| 1800 1929 Keynesian Economics |----------------------------| 1936 1979 NeoClassical Economics |--------------------------------| 1980 2008 Housing Bubble Great Depression? Prices were not flexible! What Now? Now What? Keynesian Economics did not help here! CLASSICAL VIEW 1. Markets are naturally self regulating • No government intervention necessary 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Recessions are temporary Wages & prices are flexible Against minimum wages, welfare, government assistance Real Variables do not depend on nominal variables Great Depression challenged Classical View Classical Model Failure: The Great Depression Price Level Real GDP ↓ 27% LRAS1 Unemployment 3% → 25% Price Levels fell AD1 AD2 Real GDP However, Wages did not adjust KEYNSIAN VIEW 1. Economy is inherently unstable • not self regulating 2. Recessions can be long & permanent 3. Major government intervention necessary 4. Wages and prices are sticky/fixed • AS curve is very flat or upward sloping 5. Support welfare and government assistance 6. Stagflation challenged Keynesian view Keynesian Failure: “Oil Shock” 1. An adverse shift in the SRAS Price Level Shifting AD would make inflation worse! LRAS SRAS2 SRAS1 B P2 A P 3. . . . and Price level ↑ . AD 0 Y2 2. . . . causes R-GDP to fall . . . Y Quantity of Output Keynesian vs. Classicial AS/AD Model “Keynesian Gov’t Intervention LRAS1 Price Level Y1 AD2 AD1 LRAS1 Price Level P1 --------- E1 Real GDP -------- -------- P1 --------- E1 SRAS1 AS/AD Model “Classical Self Regulation” Y1 End Result: Same Real GDP & Employment Keynesian leads to more debt & higher price level AD1 Real GDP SRAS1 SRAS2 Reconciling 2-Views • Most economists believe classical theory describes world in the long run but not short run • Prices, Wages & interest rates are at least somewhat sticky in the short run • Keynesian economics focuses on AD and failed to explain the Stagflation of the late 1970’s Worksheet #2 What creates Economic Growth? GDP GDP GDP INCENTIVES MATTER!!! Classical, Keyensian and Supply Side Economists approach the same economic problems in different ways! Supply-Side Policy • Basic Belief: Government Incentives Matter • Goal: use incentives to encourage new business! Cars AS United States 100 50 • The supply-side toolbox consists of: Price Level . ---------- B ----------- – shift the aggregate supply curve right – when PPF shifts right => AS shifts right 50 AD 100 Technology Goods – Tax cuts to stimulate work, saving, and investment (I↑) – Deregulation to reduce production cost/stimulate investment. – Expenditures on education training/research expands capacity to produce Real GDP Innovation Innovation & Schools Movies on Education Reform