* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 35-2 Cnidaria and Ctenophora
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
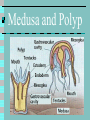
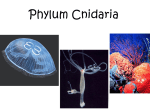
35-2 Cnidaria and Ctenophora 2 phyla of radially symmetrical invertebrates. More complex than sponges *have tissues and some simple organs. All are aquatic. Most live in the oceans. Phylum Cnidaria (cnidarians) Freshwater Jellyfish Coral hydra Freshwater Hydra Molecular Expressions: Science, Optics & You Olympus MIC-D: Pond Life Digital Movie Gallery - Hydra (Coelenterata) Jellyfish Coral Body Structures 2 forms ( stages of life) *V shape polyp: sessile, like sponge *Bell shape medusa: swimming form p. 696 35-3 Medusa and Polyp Body Structures 2 cell layers (also known as germ layers) *epidermis: outer layer of cells *gastrodermis: inner layer of cells esoglea: jellylike substance between layers Gastrovascular cavity: hollow gut outh: single opening Tentacles: flexible extensions around mouth Feeding and Defense ll have cnidocytes *Specialized cells for defense and capturing prey. *Each cnidocyte has a nematocyst, which has a long filament coiled inside it. *When cnidocyte is “triggered”, the nematocyst pushes filament out: capture prey with poison then tentacles push prey into gastrovascular cavity through the mouth. Enzymes digest the food, lining of gut absorbs nutrients. The waste products out through mouth. Cnidocyte To the right is a nematocyst prior to firing and after. You can see the stinging portion which would embedded in the skin. Nervous System *Nerve net is a diffuse web of nerve cells. *No brain. *Enables cnidarians to respond to stimuli in the environment. *Coordinates feeding and traveling. Classification 3 classes under the phylum Cnidaria. 1. Hydrozoa: medusa form or polyp form or both. 2. Scyphozoa: most of life as medusa form. 3. Anthozoa: only as polyp form. 1. Class Hydrozoa 3,700 species (fresh water and salt water which means marine habitats) Live as colonial organisms Exs: A.Obelia: all polyp forms B. Portuguese Man-of-War: live as a colony of polyps and medusa forms C. Fresh water hydra Obelia Portuguese Man-of-War Hydra Only as polyp forms Not colonial 1 to 4 cm in length ost are white or brown, some green because of symbiotic algae that live in it. Attach to rocks or water plants in ponds Can move from one place to another Asexual Reproduction Done by buds during warm weather Sexual Reproduction Only in the fall when temperatures are cool Eggs produced in ovaries Sperm produced in testes Either male or female or hermaphrodite Fertilized egg develops into embryo which then forms into new hydra 2. Class Scyphozoa Cup animals Dominant life form is medusa 200 species Jellyfish (Aurelia) 2 cm to 4 m Life Cycle of Jellyfish 3. Class Anthozoa Flower animals 6,100 marine species Sea anemones and corals Only in polyp form Sea Anemones ttach to rocks in coastal areas Feed on fish and smaller animals that come near their tentacles ne exception: the clownfish has a symbiotic relationship with the anemone. The tentacles of the anemone protect the clownfish from predators and the clownfish drives away other fish that would eat the anemone. Corals Live in colonies Cements its calcium carbonate skeleton to each other. When it dies, other polyps continue to live on this foundation. Thousands of years later, a coral reef is formed, but only the top layer is living. This coral reef provides food and shelter for fish and other invertebrates. Coral reefs are usually in shallow depths, and in warm, clear waters. The coral reefs have symbiotic algae that live in them. This is one reason why they are in shallow depths, so that the algae can photosynthesize. Corals Corals Phylum Ctenophora 100 marine species Comb holders *comb-like rows of cilia *look like jellyfish, so sometimes called comb jellies Difference from Cnidarians Do not pulsate through water but use cilia to move Do not have cnidocytes but have colloblasts, which secrete sticky substance, which sticks to prey. Have sensory structure called apical organ at one end of body. Most are hermaphrodites They are bioluminescent which means they are able to produce light. Comb Jellies Review p.704 1-19, 21-25 ?